Study Guide: From RNA to protein 1. Understand the
advertisement

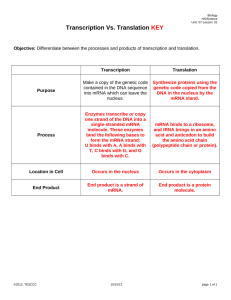
Study Guide: From RNA to protein 1. Understand the differences between mRNA, rRNA and tRNA 2. What is transcription and where does it occur in the cell 3. What is translation and where does it occur in a cell 4. What is the anti-sense strand of DNA and is it always the same strand 5. What are the key stages in transcription and what is the code for initiation 6. What is the switch for termination of transcription 7. What occurs at the 5’ and 3’ ends in processing the pre-mature mRNA into mRNA 8. What is splicing and what are the implications of alternative splicing events upon protein formation 9. Why is the genetic code called degenerate 10. What is the significance of the A, P, and E sites in the large sub-unit of the ribosome 11. What happens to mRNA and the ribosome after transcription termination 12. Which DNA strand is listed in sequence databases and why? 13. How can a ‘frameshift’ occur and what are the probable consequences 14. Be aware that post-translational modification can also affect protein structure and function For some more detail on transcription and where transcription factors and promoters fit in, see http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/P/Promoter.html#Transcriptio n_start_site See http://www.preservearticles.com/2011121218368/what-are-the-six-steps-oftranslation-in-eukaryotes.html for some more detail on translation. Also see http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/T/Translation.html for a slightly more detailed overview and some clickable links for further detail. Note that this site doesn’t refer to the E site in the ribosome. Check http://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/ for some animations on transcription & translation,