1
2013, Study Session # 8, Reading # 27
“UNDERSTANDING CASH FLOW STATEMENTS”
CFS
CFO
CFI
CFF
NI
BV
=
=
=
=
=
=
Cash Flow Statement
Cash Flow from Operations
Cash Flow from Investing
Cash Flow from Financing
Net Income
Book Value
IS
BS
FCFE
NCC
FCFF
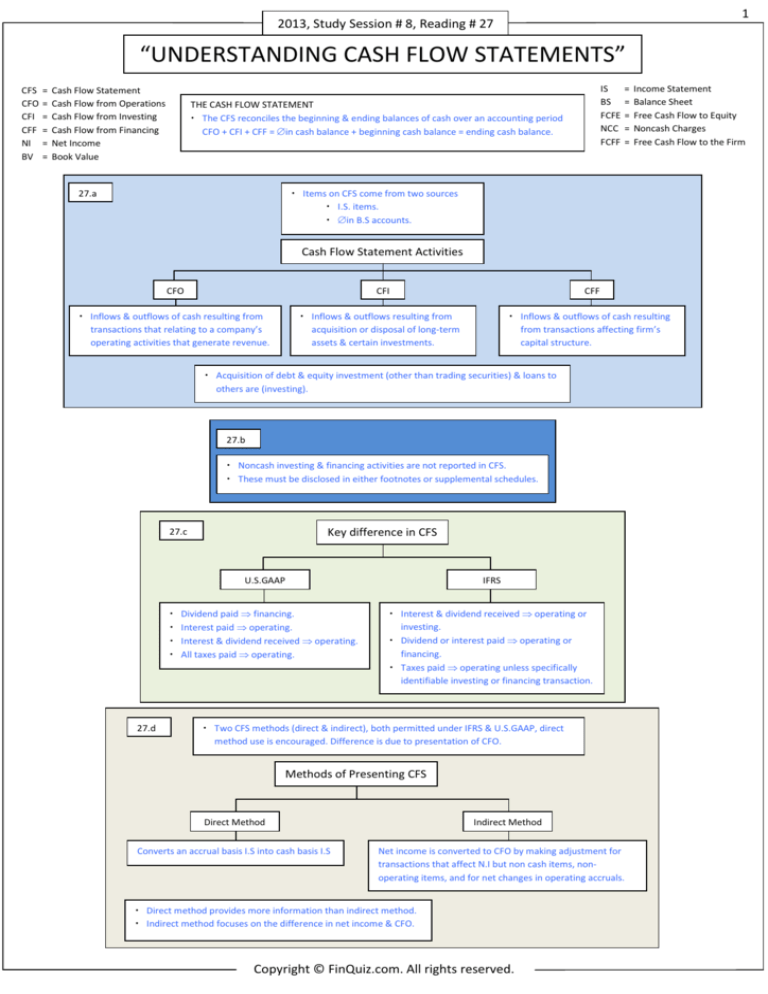
THE CASH FLOW STATEMENT
The CFS reconciles the beginning & ending balances of cash over an accounting period
CFO + CFI + CFF = ∆ in cash balance + beginning cash balance = ending cash balance.
27.a
=
=
=
=
=
Income Statement
Balance Sheet
Free Cash Flow to Equity
Noncash Charges
Free Cash Flow to the Firm
Items on CFS come from two sources
I.S. items.
∆ in B.S accounts.
Cash Flow Statement Activities
CFO
CFI
Inflows & outflows of cash resulting from
transactions that relating to a company’s
operating activities that generate revenue.
CFF
Inflows & outflows resulting from
acquisition or disposal of long-term
assets & certain investments.
Inflows & outflows of cash resulting
from transactions affecting firm’s
capital structure.
Acquisition of debt & equity investment (other than trading securities) & loans to
others are (investing).
27.b
Noncash investing & financing activities are not reported in CFS.
These must be disclosed in either footnotes or supplemental schedules.
27.c
Key difference in CFS
U.S.GAAP
27.d
Dividend paid ⇒ financing.
Interest paid ⇒ operating.
