Auditing Strategic Objectives
advertisement

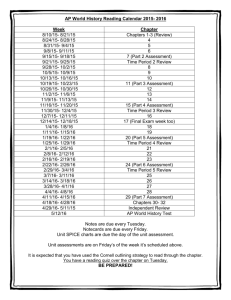
8/30/2011 Auditing Strategic Objectives: Turning Risk into Opportunity August 30, 2011 Presenter’s Name Tony Popanz – Risk Advisory Services Engagement Manager Alec Arons – Risk Advisory Services Director Audio and Tech Support • This meeting is being broadcast, and you can listen through your computer speakers by choosing “Use Use Mic & Speakers Speakers” (figure 1) • To turn up your computer’s volume, please select: Start My Computer Control Panel Sounds and Devices Or • Please select “Use Telephone” option on the GoToMeeting Control Panel and a number and ID will be generated along with a PIN number associated with you. (figure 1) • PLEASE NOTE – All lines will be muted during this presentation. If you would like to ask a question, please use “Questions” (figure 2) function and your question will be addressed. Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 2 1 8/30/2011 Earning CPE Credit To receive 1.5 CPE credits for this Webinar, participants must: − Attend the Webinar for at least 75 minutes on individual computers (one person per computer) − Answer polling questions asked throughout the Webinar At the end of today’s presentation, a link to our CPE Learning Event Survey will be posted in the chat box in the control panel Please take a few moments to complete the survey as we appreciate your feedback Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 3 Auditing Strategic Objectives: Turning Risk into Opportunity August 30, 2011 Presenter’s Name Tony Popanz – Risk Advisory Services Engagement Manager Alec Arons – Risk Advisory Services Director 2 8/30/2011 Agenda • Building the case for auditing strategic objectives • Preparing internal audit for auditing strategic objectives • Examples of strategic audit engagements • Incorporating strategic risks into the audit plan • Developing the competencies of the audit staff • Final thoughts Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 5 What Internal Audit Offers • One of the great strengths of internal audit is its breadth and depth of cross-functional knowledge of the business and the relationships built over time with various parts of the organization – Proven methodologies – Understanding of risk appetite/tolerance, culture, governance practices, and roles and responsibilities – Familiarity with process flows, policies, and procedures • Risk and exposures • Internal controls – Visibility across individual silos –understanding of the interdependencies of various areas of the organization – Interpersonal relationships (“Trusted Advisor”) – objectivity and the sharing of insights across the organization Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 6 3 8/30/2011 Value Creating Evolution of Internal Audit Value Protection Managing Compliance, Managing Crisis Complying with corporate governance standards (fiduciary responsibility) Avoiding personal liability failure (the personal fear factor) Value Creation Minimizing Business Uncertainty Achieving global best practices Understanding and evaluating business risks Understanding full range of risks facing business today Exploiting Opportunity Improving returns through value-based management Enhancing capital allocation Protecting corporate reputation Owning company crises Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 7 IIA Professional Practices Framework • Standard 2010: The chief audit executive must establish risk based plans to determine the priorities of the internal risk-based audit department, consistent with the organization’s goals – Standard 2010.C1: The chief audit executive should consider accepting proposed consulting engagements based on the engagement’s potential to improve management of risks, add value, and improve the organization’s operations. Accepted engagements g g must be included in the p plan Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 8 4 8/30/2011 Types of Risks • Exposure risk – potential negative events such as adverse natural disasters, disasters accidents, accidents and lawsuits resulting in a financial or reputation downside (uncertain future events) • Uncertainty risk – distribution of all possible outcomes, both positive and negative. In this context, risk management seeks to reduce the variance between anticipated outcomes and actual results (business decisions) • Opportunity risk – implicit in the concept is that a relationship exists between risk and return (business initiatives) Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 9 COSO Categories of Risk • Reporting risk – relating to the effectiveness of the entity’s financial reporting process • Compliance risk – relating to the entity’s compliance with applicable laws and regulations Source: COSO Enterprise Risk Management – Integrated Framework (September 2004) Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 10 5 8/30/2011 COSO Categories of Risk • Operations risk – relating to the effectiveness and efficiency of the entity’s operations, including performance and profitability goals • Strategic risk – relating to the entity’s effective utilization of its resources to accomplish its goals and objectives, which are aligned with and supporting the entity’s mission/vision Source: COSO Enterprise Risk Management – Integrated Framework (September 2004) Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 11 Traditional vs. Nontraditional Auditing • Traditional focus – – – – Operational O ti l Financial reporting Compliance Fraud risks • Nontraditional focus – Auditing risks to achieving strategic objectives – May encompass strategic initiatives such as acquisition due diligence and integration or in-process reviews of