Biology Midterm Review
advertisement

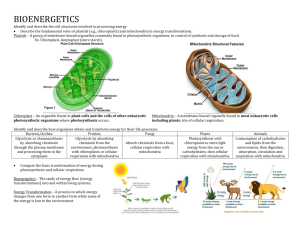
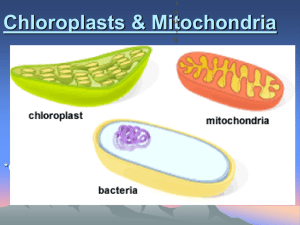
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 – Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic particle and ending with biosphere. What is meant by the term “emergent properties”? Explain using 3 consecutive levels of organization that you listed above (example: macromolecule -> organelle -> cell). 1.2 – Biology explores life in its diverse forms. What are the 7 characteristics shared by all living things? Give a brief explanation of each. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Fill in the chart below explaining the three domains of life: Name of Domain Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic? Description of Domain List the taxa used to classify organisms, starting with domain and ending with species. Circle the two that contribute to the scientific name of the organism. 1.3 – Ten themes unify the study of life. Identify and briefly explain the 10 themes of biology. 1. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. _________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ In the experiment below, identify the independent variable, the dependent variable, and at least three controlled variables: You want to test to see whether blue light helps a plant grow better than red light. You take two identical plants and put one under blue light and one under red light and measure their growth after 6 days. Graph the results of the experiment: Table 1. Growth of plants Day Blue Red Light Light 2 2 cm 1 cm 4 4 cm 2 cm 6 6 cm 3 cm Unit 2 Keystone Objectives: A.2.1, A.2.2 4.1 – Life requires about 25 chemical elements. List the top 5 most common elements in living things. Fill in the chart below: Formula Number of elements Number of atoms of each element He O2 CO2 C6H12O6 H2O 4.2 – Chemical properties are based on the structure of atoms. Label the parts of the atom. Molecule, compound, or both? Fill out the chart below for each subatomic particle. Name of subatomic particle Location Charge Does it contribute to the atom’s mass? Fill out the chart below for each element. Name of element C H O N Na Atomic number Mass number # protons # neutrons # electrons # valence electrons electronegativity From the chart below, which element is the most reactive? Why? 4.3 – Chemical bonds join atoms to one another. What is the main difference between ionic and covalent bonds? What subatomic particles are involved in chemical bonding? 4.4 – Life depends on the unique properties of water. Draw the structure of a water molecule. Using electronegativity, explain and diagram why water is considered polar. List and describe water’s unique properties. Property of water Explanation of property Why is this property important? What is the difference between an acid and a base? Explain using the pH scale (numbers). 5.1 – Carbon is the main ingredient in organic molecules. Draw the following functional groups, then add them to the carbon chain below. Make sure the carbon atoms have the appropriate number of bonds by adding hydrogens. (Carbon chain on next page) Functional group Hydroxyl Carbon chain location 3rd carbon Carbonyl 2nd carbon Carboxyl 5th carbon Amino 1st carbon C-C-C-C-C Drawing Describe the 3 properties of carbon that make it suitable for forming large macromolecules. Draw and explain dehydration synthesis and what it is used for. Draw and explain hydrolysis and what it is used for. 5.2 – Carbohydrates provide fuel and building materials. 5.3 – Lipids include fats and steroids. 5.4 – Proteins perform most functions in cells. Label the structures below as either carbohydrate, lipid, or protein. What is the difference between a monosaccharide, a disaccharide, and a polysaccharide? Fill out the chart below for the 3 basic macromolecules. Macromolecule Name of monomer Functions Examples Carbohydrate Lipid Protein What are two things that can affect protein shape? 5.5 – Enzymes are proteins that speed up specific reactions in cells. What type of macromolecule is an enzyme? Are enzymes used up in a reaction? What do enzymes do? Use a picture in your explanation. Food Unit 3 Keystone Objectives: A.1.2.1, A.1.2.2, A.3.1, A.4.1, B.2.2.2 6.1 – All organisms are made of cells. What are the three parts of the cell theory? Label the parts of the microscope: Fill out the chart below: Animal cells only Both cells (give at least 5) Plant cells only 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. Put check marks in the boxes that describe each type of cell: Prokaryotic Has DNA Has a nucleus Has membrane-bound organelles Has ribosomes Animal cells are an example Bacterial cells are an example Plant cells are an example Has cytoplasm Eukaryotic 6.2– Membranes organize a cell’s activities. The cell (plasma) membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer. Draw what that looks like, and label the parts of the phospholipids as either hydrophilic or hydrophobic. 6.3 – Membranes regulate the traffic of molecules. Draw pictures showing the following processes: Diffusion Facilitated diffusion Active transport What does the word “equilibrium” mean? Draw pictures showing the following solutions and use arrows showing the direction of water movement. Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic What does endocytosis mean? What does exocytosis mean? 6.4 – The cell builds a diversity of products. In the picture of the cell, label the nucleus, ribosomes, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus. State the function of each organelle identified above. Organelle Nucleus Function Ribosome Rough ER Smooth ER Golgi apparatus What is the relationship between the organelles listed above? Discuss how they move things through the cell. State the function of the organelles below. Organelle Lysosome Function Peroxisome Vacuole 6.5 – Chloroplasts and mitochondria energize cells. Compare and contrast the function of chloroplasts and mitochondria. In the picture of the plant and animal cells, label the chloroplast and mitochondria. Remember, both plant AND animal cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. 6.6 – An internal skeleton supports the cell and enables movement. What are two important functions of the cytoskeleton? Unit 4 Keystone Objectives: A.3.1, A.3.2.1, A.3.2.2 7.1 – Sunlight powers life. What does autotroph mean? Give an example of an autotroph. What does heterotroph mean? Give an example of a heterotroph. What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? 7.2 – Food stores chemical energy. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? Give an example of each. Fill out the chart below: Name of energy form M R S C H E N Kinetic or potential? Explanation and alternative names 7.3 – ATP provides energy for cellular work. Draw and label the three parts of ATP, and label where energy is stored. Fill out the chart below for the three types of work done by the cell: Name of work type Description and example 7.4 – Electrons “fall” from food to oxygen during cellular respiration. 7.5 – Cellular respiration converts energy in food to energy in ATP. Label the parts of the mitochondria: Write the formula for cellular respiration. List the three steps, where the steps take place, and where the reactants are used and the products are made. 7.6 – Some cells can harvest energy without oxygen. How is cellular respiration similar to and different than fermentation? 8.1 – Photosynthesis uses light energy to make food. Label the parts of the chloroplast. 8.2 – The light reactions convert light energy to chemical energy. 8.3 – The Calvin cycle makes sugar from carbon dioxide. Write the formula for photosynthesis. List the two steps, where the steps take place, and where the reactants are used and the products are made.