GLP 000 Laboratory Procedure FORMAT
advertisement

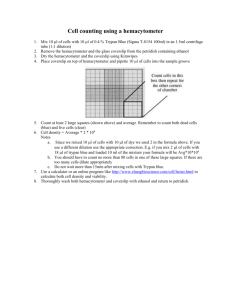
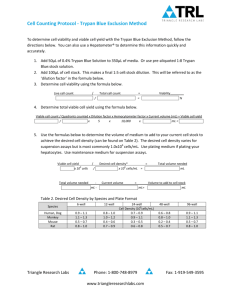
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE- DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE PROCEDURE NO: MOD: Page: GLP 079 1st Issue 1 of 7 Procedure Type: General Laboratory Procedure Title: Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method 1. Risk Assessment: This Risk Assessment is to be used as a general guide and as such, cannot accommodate all the varying factors that may be encountered when using this procedure. Therefore, personnel are requested to conduct their own Risk Assessment before using this procedure to include any extra hazards introduced by the task performed. TASK PERFORMED Cell count to determine both cell concentration and viability in a specific sample. HAZARDS 1. Refer to GLP 102 Working with human, murine and GM cell lines for a risk assessment covering general aspects of this work. 2. Chemical hazard – Trypan blue Risk phrases: R45(2) - May cause cancer RISK ASSESSMENT 1. Refer to GLP 102 Working with human, murine and GM cell lines for a risk assessment covering general aspects of this work. 2. The risk of chemical exposure is low if the Risk Controls are followed. RISK CONTROL 1. Wear suitable PPE - lab coat, disposable gloves and safety glasses. 2. Refer to GLP 102 Working with human, murine and GM cell lines for a risk assessment covering general aspects of this work. 3. Trypan blue Safety phrases: S01 – Keep locked up S53 - Avoid exposure - obtain special instructions before use S40 – To clean the floor and all objects contaminated by this material use water S35 - This material and its container must be disposed of in a safe way NAME (signed) DATE WRITTEN BY CHECKED BY AUTHORIZED BY Lynn Herd Leonie Ashman Leonie Ashman th 9 February 2005 Distributed To: GLP Master File / GLP Lab File st 21 February 2006 22nd February 2006 DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PROCEDURE NO: Page: Title: GLP 079 2 of 7 Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method 4. Training should be provided by personnel experienced in this procedure. 5. Training should be undertaken in General Laboratory Safety. I have read and understood the Risk Assessment for GLP 079 – Cell Counts using the Trypan Blue exclusion method. I agree to abide by the Risk Controls outlined in this Assessment. Name Signature Date DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PROCEDURE NO: Page: Title: 2. GLP 079 3 of 7 Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method Purpose: 2.1. This document describes the procedure to count cells using the Trypan blue exclusion method. 3. 4. 5. Equipment: 3.1. Microscope 3.2. Counter 3.3. Pipettors and associated yellow tips 3.4. Haemocytometer and glass coverslip Materials: 4.1. 0.5mL microfuge tubes 4.2. Kimwipes 4.3. 96-well plate or small plastic disposable tubes 4.4. 0.4 – 0.8% Trypan blue 4.5. Cell suspension Set Up: 5.1. Ensure that you have read and understood the safety precautions (Section 6 of this SOP) prior to commencing this procedure. 5.2. 6. Turn on microscope and turn to low objective. Safety Precautions: 6.1. Good laboratory techniques are to be used at all times. 6.2. Any material that has been in contact with human, murine, or GM cell lines is treated as potentially infectious. 6.3. Wear gloves and lab gown at all times. 6.4. Always decontaminate waste as soon as possible. DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PROCEDURE NO: Page: Title: 7. GLP 079 4 of 7 Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method Method: 7.1. Clean the haemocytometer and glass coverslip by spraying with 70% ethanol and wiping dry with a kimwipe. 7.2. Position the haemocytometer correctly with the glass coverslip in the middle of the haemocytometer. Haemocytometer 7.3. Make the appropriate dilution to the cell suspension just prior to counting. 7.4. A suggested initial dilution is 50μl cell suspension diluted with 50μl 0.4-0.8% Trypan blue in one well of a 96-well plate or in a disposable plastic tube. 7.5. The optimal concentration of cells for counting is 5 -10 x 105 cells/ml (50 -100 cells per large square) after dilution in the Trypan blue. 7.5.1. Pipette approximately 10μl of the cells/trypan blue mixture into a haemocytometer. 