1 2/28/06 Lab - Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. Axial Skeleton
advertisement

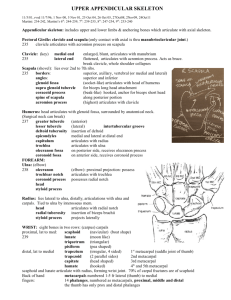
1 2/28/06 Lab - Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. Axial Skeleton (Table 7-1) A. Skull 1. Cranial vault - brain case of 8 bones - function? a. paired parietal (1) sagittal suture b. paired temporal (1) mastoid process (2) mandibular fossa - mandible articulates w/ skull (3) external acoustic canal (4) squamous suture c. unpaired frontal - sinus (1) coronal or frontal suture d. unpaired occipital (1) occipital condyle - articulation of skull w/ vertebrae (2) foramen magnum (3) lambdoid suture joins parietal & occipital bones e. unpaired sphenoid - sinus (1) pterygoid process (2) sella turcica - Turk’s saddle (pituitary) (3) optic canal (4) superior orbital fissure - cranial nerves III, IV, V- ophthalmic, VI f. unpaired ethmoid - sinus (1) perpendicular plate - nasal septum (2) crista galli - dura mater (brain) connects (3) cribriform plate - olfactory nerves (4) superior & middle nasal conchae 2. Facial bones a. paired maxillae - sinus (upper jaw) (1) forms part of hard palate b. paired zygomatic - forms cheek (1) zygomatic arch joins zygomatic & temporal bones c. paired palatine - forms part of hard plate d. paired lacrimal bone e. paired nasal - bridge of nose f. unpaired vomer - forms posterior nasal septum g. unpaired mandible - only bone freely moveable (1) condylar process - mandible articulates with skull 2 3. paranasal sinuses (see heads of torsos) a. frontal b. ethmoid c. sphenoid d. maxillary B. Vertebral Column1. 5 regions a. 7 cervical b. 12 thoracic c. 5 lumbar d. 1 sacral (5 bones fused) e. 1 coccygeal (4 or 5 fused) 2. General Plan of Vertebrae a. structure of vertebra (1) body weight bearing (2) lamina - flat surface divided by spinous process (3) transverse process (4) spinous process (5) articular processes facets (6) vertebral foramen (7) intervertebral foramen opening between vertebrae through which spinal nerves exit b. intervertebral disks - fibrocartilage between bodies of vertebrae 3. Regional Differences in Vertebrae a. cervical vertebrae (1) transverse foramen (2) atlas (C-1) (a) articulates w/ occipital condyles (b) nodding or tilting side to side (3) axis (C-2) (a) dens or odontoid process (b) rotation (4) vertebra prominens (C-7) b. thoracic vertebrae (1) first 10 articulating facets for ribs c. lumbar vertebrae (1) superior articular facets face medially (2) inferior articular facets face laterally d. sacral vertebrae fused into single bone, sacrum (1) sacral promontory (a) anterior edge of 1st sacral vertebra (b) landmark separating abdominal & pelvic cavities (c.) reference for measurement of pelvic outlet 3 (e.) coccyx C. Thoracic Cage 1. 12 pairs ribs a. 7 pairs true or vertebrosternal attach directly to sternum by way of costal cartilages b. false ribs do not attach directly to sternum (1) vertebrochondral ribs join at common cartilage which attaches to sternum (2) floating ribs or vertebral ribs have no attachment to sternum 2. Sternum II. a. manubrium b. body c. xiphoid process Appendicular Skeleton A. Pectoral girdle - attaches upper limb to body 1. scapula a. acromion process b. spine c. supraspinous fossa d. infraspinous fossa e. subscapular fossa f. coracoid process g. glenoid cavity- articulates with ? 2. clavicle B. Arm 1. humerus a. intertubercular or bicipital groove b. deltoid tuberosity - attachment site for deltoid muscles c. capitulum - articulates w/ radius d. trochlea - articulates w/ ulna e. medial epicondyle f. coronoid fossa g.olecranon fossa h. radial fossa 4 C. Forearm 1. ulna a. b. c. d. olecranon process coronoid process trochlear or semilunar notch radial notch 5 2. radius a. b. D. head - proximal end radial tuberosity Wrist & Hand 1. carpals a. scaphoid b. lunate c. triquetrum d. pisiform e. trapezium f. trapezoid g. capitate h. hamate mnemonic - Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle 2. metacarpals 3. phalanges E. Pelvic Girdle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. F. obturator foramen acetabulum ilium a. iliac crest b. iliac fossa ischium a. ischial tuberosity b. greater sciatic notch c. ischial spine pubis pelvic brim - imaginary plane passing through sacral promontory to pubic crest a. true pelvis - inferior to pelvic brim b. pelvic inlet - at level of pelvic brim c. pelvic outlet - inferior to true pelvis, bordered by (1) inferior margin of pubis (2) ischial spines (3) ischial tuberosities (4) coccyx Thigh 1. femur a. head b. neck 6 2. c. d. e. f. patella greater trochanter lesser trochanter medial condyle lateral condyle 7 G. Leg 1. 2. H. tibial tuberosity medial condyle lateral condyle intercondylar eminence - ligament attachment medial malleolus lateral malleolus Ankle 1. I. tibia a. b. c. d. e. fibula a. tarsal bones a. talus - articulates with tibia & fibula b. calcaneus - heel Foot 1. 2. metatarsals phalanges Bone Model in the Lab There are no numbers. Black spiders - osteocytes Legs of spider - canaliculi Towers are concentric rings of lamellae which make up an osteon. Blood vessels running vertically are in central canals. Blood vessels running horizontally are in perforating canals. Towards the apex of the model, pale blue cells form endosteum, cells lining the marrow cavity. Flat plates standing up toward the base of the model are circumferential lamellae. Interstitial lamellae are between the osteons. Periosteum is light blue covering surrounding the bone. ID following parts of cow bone articular cartilage cancellous (spongy) bone compact bone diaphysis epiphyseal plate epiphysis 8 marrow cavity periosteum yellow marrow