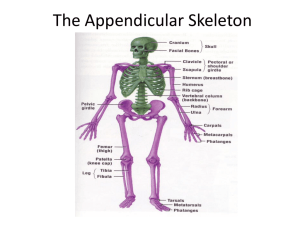
Appendicular skeleton: Pre-lab exercise
advertisement

Biology 325 Human anatomy and physiology Fall 2004 Pre-lab exercise Name: _______________________________ Appendicular skeleton: Pre-lab exercise – due at the beginning of your lab session. Matching I: Upper limb and pectoral girdle. You can use a term more than once. A. B. C. D. E. Acromium Capitulum Carpals Clavicle Coracoid process 1. 2. 3. ______ 4. 5. ______ 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. ______ 18. 19. 20. F. G. H. I. J. Coronoid fossa Deltoid tuberosity Glenoid cavity Humerus Metacarpals K. Olecranon fossa L. Olecranon process M. Phalanges N. Radial tuberosity O. Radius P. Q. R. S. T. Scapula Sternum Styloid process Trochlea Ulna Raised area on the lateral surface of humerus to which deltoid muscle attaches. Arm bone Bones comprising the shoulder girdle. Articulates with manubrium Lateral forearm bone in anatomical position. Point where the clavicle and scapula connect. Shoulder girdle bone that has no attachment to the axial skeleton. Shoulder girdle bone that articulates anteriorly with the sternum. Socket in the scapula for the arm bone. Process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment. Commonly called the collarbone. Distal medial process of the humerus; joins the ulna. Medial bone of the forearm in the anatomical position. Rounded knob on the humerus that articulates with the radius. Anterior depression; superior to the trochlea; receives part of ulna when forearm flexed. Forearm bone involved in formation of elbow joint. Bones that articulate with the clavicle. Bones of the wrist. Bones of the fingers. Heads of these bones form the knuckles. Biology 325 Human anatomy and physiology Fall 2004 Pre-lab exercise Matching II: Lower limb and pelvic girdle; you can use a term more than once and you can use more than one term per blank. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Acetabulum Calcaneus Femur Fibula Gluteal tuberosity Greater sciatic notch Greater and lesser trochanters Iliac crest I. Ilium J. Ischial tuberosity K. Ischium L. Lateral malleolus M. Lesser sciatic notch N. Medial malleolus O. Metatarsals P. Obturator foramen Q. Patella R. Pubic symphysis S. Pubis T. Sacroiliac joint U. Talus V. Tarsals W. Tibia X. Tibial tuberosity Fuse to form the coxal bone (hip bone). Receive weight of the body when sitting. Point where coxal bones join anteriorly. Upper margin of iliac bones. Deep socket in the hip bone that receives the head of the femur. Point where the axial skeleton attaches to the pelvic girdle. Longest bone in the body; articulates with the coxal bone. Lateral bone of the leg. Medial bone of the leg. Bones forming the knee joint. Point where the patellar ligament attaches. Kneecap. Shinbone. Distal process on the medial tibial surface. Process forming the outer ankle. Heel bone. Bones of the ankle. Bones forming the instep of the foot. Opening in a coxal bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami. Sites of muscle attachment on the proximal end of the femur. Tarsal bone that articulates with the tibia.