Redox and Electrochemistry Name: Thursday, May 08, 2008 1. A
advertisement
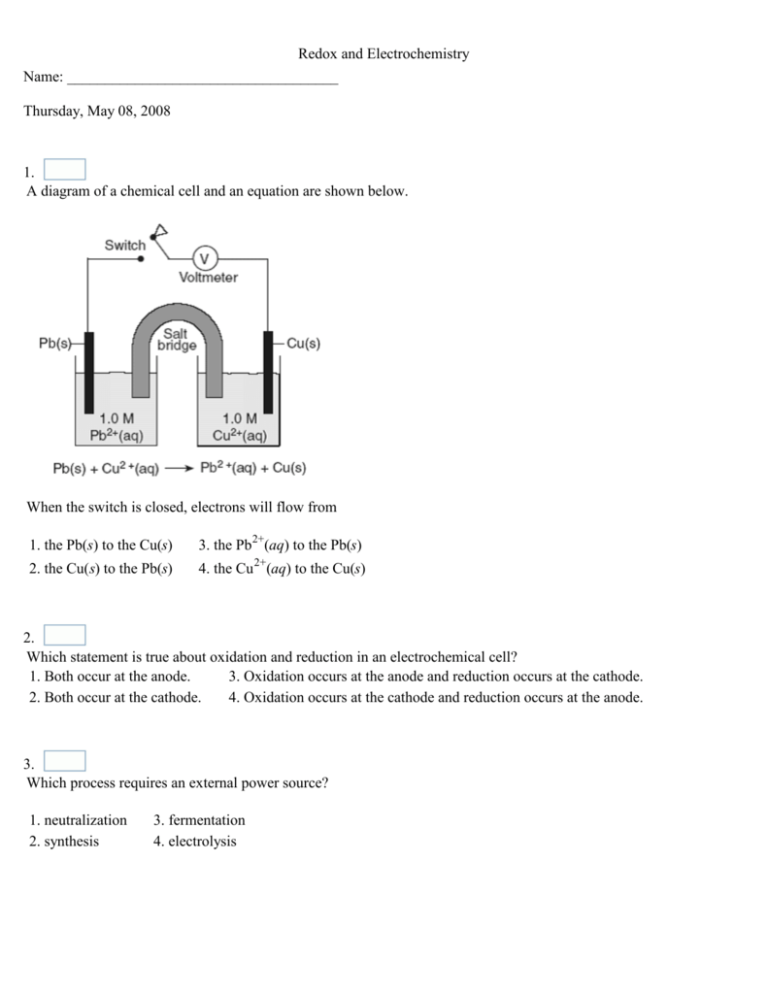
Redox and Electrochemistry Name: ____________________________________ Thursday, May 08, 2008 1. A diagram of a chemical cell and an equation are shown below. When the switch is closed, electrons will flow from 1. the Pb(s) to the Cu(s) 3. the Pb2+(aq) to the Pb(s) 2. the Cu(s) to the Pb(s) 4. the Cu 2+(aq) to the Cu(s) 2. Which statement is true about oxidation and reduction in an electrochemical cell? 1. Both occur at the anode. 3. Oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction occurs at the cathode. 2. Both occur at the cathode. 4. Oxidation occurs at the cathode and reduction occurs at the anode. 3. Which process requires an external power source? 1. neutralization 2. synthesis 3. fermentation 4. electrolysis Redox and Electrochemistry 4. An electrolytic cell is different from a voltaic cell because in an electrolytic cell 1. a redox reaction occurs 2. a spontaneous reaction occurs 3. an electric current is produced 4. an electric current causes a chemical reaction 5. What is the oxidation number of nitrogen in NO(g)? Answer: 6. Which half-reaction correctly represents a reduction reaction? 1. Sn0 + 2eSn2+ 0 2. Na + e Na+ 3. Li0 + eLi+ 0 4. Br2 + 2e 2Br- 7. What is the oxidation number of chlorine in HClO4? 1. +1 2. +5 3. +3 4. +7 8. Which type of reaction is occurring when a metal undergoes corrosion? 1. oxidation-reduction 2. neutralization 3. polymerization 4. saponification Redox and Electrochemistry 9. Which statement best describes the reaction represented by the equation below? 2NaCl + 2H 2O + electricity Cl2 + H 2 + 2NaOH 1. The reaction occurs in a voltaic cell and releases energy. 2. The reaction occurs in a voltaic cell and absorbs energy. 3. The reaction occurs in an electrolytic cell and releases energy. 4. The reaction occurs in an electrolytic cell and absorbs energy. 10. Which changes occur when Pt2+ is reduced? 1. The Pt2+ gains electrons and its oxidation number increases. 3. The Pt2+ loses electrons and its oxidation number increases. 2. The Pt2+ gains electrons and its oxidation number decreases. 4. The Pt2+ loses electrons and its oxidation number decreases. 11. Which quantities are conserved in all oxidation-reduction reactions? 1. charge, only 2. mass, only 3. both charge and mass 4. neither charge nor mass 12. In the reaction: Pb + 2Ag+ → Pb2+ + 2Ag, the Ag+ is 1. reduced, and the oxidation number changes from +1 to 0 2. reduced, and the oxidation number changes from +2 to 0 3. oxidized, and the oxidation number changes from 0 to +1 4. oxidized, and the oxidation number changes from +1 to 0 Redox and Electrochemistry 13. In the redox reaction: Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s), there is a conservation of 1. mass, only 2. charge, only 3. both mass and charge 4. neither mass nor charge 14. Which statement correctly describes a redox reaction? 1. The oxidation half-reaction and the reduction half-reaction occur simultaneously. 2. The oxidation half-reaction occurs before the reduction half-reaction. 15. Given the reaction: Fe(s) + Sn4+(aq) The oxidizing agent is 1. Fe(s) 3. Fe2+(aq) 2. Sn4+(aq) 4. Sn2+(aq) 3. The oxidation half-reaction occurs after the reduction half-reaction. 4. The oxidation half-reaction occurs spontaneously but the reduction half-reaction does not. Fe2+(aq) + Sn2+(aq) 16. What is the oxidation number of carbon in NaHCO3? 1. +6 2. +2 3. -4 4. +4 17. Which equation shows conservation of both mass and charge? 