strategic projects and initiatives Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 12 6 8/30/2011 Strategic Risks • Risks related to achieving strategic objectives relating to: – Revenue growth – New product development – Expansion into new markets – Acquisition and divestitures – Restructuring – Supply chain management – Expense control – Systems implementation – Talent acquisition and retention Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 13 Synergies with the Internal Audit Mission • Optimize deployment of limited resources commensurate with risk-based risk based performance • Reduce losses through coordinated risk awareness • Achieve sustainable competitive advantage through business performance enhancement • Reduce costs through risk consolidation and cross-functional efficiencies • Integrate governance, risk and compliance with business planning, investment and M&A • Facilitate communication and awareness related to risk across the organization Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 14 7 8/30/2011 Polling Question #1 What percent of your organization’s audit plan is linked to strategic objectives? A. Under 10 percent B. 10-25 percent C. 25-50 percent D. Over 50 percent E. Don’t know Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 15 Preparing Internal Audit to Audit Strategic Risk • For internal audit to be effective in auditing strategic risk there are a number of critical success factors – Understand the strategic planning process – Clearly define the role of internal audit – Assess the process and not the plan – Deepen knowledge of the business, industry and competitive threats – Leverage relationships to broaden understanding – Link knowledge g of risks and controls to strategy gy – Promote a dialogue - develop a series of open-ended questions rather than audit programs and questionnaires – Share knowledge and facilitate discussion – Communicate effectively Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 16 8 8/30/2011 Strategic Planning Lifecycle Overview • Evolution of Vision, Mission, Goals and Strategy Vision Mission Goals Strategy Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 17 Strategic Planning Lifecycle Overview • Start with the goals linked to vision and mission • Examine strategic alternatives against assumptions – Internal and external issues – SWOT analysis – Forecasting Vision Vision Mission Mission Assess Outcomes Identify Tasks Goals Goals Strategy gy Strategy • Formulate strategy • Execute strategy Formulate Strategic Objectives Continuously Improve Define Metrics Assign Resources • Sustain strategy Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 18 9 8/30/2011 Auditing the Strategic Lifecycle • Existence of a formal documented process • Level of compliance with the process • Adequacy of communication and vetting process among alternative strategies – Internal vs. external impacts – Cross-functional involvement • Review and approval process • Documentation of the strategic objectives and underlying assumptions • Measurability of strategic objectives Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 19 Auditing the Strategic Lifecycle • Auditing key assumptions supporting strategic decision making – O Optimal ti l timing ti i iis after ft strategy t t formulation f l ti but b t before b f the th organization i ti is committed (i.e., resources are committed and deployed) – Examples • Accuracy of assumptions regarding internal and external opportunities and threats • Pressure testing against adverse but plausible scenarios • Recognition of interdependencies among risk factors • Existence of evidence from unbiased sources • Adequacy of support for conclusions drawn • Mechanisms to continuously monitor for changes that may invalidate original assumptions and expected outcomes Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 20 10 8/30/2011 Auditing the Strategic Lifecycle • Examples of risk monitoring mechanisms – Processes to continuously assess for changes to underlying risks or the existence of newly discovered or emerging risks – Early detection and reporting protocols for risk events originating inside and outside of the organization Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 21 Strategic Alignment • Alignment between enterprise and business unit strategies • Alignment between short term and long term • Alignment with stakeholder interests – – – – – – – Customers Employees Shareholders Creditors Suppliers Regulators Public Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 22 11 8/30/2011 Strategic Metrics • Metric Selection (e.g., KPIs, KRIs, Ratios) – – – – Relevance Reliability / Objectivity Leading vs. Lagging Risk Indicators Benchmarking – internal vs. external • Metric Gathering Controls – Inputs / Sources (accuracy, completeness, validity) – Calculation (accuracy (accuracy, validity) – Outputs / Destinations (accuracy, timeliness) • Monitoring and Reporting – Monitoring performance gaps against interim targets – Reporting frequency, medium, audience, escalation Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 23 Performance Incentives • Alignment to support the intended outcome – Unintended side effects (e.g., diversion of resources from critical operational or investment activities to bring the project in well ahead of schedule) – Gaming risks (i.e., sandbagging, distortions, and other counterproductive behaviors) • Should be SMART – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound • Consider industry norms Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 24 12 8/30/2011 Strategic Awareness • Awareness and understanding of the vision and strategy – Quality Q lit off communication i ti • Top-down • Bottom-up – Across