Meteorology Final Study Guide

Meteorology Final-Exam Study Guide
Fall 2014, SJHS
Mr. J Varco advection aerosols air
Air-mass thunderstorm albedo aphelion atmosphere atmospheric window aurora australis aurora borealis autumnal equinox backscattered biosphere blackbody circle of illumination climate climate system climate-feedback mechanism closed system conduction convection
Cumulus stage
Dart leader diffused light
Dissipating stage
Doppler radar
Dryline easterly wave eccentricity elements of weather and climate energy
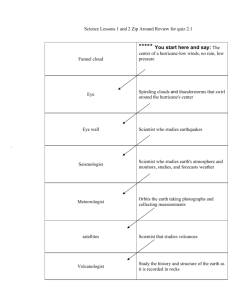
Entrainment environmental lapse rate eye eye wall
Flash
Fujita Intensity Scale (F-scale) greenhouse effect
Gust front heat heat budget hurricane hurricane warning hurricane watch hydrosphere inclination of the axis infrared radiation ionosphere kinetic energy
Leader
Lightning lithosphere longwave radiation
Mature stage
Mesocyclone mesopause
Mesoscale convection complex mesosphere
Milankovitch cycles
Multiple vortex tornado negative feedback mechanism negative-feedback mechanism obliquity open system ozone oxygen isotope analysis perihelion plane of the ecliptic plate-tectonics theory positive feedback mechanism positive-feedback mechanism potential energy precession radiation or electromagnetic radiation radiosonde reflection
Return stroke revolution rotation
Saffir-Simpson scale scattering
Severe thunderstorm shortwave radiation spring equinox
Squall line
Step leader storm surge stratopause stratosphere
-
Stroke summer solstice sunspot(s)
Supercell system temperature thermal thermosphere
Thunder
Tropic of Cancer
Tropic of Capricorn tropical depression tropical disturbance tropical storm tropopause troposphere
Ultraviolet radiation
Visible light
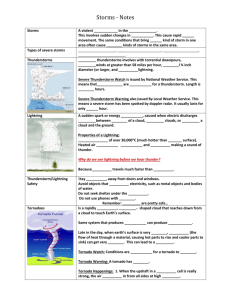
Thunderstorm
Tornado
Tornado warning
Tornado watch
Wavelength weather
Winter solstice
Characteristics of a hurricane
F-Scale and the qualifications for each (F1 – F5)
Characteristics of a lightning storm
Weather seeding and the attempt to control weather
Climate versus weather
Light pollution
The role of weather in the D-Day Invasion of WWII