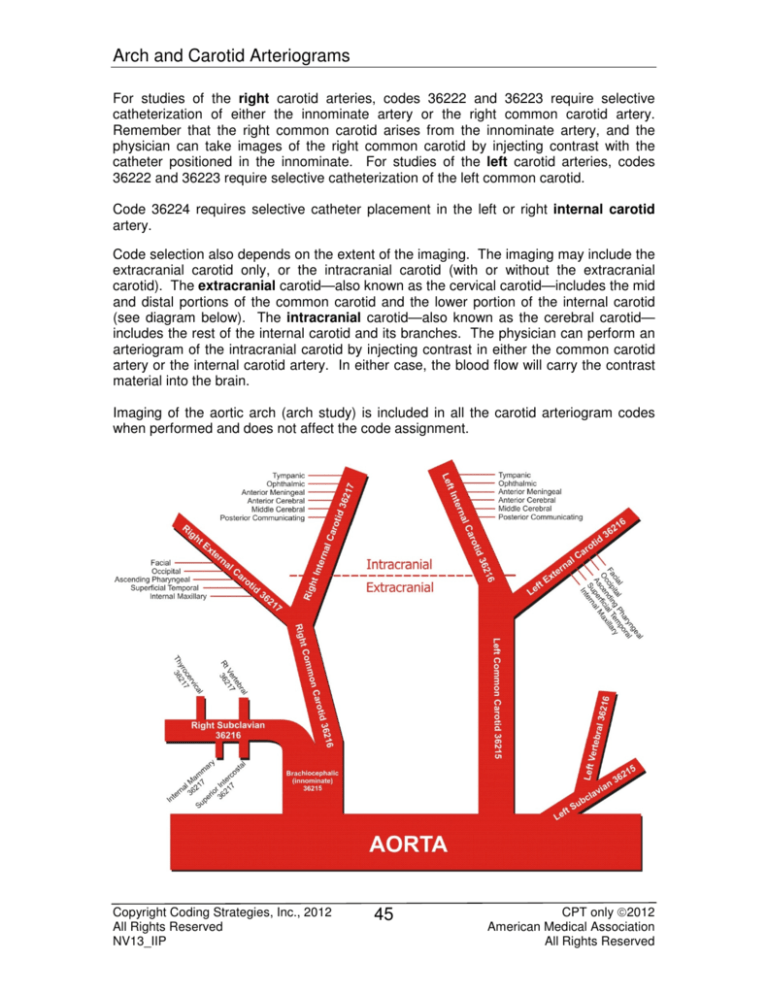
Arch and Carotid Arteriograms
For studies of the right carotid arteries, codes 36222 and 36223 require selective
catheterization of either the innominate artery or the right common carotid artery.
Remember that the right common carotid arises from the innominate artery, and the
physician can take images of the right common carotid by injecting contrast with the
catheter positioned in the innominate. For studies of the left carotid arteries, codes
36222 and 36223 require selective catheterization of the left common carotid.
Code 36224 requires selective catheter placement in the left or right internal carotid
artery.
Code selection also depends on the extent of the imaging. The imaging may include the
extracranial carotid only, or the intracranial carotid (with or without the extracranial
carotid). The extracranial carotid—also known as the cervical carotid—includes the mid
and distal portions of the common carotid and the lower portion of the internal carotid
(see diagram below). The intracranial carotid—also known as the cerebral carotid—
includes the rest of the internal carotid and its branches. The physician can perform an
arteriogram of the intracranial carotid by injecting contrast in either the common carotid
artery or the internal carotid artery. In either case, the blood flow will carry the contrast
material into the brain.
Imaging of the aortic arch (arch study) is included in all the carotid arteriogram codes
when performed and does not affect the code assignment.
Copyright Coding Strategies, Inc., 2012
All Rights Reserved
NV13_IIP
45
CPT only 2012
American Medical Association
All Rights Reserved
PelvisError! Bookmark not defined.
The pelvic arteries include the iliac arteries on both sides as well as the branches that
arise from them.
As mentioned previously, the aorta splits (bifurcates) into the left and right common iliac
arteries. Each common iliac subsequently splits into the internal iliac, which supplies the
pelvic organs, and the external iliac, which supplies the leg. Each internal iliac then
divides into anterior and posterior divisions. Each of these divisions is a third order
vessel.
As with leg arteriograms, it is important when coding pelvic arteriograms to determine
whether the catheter placement is ipsilateral (on the same side of the body as the
puncture site) or contralateral (opposite side).
Catheterization Codes
When the puncture site is in the femoral artery, the catheter placement is nonselective if
the catheter stays in the common femoral artery, the external iliac artery, or the aorta.
This type of catheter placement is reported with 36140 if the catheter stays in the
common femoral, external iliac, or common iliac, or with code 36200 if the catheter is
advanced into the aorta.
Selective pelvic artery catheterization is reported with codes 36245-36248. If the
physician passes the catheter into the internal iliac artery on the same side as the
puncture site, this is a first order selective catheterization. On the other hand, if the
physician passes the catheter over the bifurcation into the contralateral common iliac,
and then advances it into the contralateral internal iliac, this is a second order selective
catheterization.
Copyright Coding Strategies, Inc., 2012
All Rights Reserved
NV13_IIP
175
CPT only 2012
American Medical Association
All Rights Reserved