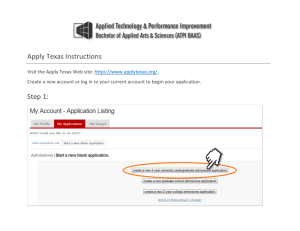
Roles and Functions of the
Correctional System
Copyright and Terms of Service
Copyright © Texas Education Agency, 2011. These materials are copyrighted © and
trademarked ™ as the property of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) and may not be
reproduced without the express written permission of TEA, except under the following
conditions:
1) Texas public school districts, charter schools, and Education Service Centers may
reproduce and use copies of the Materials and Related Materials for the districts’
and schools’ educational use without obtaining permission from TEA.
2) Residents of the state of Texas may reproduce and use copies of the Materials and
Related Materials for individual personal use only, without obtaining written
permission of TEA.
3) Any portion reproduced must be reproduced in its entirety and remain unedited,
unaltered and unchanged in any way.
4) No monetary charge can be made for the reproduced materials or any document
containing them; however, a reasonable charge to cover only the cost of
reproduction and distribution may be charged.
Private entities or persons located in Texas that are not Texas public school districts,
Texas Education Service Centers, or Texas charter schools or any entity, whether
public or private, educational or non-educational, located outside the state of Texas
MUST obtain written approval from TEA and will be required to enter into a license
agreement that may involve the payment of a licensing fee or a royalty.
Contact TEA Copyrights with any questions you may have.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
2
Correctional Careers
•
•
•
•
•
•
Probation Officers
Parole Officers
Jailers or Detention Officers
Correctional Officers
Juvenile Detention Officers
Federal Correctional Officers
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
3
Probation Officers
•
•
•
•
Work under county, state, or federal agencies
Make reports to court on offender behavior
Conduct pre-trial investigations for the court
Monitor compliance with court-ordered
conditions of release
• Complete offender risk assessments
• Report non-compliance to the court
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
4
Parole Officers
• Supervise previously incarcerated offenders
in the community
• Monitor compliance with special conditions
of release
• Report non-compliance to the paroling
authority
• Conduct home, work, and officer visits with
offenders
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
5
Parole Officers (continued)
District Parole Officers supervise offenders who have
been released on parole, or mandatory supervision, to
complete their sentences while living in Texas
communities.
Institutional Parole Officers are physically assigned to
TDCJ units. They interview incarcerated offenders at
TDCJ Units, federal correctional institutions, contracted
facilities, and county jails statewide to prepare Parole
Case Summaries.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
6
Jailers and Detention Officers
• Supervise inmates in correctional facilities
(generally county or local level)
• Work with adults or juveniles
• Fingerprint, photograph, and book offenders
upon intake
• Manage offenders in correctional facilities
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
7
Average Correctional Salaries
•
•
•
•
•
Probation: $31,292 – $47,489
Parole: $32,459 – $44,709
Correctional Officer: $28,241 – $45,579
Jailer: $28,24 – $41,383
Federal Probation Officer: $21,083 –
$112,800
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
8
Correctional Officer Duties
•
•
•
•
Supervise offenders
Maintain the security of the facility
Transport offenders
Conduct searches of offenders and their
property
• Respond to emergencies
• Read, review, and properly apply information
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
9
Prison Administration
• Correctional Officer
– Uniformed jail or
prison employees
whose primary job is
the security and
movement of inmates
• Warden:
– The chief administrator
of a prison
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
10
Your local Bed and Breakfast:
We’ll even leave the light on!