1. Cl2 + Br- → Cl- + Br2 3. Zn + Cr3+ → Zn2+ + Cr 2. Cu + 2 Ag+ → Cu2+ + Ag 4. Ni + Pb2+ → Ni2+ + Pb Redox and Electrochemistry 18. An electrochemical cell that generates electricity contains half-cells that produce 1. oxidation half-reactions, only 2. reduction half-reactions, only 3. spontaneous redox reactions 4. nonspontaneous redox reactions 19. Which half-reaction correctly represents reduction? 1. Fe2+ + 2eFe0 2+ 2. Fe + e Fe3+ 0 3. Fe + 2e Fe2+ 4. Fe0 + eFe3+ 20. A discharging lead-acid battery is best described as 1. chemical cells that use an electric current 2. chemical cells that produce an electric current 3. electrolytic cells that use an electric current 4. electrolytic cells that produce an electric current 21. A voltaic cell differs from an electrolytic cell in that a chemical cell uses 1. half-reactions 2. a solution of ions 3. an applied electric current 4. a redox reaction to produce electricity 22. Which is a redox reaction? 1. H+ + Cl- → HCl 3. Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + H2 2. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2O 4. MgO + H 2SO4 → MgSO4 + H 2O Redox and Electrochemistry 23. Which change occurs when an Sn 2+ ion is oxidized? 1. Two electrons are lost. 2. Two electrons are gained. 3. Two protons are lost. 4. Two protons are gained. 24. Given the balanced ionic equation representing a reaction: 2Al3+(aq) + 3Mg(s) 3Mg2+(aq) + 2Al(s) In this reaction, electrons are transferred from 1. Al to Mg2+ 3. Mg to Al3+ 2. Al3+ to Mg 4. Mg2+ to Al 25. Which type of reaction occurs when nonmetal atoms become negative nonmetal ions? 1. oxidation 2. reduction 3. substitution 4. condensation Redox and Electrochemistry 26. Figure 1 Which type of cell does the diagram represent? 1. electrolytic, with the anode at A 2. electrolytic, with the cathode at A 3. voltaic , with the anode at A 4. voltaic , with the cathode at A 27. A student collects the materials and equipment below to construct a voltaic cell. two 250-mL beakers wire and a switch one strip of magnesium one strip of copper 125 mL of 0.20 M Mg(NO3)2(aq) 125 mL of 0.20 M Cu(NO3)2(aq) Which additional item is required for the construction of the voltaic cell? 1. an anode 3. a cathode 2. a battery 4. a salt bridge Redox and Electrochemistry 28. Figure 2 The diagram slows the electrolysis of fused KCl. What occurs when the switch is closed? 1. Positive ions migrate toward the anode, where they lose electrons. 2. Positive ions migrate toward the anode, where they gain electrons. 3. Positive ions migrate toward the cathode, where they lose electrons. 4. Positive ions migrate toward the cathode, where they gain electrons. 29. Which particles are gained and lost during a redox reaction? 1. electrons 2. protons 3. neutrons 4. positrons 30. Given the reaction: 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g ) Which substance undergoes oxidation? 1. Na 2. NaOH 3. H2 4. H2O Redox and Electrochemistry 31. Which balanced equation represents an oxidation-reduction reaction? 1. BaCl2 + Na2SO4 BaSO4 + 2NaCl 2. C + H 2O CO + H2 3. CaCO3 CaO + CO2 4. Mg(OH)2 + 2HNO3 Mg(NO3)2 + 2H2O 32. When the equation __Pb2+ + __Au 3+ → __Pb4+ + __Au is correctly balanced using the smallest whole-number coefficients, the coefficient of Pb2+ will be 1. 1 2. 2 3. 3 4. 4 33. Which half-cell reaction correctly represents reduction? 1. Cu+(aq) + eCu(s) 2+ 2. Cu(s) Cu (aq) + 2e3. H(g) + e H+(aq) 4. H2(g) 2H+(aq) + 2e- Redox and Electrochemistry 34. Figure 3 Write the balanced half-reaction for the reduction that occurs in this electrolytic cell. 1. Cl2 + 2e2Cl2. Cl2 2Cl- + 2e3. 2Na+ + 2e2Na 4. 