7.5.2. It is possible to use both sides of the haemocytometer, pipetting sample into the chamber on each side, and then counting 2 large squares on each side. If results from one side are obviously different to the other, then the sampling should be repeated. 7.6. The cell suspensions should be allowed to flow under the coverslip until the grid area is just full and not overflowing into the overflow well. 7.7. If the chamber is loaded too heavily, clean it and begin again. 7.8. Allow cells to settle. If greater than 10% of the cells appear clustered, repeat entire procedure making sure the cells are dispersed by vigorous pipetting in the original cell suspension as well as the Trypan Blue-cell suspension mixture. 7.9. Viable cells exclude the Trypan blue, while nonviable cells take up the dye. After being stained with Trypan blue, the cells must be counted within three minutes; after that time viable cells begin to take up the dye. DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PROCEDURE NO: Page: Title: GLP 079 5 of 7 Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method 7.10. Count cells on 10x magnification on the microscope or higher if necessary to clearly visualise the cells. Ideally, count 100-200 cells to ensure accuracy 7.11. Count numbers of both viable and non-viable cells using the counter. 7.12. Select which size squares to count based on the number of cells in each square. Eg. Smaller cells such as splenetic lymphocytes will need to be counted in medium squares, using a higher magnification lens on the microscope, than many cultured cell-lines. 7.13. Refer to the Haemocytometer grid provided below. 1 medium square XXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXXXX Large square 7.14. For many cultured cell lines, the cells in 4 – 5 large squares should be counted and the counts from each square averaged. eg. Count 5 large squares: the 4 large corner squares and the central square of equal size would each be counted. If instead you wish to count 2 squares from each side of the haemocytometer, count the central squares and one of the corner squares for each grid. DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PROCEDURE NO: Page: Title: 8. GLP 079 6 of 7 Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method POINTS TO NOTE: 8.1. The haemocytometer grid is divided into 9 large squares. Each of these large squares can be further divided into 25 medium squares. The central large square is further divided into 400 small squares. Each large square has a surface are of 1mm2 and the depth of the chamber is 0.1mm. 8.2. Cell suspensions should be dilute enough so that the cells do not overlap each other on the grid, and should be uniformly distributed. 8.3. When counting cells in any given square the convention is to include all cells that touch the upper or left boundaries, whereas those that touch the bottom or right boundaries are excluded 8.4. For accuracy and reproducibility, counts should be carried out in the same manner each time. Decide on a specific counting pattern to avoid bias. 8.5. When the haemocytometer is loaded properly, the volume of cell suspension that will occupy one large square is 0.1 mm3 (1.0 mm2 x 0.1 mm) or 1.0 x10-4 ml. 8.6. Total cell concentration in the original suspension (in cells/ml) is then: Cells/ml = total count (average no cells per large square) x 104 x dilution factor. 8.7. Cell viability is calculated using the following formula: % viable cells = Number of viable cells x100% Number of viable cells + number of dead cells 9. Maintenance: 9.1. Clean haemocytometer with 70% ethanol and kimwipes and return to storage in LS3.17. 9.2. Turn off the microscope. 9.3. Kimwipes used to clean haemocytometer and other solid waste should be placed into the infectious waste bags for autoclaving. 10. Change History: 10.1. Issue Number: Date Issued: 10.2. Issue Number: 1st Issue 22nd February 2006 DISCIPLINE OF MEDICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PROCEDURE NO: Page: Title: Cell Counts Using the Trypan Blue Exclusion Method Date Issued: Reason for Change: GLP 079 7 of 7