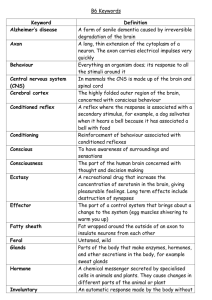
The Nervous System Vocabulary 18. Cerebellum 19. somatic
advertisement

The Nervous System Vocabulary 1. Stimulus 1. Any change or signal in the environment that can make an organism react in some way. 2. Response 2. What the body does in reaction to a stimulus. 3. Neuron 3. A cell that carries information through the nervous system. 4. nerve impulse 5. dendrite 5. A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cells body. 6. axon 6. A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. 7. nerve 7. A bundle of nerve fibers. 8. sensory neuron 8. A neuron that picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment and converts each stimulus into a nerve impulse. 9. interneuron 10. motor neuron 9. A neuron that carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another. 11. The junction where one neuron can transfer an impulse to the next structure. 12. central nervous system (CNS) 12. The division of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. 13. peripheral nervous system (PNS) 14. brain 15. brain stem 13. The division of the nervous system consisting of all the nerves located outside the central nervous system. 14. The part of the central nervous system that is located in the skull and controls most functions in the body. 15. The part of the brain that lies between the cerebellum and the spinal cord that controls involuntary actions. 16. spinal cord 16. The thick column of nervous tissue that links the brain to most of the nerves in the PNS. 17. cerebrum 10. A neuron that sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, causing the muscle or gland to react. 11. synapse 4. The message carried by a neuron. 17. The part of the brain that interprets input from the senses, controls movement, and carries out complex mental processes. 18. Cerebellum 18. The part of the brain that coordinates the actions of the muscles and helps maintain balance. 19. somatic nervous system 20. cornea 19. The group of nerves in the PNS that controls voluntary actions. 20. The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye. 21. 22. 21)autonomic nervous system 22)reflex 23)concussion 24)ciliary muscle 25)pupil 28)retina 30)optic nerve 31)nearsightedness 32)farsightedness 33)eardrum 34)cochlea 25)The opening through which light enters the eye. 26)The circular structure that surrounds the pupil and regulates the amount of light entering the eye, and is controlled by the ciliary muscle. 27)The flexible structure that focuses light that has entered the eye. 29)Point where the retina attaches to the optic nerve. 30)The bundle of nerve fibers that send the impulse to the brain to be interpreted. 32)The condition in which a person can see distant objects clearly. 33)The membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear, and that vibrates when sound waves strike. 34)A snail-­‐shaped tube in the inner ear that is lined with receptor cells that respond to sound. 37)olfactory cells 38)myelin sheath 24)Controls the size of the pupil and helps the lens to focus. 31)The condition in which a person can see nearby objects clearly. 35)semicircular canal 23)A bruise-­‐like injury of the brain that occurs when the soft tissue of the brain collides against the skull. 28)The layer of receptor cells at the back of the eye on which an image is focused, upside down. 36)neurotransmitter 27)lens 26)iris 29)blind spot group of nerves in the PNS that controls involuntary 21)The actions. 22)An automatic response that occurs rapidly and without conscious control. 35)Structures in the inner ear that are responsible for the sense of balance. 36) chemicals which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. 37) Sensory receptors in the nose. 38) The insulating envelope of myelin that surrounds the core of a nerve fiber or axon and facilitates the transmission of nerve impulses.