levels of the organization – Across functions and departments – Recognition R iti how h their th i role l impacts i t strategic t t i objectives bj ti – Ability to recognize day to day impacts and leading indicators – Level of confidence in the organization’s strategy Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 25 Auditing Risks to Attainment • Identify gaps between current state and required capabilities – Process P – People – Systems • Assess likelihood of achieving strategic objectives within a specified timeframe with current constraints in budget, timeframe, and talent • Recommend improvements to organizational capabilities Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 26 13 8/30/2011 Assessment tools • Interviews • Observation • Testing • Surveys • Facilitated sessions • Use of voting software Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 27 Example: New product development • Process – D Degree off pioneering i i – risk i kb brought ht about b tb by th the process being new to the company or industry – Complexity – difficulty or level of skill involved in new processes to be performed – Compliance – intellectual property rights, production (e.g., data privacy, environmental), product liability, consumer protections • People – Qualifications of management and staff – Level of management oversight • Systems – Impact of technological change – Data integrity and the impact of inaccurate information Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 28 14 8/30/2011 Example: Due diligence for acquisition • Process – D Do similarities i il iti exist i tb between t acquirer i and d acquiree i processes so as to facilitate integration? – Will the acquiree’s processes meet the current customer service level agreements in place? – Are adequate controls in place to ensure the accuracy and completeness of internal and external reporting? • People – Is the organizational culture a fit, including common values, goals and sense of accountability? • Systems – Will acquiree systems accommodate a shared service back-office model and anticipated efficiencies? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 29 Strategic Project Auditing • Definition of a project • Examples E l off strategic t t i projects j t – – – – New facility or plant System deployment New product development Consolidation of operations • Project lifecycle – – – – – Inception Planning Execution Wrap-up Post mortem Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 30 15 8/30/2011 Strategic Project Auditing • Inception – Is there a formal, documented project management methodology for overseeing the project? – Has a project risk assessment been performed, identifying risks to achieving project objectives, and a mitigation plan? – Do risks appear to be reasonably mitigated within the budget and timeframe constraints set by b the project? – Is there a charter documenting project governance and oversight, roles and responsibilities, timeline, communication plan, deliverables and success metrics? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 31 Strategic Project Auditing • Planning – A Are the th planned l d ttasks, k milestones, il t assigned i d resources, and d ti timelines li documented and appear realistic? – What resources must each area contribute to the initiative and when? Can the areas accommodate and maintain current service levels? – Have the adequate internal and/or external resources with sufficient skillsets been procured and scheduled? – Are there any contingencies in what must be provided? Have those contingencies been addressed with mitigation plans? – What about task dependencies? Which tasks can indefinitely delay the initiative as a whole? – What controls are in place to monitor that the right things are accomplished at the right time and within budget? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 32 16 8/30/2011 Strategic Project Auditing • Execution – What about quality assurance and oversight controls over work in process and the end product? – Are milestone dates being met or are on track to being met? – Are there review points or decision making gates between phases to obtain approval to move forward? – When changes to schedule, budget, or scope occur, is a formal change order process being followed? – What information and communication controls are in place to ensure management is apprised of status and can intervene in a timely manner as risks emerge to cost effectively influence outcomes? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 33 Strategic Project Auditing • Wrap-up – Are the criteria satisfied in the final decision gate to consider the initiative “live”? Can the information supporting this decision be audited? – Has a readiness assessment been completed? Will the organization structure sustain the implementation going forward? – Has change management occ occurred rred to ens ensure re that the organization accepts the changes, has been sufficiently prepared and trained, and is willingly accountable for the results? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 34 17 8/30/2011 Strategic Project Auditing • Post mortem – Post implementation, were the expected outcomes achieved (expected vs. actual results)? – Will the desired outcomes be sustainable long term (operationalized in the day-to-day, localized)? – Are recommendations and lessons learned documented and follo followed ed up p on? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 35 Polling Question #2 The area our internal audit department intends to allocate the most resources to strategically assist management in the next year: A. Merger/Acquisition due diligence or integration B. New product development C. Organizational restructuring or reengineering D Shared services / Systems integration D. E. Expansion / New facilities Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 36 18 8/30/2011 Incorporating into the Audit Plan • Risk assessment – D During i th the risk i k assessment, t iincorporate t as a risk i k ffactor t assessed d against the risk universe (e.g., “Impact to Achieving Objectives”) Impact to Achieving Objectives - Weighs the importance of the component risk in terms of meeting entity objectives. 3 0 1 2 3 4 Risk events have negligible impact to entity objectives. Risk events have minimal impact to entity objectives. Moderate risk to entity objectives; management acknowledges impact to entity objectives may be substantial in the short term (i.e. next 12 months) but will be surmountable in the longer term. Major risk to entity objectives; management acknowledges impact will likely impair the organization's ability to achieve objectives in the short term (i.e. next 12 months) but will be surmountable in the longer term. Or, moderate risk to entity objectives; management acknowledges a substantial and continued, longer term impact to entity objectives. Major risk to entity objectives; management has indicated that risk events may permanently impair the organization's ability to achieve certain objectives. – Also leverage another risk factor, “Management Concern”, to explore potential avenues into strategic risk Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 37 Incorporating into the Audit Plan • Conduct structured facilitative sessions with cross functional groups of executives – Discuss the known and emerging risks to strategic plans and metrics business by business • What must each function contribute to achieve the strategic plan? • Which contributions are most at risk for success? • What are the cause and effect issues and interdependencies among risks? – Cross-functional facilitation may involve Finance, Operations, Information Technology, Sales/Marketing, Human Resources, Compliance, Legal, Research and Development, Public Relations Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 38 19 8/30/2011 Additional Examples of Questions to Initiate a Strategic Risk Dialogue • What concerns do you have regarding revenue growth given that competition is pricing to grow market share? • The plan calls for margin improvement of 4 percent. Have you factored on any potential commodity price increases or issues with supplier availability? • Do you have any specific concerns about the financial health of key customers? • Given staff reductions over the past 24 months, months will your current infrastructure support growth? • What key metrics are being leveraged to measure progress and detect early signs of under performance? • What other tools or resources are required to achieve success? Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 39 Incorporating into the Audit Plan • Allocation for management requests – T Typical i l allocation ll ti may b be 10 10-20 20 percentt off resources – Inquire of management regarding anticipated initiatives (e.g., project proposals) – Propose various alternatives to management for supporting strategic initiatives • Demonstrate Value – Report cumulative bottom line contribution (cost recovery, recovery revenue and profitability enhancements) – Report the number of strategic audits completed and proportion of the total audit plan committed to strategic audits – Follow-up on recommendations Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 40 20 8/30/2011 Polling Question #3 The biggest challenge in providing strategic value to management is: A. Lack of needed resource skillsets in internal audit B. Lack of familiarity with management’s strategic objectives or initiatives C. Management resistance to engage internal audit in strategic initiatives D. Insufficient resources to address strategic initiatives E No “seat E. seat at the table” during the strategic decision making process Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 41 Positioning Internal Audit for success • The audit committee and management need to be confident in the capability of IA to perform the assessment • In many organizations the reputation of audit is that they are not strategic • Focus on value creation versus value preservation • Define the skills and competencies needed to assess strategic g risks • Identify who on the staff has the requisite skills and capabilities • Create plans to develop / acquire the needed competencies Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 42 21 8/30/2011 Core competencies for internal auditors • Released in 2010 in conjunction with the CBOK Study the IIA Research Foundation released the Global Internal Audit Survey • Survey included a report on Core Competencies for Today’s Internal Auditor • Report recognizes the changing expectations of audit and discusses the required core competencies for auditors relating to general competencies, behavioral skills and technical skills for CAE’s, audit managers and audit staff • Report highlights that there are certain competencies expected at each level and also a common set of competencies for each level Source: 2010 IIA Global Internal Audit Survey Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 43 Core competencies for internal auditors • The survey identifies four competencies as common to each role: – C Communications i ti skills kill (including (i l di oral, l writing, iti report writing and presentations). – Problem identification and solution skills (including core conceptual analytical thinking). – Keeping up to date with industry and regulatory changes and professional standards. – Understanding the business. • While each