Ideal Gas Mixture
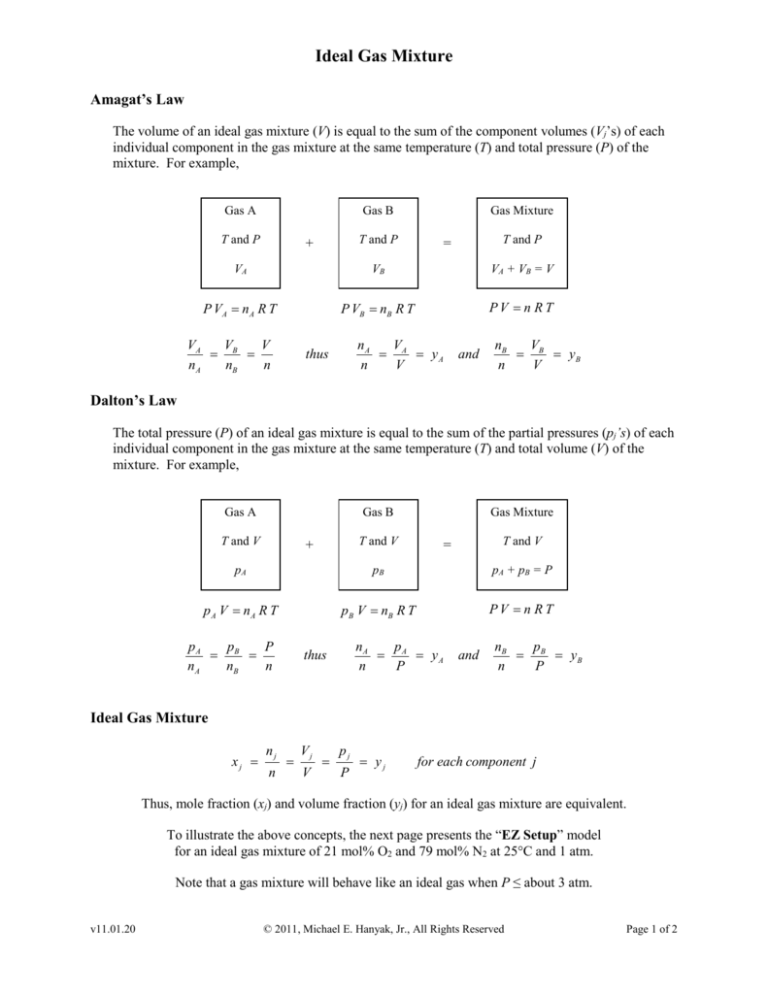
Amagat’s Law
The volume of an ideal gas mixture (V) is equal to the sum of the component volumes (Vj’s) of each
individual component in the gas mixture at the same temperature (T) and total pressure (P) of the
mixture. For example,
Gas A
Gas B
T and P
+
T and P
Gas Mixture
T and P
=
VA
VB
VA + VB = V
P VA = n A R T
P VB = nB R T
PV = n RT
VA
=
nA
VB
=
nB
V
n
thus
nA
=
n
VA
=
V
yA
and
nB
=
n
VB
=
V
yB
Dalton’s Law
The total pressure (P) of an ideal gas mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures (pj’s) of each
individual component in the gas mixture at the same temperature (T) and total volume (V) of the
mixture. For example,
Gas A
Gas B
T and V
+
T and V
Gas Mixture
=
T and V
pA
pB
pA + pB = P
p A V = nA R T
pB V = nB R T
PV = n RT
pA
=
nA
pB
=
nB
P
n
thus
nj
=
n
Vj
=
V
nA
=
n
pA
=
P
yA
nB
and =
n
pB
=
P
yB
Ideal Gas Mixture
=
xj
pj
=
P
yj
for each component j
Thus, mole fraction (xj) and volume fraction (yj) for an ideal gas mixture are equivalent.
To illustrate the above concepts, the next page presents the “EZ Setup” model
for an ideal gas mixture of 21 mol% O2 and 79 mol% N2 at 25°C and 1 atm.
Note that a gas mixture will behave like an ideal gas when P ≤ about 3 atm.
v11.01.20
© 2011, Michael E. Hanyak, Jr., All Rights Reserved
Page 1 of 2
Ideal Gas Mixture
click here to download this model and solve it using the "EZ Setup"/Solver Add-Ins.
"EZ Setup" Mathematical Model
//
//
//
//
//
Amagat's Law and Dalton's Law for Ideal Gas Mixture
21 mol% O2 and 79 mol% N2 at 25°C and 1 atm
Given Information:
R
=
0.08205746
//
L atm/mol K
T
P
n
=
=
=
25 + 273.15
1
1
//
//
//
K
atm
moles of mixture
n_O2
n_N2
=
=
0.21 * n
0.79 * n
//
//
moles of oxygen
moles of nitrogen
Amagat's Law:
/* mixture */
P * V
=
/* oxygen */
/* nitrogen */
P * V_O2
P * V_N2
/* total volume */
V_total =
/* volume fraction O2 */
/* volume fraction N2 */
y_O2
y_N2
=
=
n * R * T
=
=
n_O2 * R * T
n_N2 * R * T
V_O2
+
V_N2
V_O2 / V_total
V_N2 / V_total
Dalton's Law:
/* partial pressure O2 */
/* partial pressure N2 */
p_O2 * V
p_N2 * V
/* total pressure */
P_total
=
/* mole fraction O2 */
/* mole fraction N2 */
x_O2
x_N2
p_O2 / P_total
p_N2 / P_total
=
=
=
=
n_O2 * R * T
n_N2 * R * T
p_O2
+
p_N2
Calculated Results
v11.01.20
V
V_N2
V_O2
V_total
=
=
=
=
24.4654
19.3277
5.13774
24.4654
y_N2
y_O2
=
=
0.79
0.21
liters
liters
liters
liters
p_N2
p_O2
=
=
0.79
0.21
atm
atm
P_total
=
1
atm
vol frac
vol frac
x_N2
x_O2
=
=
0.79
0.21
© 2011, Michael E. Hanyak, Jr., All Rights Reserved
mol frac
mol frac
Page 2 of 2