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
11
Early Jail Conditions
16 people in Prisoners
a 12 x 12 cell provided
their own
food and
medical needs
Men, women,
and children
were all
housed
together
Sick and
healthy
housed
together
Could buy: Indigents
alcohol, food, had to work
privileges,
for their keep
and cell
space
No heat, no
plumbing, no
adequate
sleeping or
living space
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
Many deaths
from sickness
and
starvation
12
Reforms:
The Walnut Street Jail
• 1790 law passed by the Pennsylvania
legislature
–
–
–
–
–
Humane physical facilities
Adequate food and water at public expense
Separation of men, women, and children
Prohibited “buying” better treatment
Debtors and the mentally ill separated from the
criminal population
– Orphans were moved to separate buildings
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
13
Reforms:
Prison Life at Walnut Street
•
•
•
•
•
Prisoners worked, but were paid for labor
Earned early release for good behavior
Attempted to rehabilitate prisoners
Became overcrowded
Conditions deteriorated and costs
skyrocketed
• Prison failed at rehabilitation
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
14
Reforms:
Eastern State Penitentiary
• Built in 1892
• Cost $500,000 to house
250 prisoners
• Most expensive building
in the new world
• First in the country to
have flushing toilets and
hot-air heating
• Designed as a
penitentiary, not a jail or
prison
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
15
Reforms:
Eastern State Penitentiary (continued)
• Penitentiary – a correctional institution
based on the concept that inmates can
change their criminality through reflection
and penitence
– Individual cells
– Must become proficient at a skill for use after
release
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
16
Reforms:
Eastern State Penitentiary (continued)
• Expected to read the Bible when not working
or exercising
• Use of the “silent system”
• Maximum security, walled, and self-contained
• Cells 12 x 7.5 and had a window
• Working, exercising, eating, and sleeping all
performed in the prisoner’s cell
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
17
Reforms:
The Auburn System
• Built in 1816 – walled,
maximum security
• Cells 7’x 4’, 7’ high, back
to back, 5 tiers located in
the center of the building
inside “cell blocks”
• Cells poorly lit, no fresh
air
• Inmates moved to other
locations in the unit for
work, exercise, and eating
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
18
Reforms:
The Auburn System (continued)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
The silent system was used, but hard to enforce
Corporal punishment used for violations
Marched from place to place
Short haircuts
Distinctive uniforms
First use of solitary confinement
Prison industries (the prison was self-sufficient)
The Prototype American Prison
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
19
Reforms:
Southern Penal Systems
• Convict lease system was implemented after
the end of slavery
• Construction work, factory work,
agricultural work
• Very poor work and living conditions
• Worked 12-15 hours a day
• Often lived in cages, and discipline was
brutal
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
20
Reforms:
Southern Penal Systems (continued)
•
•
•
•
•
The origin of “chain gangs”
The 1930 Prison Farm System replaced the lease system
Inmate labor used to sustain prisons and other profit industries
Used prisoners as guards and supervisors to cut costs
Arkansas and Texas brought about U.S. Supreme Court decisions
on the 8th amendment
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
21
Prison Reforms
• 1930s laws prohibited the sale of inmate
goods
• Prisons began supplying products to the
government (license plates)
• Between 1950 and 1966, over 100 riots
• In September 1971, 43 inmates died in the
Attica State Prison riot
• In February 1980, 36 died in New Mexico
riots
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
22
Prison Reforms (continued)
• 1980s – the US
Supreme Court
decided that inmates
could sue over
–
–
–
–
Living conditions
Medical treatment
Inmates’ rights
Prison policies
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
23
Jails
• Jail – a short-term, multipurpose holding
facility that serves as a gateway for the
criminal justice system
• Jails hold
– Defendants awaiting trial
– Defendants convicted of misdemeanors
– The mentally ill pending movement to a health
facility
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
24
Jails (continued)
• Jails hold
– Local, state, federal, and
military prisoners
– Adults of both genders
– Juveniles
– Convicted prisoners
– Absconders
– Witnesses
– Most awaiting trial or
transport
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
25
Punishment Range for Jail
• Class C Misdemeanor
