Test 1
advertisement
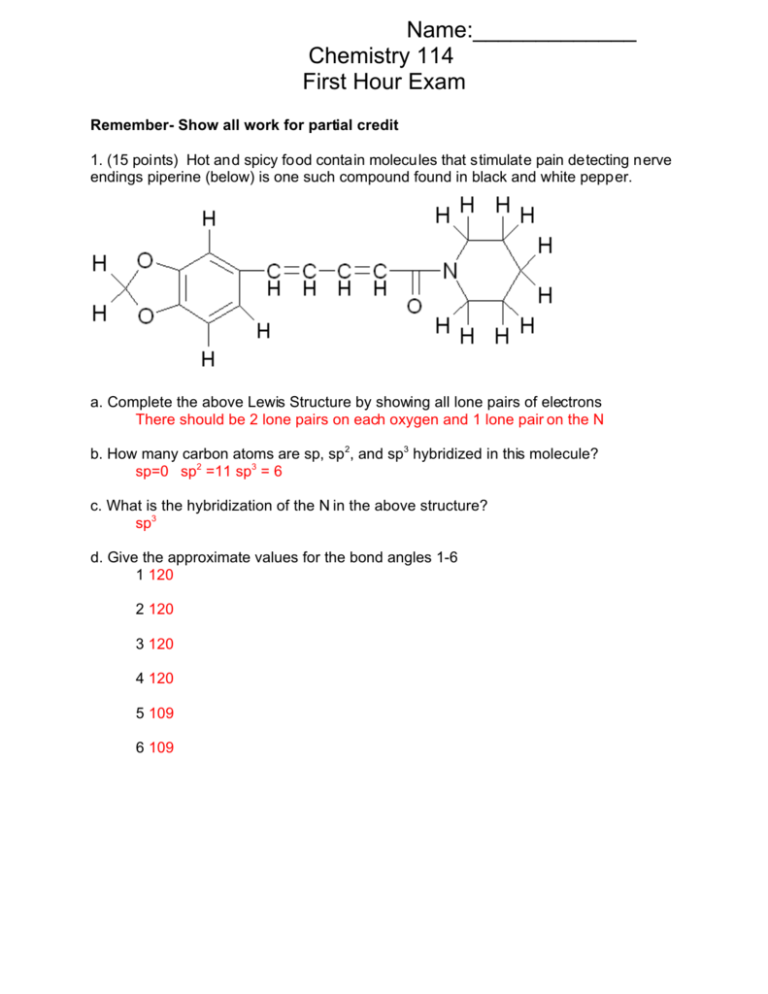
Name:_____________ Chemistry 114 First Hour Exam Remember- Show all work for partial credit 1. (15 points) Hot and spicy food contain molecules that stimulate pain detecting nerve endings piperine (below) is one such compound found in black and white pepper. a. Complete the above Lewis Structure by showing all lone pairs of electrons There should be 2 lone pairs on each oxygen and 1 lone pair on the N b. How many carbon atoms are sp, sp2, and sp3 hybridized in this molecule? sp=0 sp2 =11 sp3 = 6 c. What is the hybridization of the N in the above structure? sp3 d. Give the approximate values for the bond angles 1-6 1 120 2 120 3 120 4 120 5 109 6 109 2 2. (15 points) Using the molecular orbital model to describe the bonding in F2+, F2, F2and F2-2, predict the bond orders and relative bond lengths for these four species. Which ones are paramagnetic? F*2p B*2p B 2p F 2p F* 2s F 2s F2+ 989 9898 98 89 89 Magnetism Para Bond Order (8-5)/2=3/2 Bond length Shortest F2 F2- F2-2 9898 9898 98 98 98 8 9898 9898 98 98 98 89 9898 9898 98 98 98 Dia Para Dia (8-6)/2=1 (8-7)/2=1/2 (8-8)/2=0 Unstable Medium Longest N.A. 3. A (5 points) What is the difference between a F bond and a B bond? A F bond has its electron density along the line connecting the two bonded atoms, a B bond has its electron density to either side of the line connecting the atoms. B (5 points) When you hybridize s atomic orbitals you can only make F type molecular orbital. When you hybridize p atomic orbitals you can make either F or B type molecular orbitals, why? Because s orbitals are spherically symmetric, when you hybridize two s orbitals together the resulting electron density is always along the line connecting the atoms and is hence a F bond. P orbitals are bi-lobed shape arranged along the three principal axes. When a bond is formed from two p orbitals aligned along the line connecting the atoms, you get electron density along the line connecting the atoms and a F type bond. When a bond is formed from the orbitals that are not on this line, the electron density is to either side of the line connecting the atoms, and you get two different B bonds. A diagram shows this more easily than words 4. (10 points) What is paramagnetism?, diamagnetism? What determines if a molecule is paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Paramagnetism is when a compound is attracted to an external magnetic field, diamagnetism is when a compound is repelled by an external magnetic field. A molecule is paramagnetic when it contains unpaired electrons, and it is diamagnetic when all of its electrons are paired. 3 5. (15 points) Draw the structures of the compounds named below. Some of these names are wrong. When you find one of these incorrectly named compounds, give the proper name for the chemical. A. 2,3-diethylheptane B. 2-cycloheptene 4-ethyl-3-methyloctane 1-cycloheptane or Cyclohepatane C. 3-chloro-2-octanol D. 4-methyl-1-ethylcyclopentene Name is OK as written 1-ethyl-4-methylcyclopentane E. p-dinitrobenzene . 