2Na+ 2Na + 2e- 35. Given the reaction: 2Li(s) + Cl2(g) 2LiCl(s) As the reaction takes place, the Cl 2(g) will 1. gain electrons 2. lose electrons 3. gain protons 4. lose protons 36. The purpose of a salt bridge in a voltaic cell is to 1. allow for the flow of molecules between the solutions 2. allow for the flow of ions between the solutions 3. prevent the flow of molecules between the solutions 4. prevent the flow of ions between the solutions Redox and Electrochemistry 37. Which statement is true for any electrochemical cell? 1. Oxidation occurs at the anode, only. 2. Reduction occurs at the anode, only. 3. Oxidation occurs at both the anode and the cathode. 4. Reduction occurs at both the anode and the cathode. 38. In which compound does sulfur have an oxidation number of -2? 1. SO2 2. SO3 3. Na2S 4. Na2SO4 39. Figure 4 The diagram represents a chemical cell at 298 K and 1 atmosphere. Which species represents the cathode? 1. Zn 2. Zn2+ 3. Cu 4. Cu2+ Redox and Electrochemistry 40. Given the reaction: Which species undergoes reduction? 1. Al 3. Al3+ 2. Fe 4. Fe3+ 41. What is the purpose of the salt bridge in a voltaic cell? 1. It blocks the flow of electrons. 2. It blocks the flow of positive and negative ions. 3. It is a path for the flow of electrons. 4. It is a path for the flow of positive and negative ions. 42. Given the balanced equation: 3Fe 3+(aq) + Al(s) → 3Fe2+(aq) + Al3+(aq) What is the total number of moles of electrons lost by 2 moles of Al(s)? 1. 1 mole 2. 6 moles 3. 3 moles 4. 9 moles 43. Given the reaction: Ca(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + Cu(s) What is the correct reduction half-reaction? 1. Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) 3. Cu(s) + 2e- → Cu2+(aq) 2. Cu2+(aq) → Cu(s) + 2e- 4. Cu(s) → Cu2+(aq) + 2e- 44. Given the redox reaction: Ni + Sn4+ Which species has been oxidized? 1. Ni 3. Ni2+ 2. Sn4+ 4. Sn2+ Ni2+ + Sn2+ Redox and Electrochemistry 45. Figure 5 The diagram shows an electrolytic cell in which the electrodes are tin and copper. When the switch is closed, what will happen to the two electrodes? 1. B will dissolve and A will become coated with tin. 2. A will dissolve and B will become coated with tin. 3. B will dissolve and A will become coated with copper. 4. A will dissolve and B will become coated with copper. 46. Figure 6 The diagram represents the electroplating of a metal fork with Ag( s). Which part of the electroplating is represented by the fork? 1. the anode, which is the negative electrode 2. the cathode, which is the negative electrode 3. the anode, which is the positive electrode 4. the cathode, which is the positive electrode Redox and Electrochemistry 47. Given the redox reaction: Fe2+(aq) + Zn(s) Which species acts as a reducing agent? 1. Fe(s) 2. Fe2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Fe(s) 3. Zn(s) 4. Zn2+(aq) 48. Given the balanced ionic equation: Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Zn 2+(aq) + Cu(s) Which equation represents the oxidation half-reaction? 1. Zn(s) + 2e- → Zn2+(aq) 3. Cu2+ (aq) →Cu(s) + 2e- 2. Zn(s) → Zn 2+(aq) + 2e- 4. Cu2+ (aq) + 2e- → Cu(s) 49. Which energy conversion occurs during the operation of a voltaic cell? 1. Chemical energy is spontaneously converted to 3. Electrical energy is spontaneously converted to electrical energy. chemical energy. 2. Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy only 4. Electrical energy is converted to chemical energy only when an external power source is provided. when an external power source is provided. 50. In which substance does chlorine have an oxidation number of +1? 1. Cl2 2. HCl 3. HClO 4. HClO2 Redox and Electrochemistry Answer Key for Redox and Electrochemistry 1. 1 2. 3 3. 4 4. 4 5. +2 6. 4 7. 4 8. 1 9. 4 10. 2 11. 3 12. 1 13. 3 14. 1 15. 2 16. 4 17. 4 18. 3 19. 1 20. 2 21. 4 22. 3 23. 1 24. 3 25. 2 26. 1 27. 4 28. 4 29. 1 30. 1 31. 2 32. 3 33. 1 34. 3 35. 1 36. 2 37. 1 38. 3 39. 3 40. 4 41. 4 42. 2 43. 1 44. 1 45. 2 46. 2 Redox and Electrochemistry 47. 3 48. 2 49. 1 50. 3