of these skills is critical to positioning internal audit as an effective resource for assessing strategic risks, understanding the business is a recurring theme encountered in many internal audit departments. Source 2010 IIA Global Internal Audit Survey Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 44 22 8/30/2011 Understanding the Business • Understanding the business implies that the auditor: – F Focuses upon emerging i risks i k tto the th key k value l d drivers i of the business – Understands the context of the findings, including the implications and mitigating factors – Understands the root cause(s) rather than symptoms – Makes recommendations that are compelling, relevant, in sufficient depth, and practical to implement (e.g. cost vs. benefit) – Is responsive to requests for consultative assistance on resolving issues while maintaining the necessary independence and objectivity – Can propose various alternatives to management for supporting strategic initiatives Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 45 Core competencies for internal auditors • The other competencies identified by level are as follows: – IA Staff St ff • Competencies with accounting frameworks, tools and techniques • Competency with IT frameworks, tools and techniques – Management • Organizational skills (including project and time management). • Conflict resolution/negotiation skills. – Chief Audit Executives • Ability to promote the value of the internal audit function within the organization • Conflict resolution/negotiation skills Source 2010 IIA Global Internal Audit Survey Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 46 23 8/30/2011 Competency Development • Leading practice within most organizations is to – Define the role based competencies required to grow – Develop learning programs to promote competency development – Create individual plans to develop and deepen the skills of the team Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 47 Competency Development • A leading practice is to create learning maps by role that highlight the competency levels required and the learning opportunities available to develop these skills • Learning maps promote an integrated learning experience that link formal learning with experiential learning • Learning maps should consist of – Structured learning– directed and self-directed – Experiential learning – Coaching and mentoring • Evaluation and updates of the learning maps should be linked to goal setting and engagement staffing so that professionals can obtain a broad range of experience Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 48 24 8/30/2011 Competency Development • Structured learning - includes formal training programs and reading relevant articles and publications specific to the industry and the skills you are trying to acquire. – In house and third party seminars and training – Book and general business magazines – Industry trade journals – Public filings – Networking through the IIA, Industry Associations and Professional Groups – Leverage access to digital content and tools available Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 49 Competency Development • Experiential learning – hands on learning opportunities to enhance or develop new skills – – – – – – – – – Focused assignments Stretch assignments Shadowing Special projects and task forces Volunteering Rotation programs (lines of business, business various disciplines) Guest auditor programs Auditor exchanges Increased exposure to executive management and audit committee Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 50 25 8/30/2011 Competency Development • Coaching and mentoring – Play a valuable role in developing talent – Formal and informal mentors – Respect the time of your mentor or coach – Clearly defined goals • Networking • Knowledge acquisition • Skills development – Honor mutual commitments Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 51 Polling Question #4 I regard the following type of learning to be the most effective in my growth and development: A. Structured learning B. Experiential learning C. Coaching and mentoring D. All of the above Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 52 26 8/30/2011 Final Thoughts • Not mutually exclusive from core traditional assurance activities – Places Pl greater t emphasis h i on th the value l d drivers i off th the b business i – Does not neglect “keeping the lights on” assurance activity • Evolutionary considerations – Management culture – Management perception of internal audit – Audit Committee-level support • Competencies and skills – Communications – Problem solving – Industry knowledge • Independence considerations Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 53 Questions? For more information please contact: Tony Popanz Risk Advisory Services Engagement Manager (414)-231-1110 Anthony.Popanz@experis.com Alec Arons Risk Advisory Services Engagement Manager (267)-765-2677 Alec.Arons@experis.com Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 54 27 8/30/2011 Webcast evaluation A link to our CPE Learning Event Survey is now located in the chat box in the control panel Please take a few minutes to provide us with your feedback Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 55 Experis™ Finance delivers innovative solutions that help companies create competitive advantage, custom tailoring our professional resourcing and project solutions to fit our clients’ needs in the areas of risk advisory, tax and finance & accounting. Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 56 28 8/30/2011 More information For more information, please visit www.experis.us Experis™ Finance | Tuesday, August 30, 2011 57 29