Interest & dividend received ⇒ operating.
All taxes paid ⇒ operating.
IFRS
Interest & dividend received ⇒ operating or
investing.
Dividend or interest paid ⇒ operating or
financing.
Taxes paid ⇒ operating unless specifically
identifiable investing or financing transaction.
Two CFS methods (direct & indirect), both permitted under IFRS & U.S.GAAP, direct
method use is encouraged. Difference is due to presentation of CFO.
Methods of Presenting CFS
Direct Method
Converts an accrual basis I.S into cash basis I.S
Indirect Method
Net income is converted to CFO by making adjustment for
transactions that affect N.I but non cash items, nonoperating items, and for net changes in operating accruals.
Direct method provides more information than indirect method.
Indirect method focuses on the difference in net income & CFO.
Copyright © FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
2
2013, Study Session # 8, Reading # 27
27.d
Disclosure Requirements
U.S.GAAP
IFRS
Direct method presentation must also disclose
adjustments to reconcile N.I to CFO.
Payment for interest & taxes can be reported in
cash flow statement or in footnotes.
Payments for interest & taxes must be
disclosed.
27.f
CFO
Indirect Method
Direct Method
Cash collected from customers.
Cash used in production of goods & services.
Cash operating expenses.
Cash paid for interest.
Cash paid for taxes.
Net income.
± G/L resulted from financing or
investing CF.
+ Noncash charges &
- Non cash revenue.
operating assets (-) while are (+)
Operating liability (+) while are (-).
CFI
Calculated by examining change in gross asset accounts that result from investing
activities.
Cash paid for new asset = ending gross asset + gross cost of old assets sold –
beginning gross assets.
Cash from asset sold = B.V of asset ± G/L on sale.
CFF
27.g
Determined by measuring CF occurring b/w firm & supplier of capital.
Net CF from creditors = new borrowings – principal amounts repaid.
Cash dividend can be calculated from an analysis of retained earnings.
CFO + CFI + CFF = total CF = ∆ in balance sheet cash.
Adjust I.S item for its corresponding B.S. account & eliminate noncash & non operating transactions.
Illustrative conversion process of frequently used accounts is:
Cash collection from customers
Revenue + (–) dec (inc) in AR.
Cash payment to suppliers
COGS + in inventory - in inventory + AP - AP.
Other items follow the same principles.
Cash operating expense
SG&A + in prepaid expense - in prepaid expense. –↑ in other accrued liabilities + ↓
in other accrued liabilities
Copyright © FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.
3
2013, Study Session # 8, Reading # 27
27.h
Major sources & uses of cash
Sources & uses of cash change as firm moves through its life cycle.
Over the long term, successful firms must be able to generate CFO that exceed capital
expenditure & provide a return to debt & equity holders.
Operating cash flow
+ CFO can be generated by earning – related activities or non cash working capital
(not sustainable).
CFO also provides a check of the quality of a firm’s earnings
Variability of N.I & CFO should also be considered.
Investing cash flow
capex, usually indication of growth.
Firm may reduce capex or even sell capital assets to save cash.
Generating CFO in excess of capex is desirable.
Financing cash flow
Provide information about debt & equity (using cash to repay
debt, reacquire stock or pay dividends).
Common-size CFS
By expressing each line item as a % of revenue.
Alternatively each inflow of cash as a % of total cash inflow &
each outflow as % of total outflow.
27.i
Free CF ⇒ measure of cash that is available for discretionary purpose (after covering capex).
If firms that follow IFRS subtracted dividend paid in calculating CFO, dividends must be added
back for FCFF.
Free Cash Flow
FCFF
FCFE
Cash available to all investors.
FCFF = N.I + NCC + [int(1-tax rate)] – FCInv – WCInv
FCFF = CFO + [int × (1- tax rate )] – FCInv
Firms that follow IFRS must consider dividend &
interest classification.
Cash flow available to common equity holders.
FCFE = CFO – FCInv + Net borrowings.
Copyright © FinQuiz.com. All rights reserved.