1,4-dinitrobenzene 6. (10 points) Identify as many functional groups as you can on the following two compounds. Do any of these compounds have acid or base properties? 4 Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)8 Thiamine (Vitamin B1)6 All OH’s are alcohols All N’s are amines Each structure has at least 1 aromatic ring The S in Thiamine is a sulfide but that is a freebie since we didn’t have that group in class Both structures can be considered bases because they contain amines 7. (10 points) What does the term catalytic reforming refer to? Catalytic reforming is one of the processes used in the petroleum industry in the refining of crude oil. It is a process in which small, nonaromatic compounds are reformed into larger aromatic compounds. These aromatic compounds raise the octane of gasoline making it a more profitable product. 8. (5 points) When toluene (C 6H5CH3) reacts with chlorine gas in the presence of iron(III) catalyst, the product is a mixture of ortho and para isomers of C6H4ClCH3. However, when the reaction is light-catalyzed, with no Fe3+ catalyst present, the product is C6H5CH2Cl. Explain. The reaction of Cl 2 with an iron catalyst is a typical substitution reaction involving an aromatic compound. The reaction of Cl 2 with light is a typical substitution reaction involving an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Thus the Fe catalyzed reaction reacts with the aromatic part of the toluene molecule, while the light reaction involves the aliphatic part of the molecule. 9. (5 points) Kevlar, used in making bullet proof vests, is made by the condensation copolymerization of the monomers 5 Draw the structure of the Kevlar chain 10. (5 points) Viscosity is a measure of how ‘thick’ a solution is. If it has low viscosity, it is thin and runny, if it has high viscosity it is thick and tends to coat objects. The viscosity of oil in a motor is very important in keeping an engine running. If the viscosity is too low, the oil doesn’t coat the hot metal parts, and the valves and cylinders get to hot and weld themselves together. If it is too viscous, the oil is thick and syrupy, and the parts of the engin can’t move (like when you try to start your engin when its -20). Poly(lauryl methacrylate) is used as an additive in motor oils to counter the loss of viscosity at high temperature. The structure is The long chain hydrocarbon of poly(lauryl methacrylate) make the polymer soluble in oil (a mixture of hydrocarbons with mostly 12 or more carbons) At low temperature the polymer is coiled into balls. At higher temperature the balls uncoil and the polymer exists as long chains. Explain how this helps control the viscosity of oil. At low temperature the polymer is coiled up so it has little interaction with the rest of the oil and it’s viscosity is low. At high temp, where the oil itself starts to lose its viscosity, this polymer uncoils, and now begins to interact with the oil. In the long, uncoiled form this has a higher viscosity, so it serves to ‘replace’ the viscosity lost by the rest of the oil.