Protein Quantification - University of Leicester
advertisement

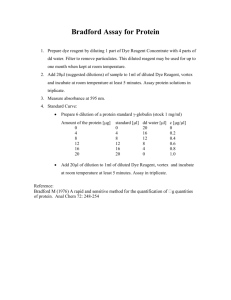
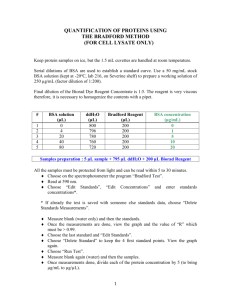
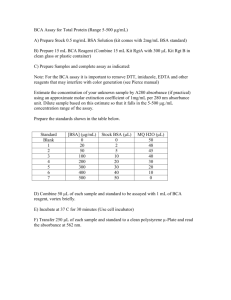
Page 1 of 3 UNIVERSITY OF LEICESTER CANCER STUDIES & MOLECULAR MEDICINE Cell Signalling Section STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SOP - 607 TITLE: VERSION - 01 Protein Quantification Written by: Angie Gillies Reviewed by: Lindsay Primrose Changes introduced: Implementation date: 19.06.08 Review date: 19.06.10 1. PURPOSE To provide a method for the quantification of protein in a sample. Note: Often referred to as a Bradford Assay. 2. SPECIAL NOTES Full details of the use of this procedure must be recorded in the appropriate laboratory notebook, in accordance with SOP 105. 3. CROSS REFERENCES 3.1 3.2 3.3 Preparation of protein lysates Preparation of conditioned media for Western Blotting Protein quantification SOP 605 SOP 606 CPA 093 4. EQUIPMENT & MATERIALS 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Protein Assay Dye Reagent Concentrate Bovine Serum Albumin Sterile ultrapure water Spectrophotometer 4.5 Gold Lysis buffer (stored at room temp) Sops\sop607 Bio-Rad 500 0006 Sigma A-3294 RPM 23 ThermoSpectronic Genesys 10uv RPM 114 Page 2 of 3 5. PROTOCOL 5.1 Prepare Dye Reagent by diluting 1:5 in UP H2O (2ml Dye + 8ml water). Store at 4°C in foil-wrapped tube Diluted Dye Reagent can be used for up to 2 weeks. Ideally a standard curve should be constructed each time an assay is performed but, at the very least, one should be made each time a fresh dilution of Dye Reagent is made. Construction of Standard Curve:Prepare a stock BSA solution (BSA in UP H2O) as accurately as possible at 10mg/ml (i.e.10µg/µl). Aliquots can be stored frozen at -20°C. Now prepare a working stock solution by diluting the stock BSA solution (A) by a factor of 1:100 (10µl Solution A + 990µl H2O). The concentration of this solution is 0.1 µg/µl. Using the 0.1 µg/µl working stock solution, make the following dilutions for the 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 standard curve: Vol of BSA (l) Vol of water (l) Dye reagent 0 5 10 20 30 40 60 80 800 795 790 780 770 760 740 720 200l 200l 200l 200l 200l 200l 200l 200l Protein concentration(g) 0 0.5 1 2 3 4 6 8 Note: we have found that anything above 8µg protein falls outside the linear range 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 5.11 5.12 Vortex the samples. Store in the dark for 10 minutes. Read the absorbance at 595nm with the white lamp, using disposable 1ml cuvettes. Use the first sample (0µg BSA) to blank the spectrophotometer. Construct a standard curve in excel and apply trend line. Use the equation of the trend line to calculate protein concentrations from absorbance readings. Absorbance readings of the samples MUST fall within the range of the standards. For this reason it may be necessary to prepare 1:10 dilutions of the samples as well as measuring them ‘neat’. Quantification of Samples:Prepare samples and relevant blanks as follows: For samples 795µl UP H2O 5µl sample 200µl diluted Dye reagent For cell lysate blank: Use 5µl Gold Lysis buffer instead of sample For Conditioned media blank: Use 5µl (any) depleted media instead of sample Sops\sop607 Page 3 of 3 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 Proceed as for the standard curve samples. Use the trend line equation obtained from the standard curve, to calculate the concentration (µg) of protein in the 5µl sample. From this, calculate the concentration of protein per µl and hence the volume of sample required for 25µg protein. 25µg of protein per well is usually loaded on a Western gel. Occasionally if the expression of the target protein is low, more can be loaded. Sops\sop607