– a fine up to $500 (ticket)
– cannot be arrested
• speeding or open container
• Class B Misdemeanor
– up to 180 days in jail, and a $2,000 fine
• Class A Misdemeanor
– up to 2 years in jail, and a $4,000 fine
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
26
County Jails
• Over 3,300 local and county jails
• Vary in size from less than 50 to
more than 7,000
• Population has more than doubled
since 1983
• Very few municipal jails
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
27
State Prisons
Prisons – correctional
institutions for prisoners
convicted of felonies
• Extended sentences
• Separated inmates by sex
• Architecture reflective of
gender bias
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
28
Prisons
Top 10 Highest Incarceration Rates
1. California 163,001
2. Texas
157,997
3. Federal
145,416
4. Florida
71,319
5. New York 70,198
6. Michigan 47,718
7. Ohio
45,833
8. Illinois
45,281
9. Georgia
44,232
10. Pennsylvania
36,847
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
29
Punishment Levels for Prison
State Jail Felony (SJF)
– 180 days to 2 years, and a $10,000 fine
3rd Degree
– 2-10 years, and a $10,000 fine
2nd Degree
– 2-20 years, and a $10,000 fine
1st Degree
– 2-99 (life), and a $10,000 fine
Capital
– Death
– Life without Parole
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
30
State Prison Security Levels
• Minimum Security
– Have few physical barriers to escape, and many
programs for inmates
• Medium Security
– Fortress-like, walled, self-contained institutions
that offer inmates education, vocation, and
rehabilitation
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
31
State Prison
Security Levels (continued)
• Maximum Security
– prisons for inmates at high risk of escape, or
who are dangerously violent to other inmates or
staff
• Administrative Segregation
– solitary confinement
– inmates are kept in single cells 23 hrs a day.
They are allowed a shower and one hour of
recreation per day.
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
32
Private Jails and Prisons
• For-profit facilities run by private security
companies
• Contracted by counties at lower cost
• Less programs
• Less training, lower pay, and conditions
often below state standards
• Escapes and assaults carry smaller penalties
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
33
Constitutional Rights
• Retain all the rights of “free” citizens
• Three government interests, however,
justify curtailing offender’s rights:
– Maintaining internal order and discipline
– Securing the institution against unauthorized
access or escape
– Rehabilitating offenders
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
34
Habeas Corpus
• The primary purpose is to seek release from
prison or jail for unlawful confinement
• Exhaust state judicial remedies before going
to federal court
• Filed in state or federal court
• Filed by one offender
• Affects only that offender
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
35
Section 1983
• The purpose is to address prison conditions
or obtain monetary damages from prison
officials
• Filed directly in federal court
• Affects all offenders
• May be filed as class action suit
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
36
First Amendment
• Freedom of
–
–
–
–
–
Religion
Speech
Press
Assembly
Petitioning the government for redress of
grievances
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
37
Fourth Amendment
• Prohibition against
unreasonable searches
and seizures
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
38
Fifth Amendment
•
•
•
•
The right to jury for capital crimes
Protects against double jeopardy
The right against self-incrimination
Prohibits taking life, liberty, or property
without due process
• Protects against taking private property
without just compensation
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
39
Sixth Amendment
• The right to a public and speedy trial
• Impartial jury
• Informed of the nature and cause of
accusations
• Confront witnesses
• Compulsory process for obtaining
witnesses
• Right to an attorney
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
40
Eighth Amendment
• Prohibits excessive bail
• Protects against cruel
and unusual punishment
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
41
Fourteenth Amendment
• The right to the privileges and immunities
of citizens
• The right to due process
• The right to equal protection under the law
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
42
Case Law
• Impingment on an offender’s constitutional
rights is valid if it is reasonably related to
legitimate penological interests
• Turner v. Safely, 482 U.S. 78 (1987)
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
43
Resources
•
•
•
•
•
•
020547893X, Fagin, James. Criminal Justice: Prentice Hall, 2007.
1593455747, del Carmen, Rolando v. Susan E. Ritter, Betsy A. Witt.
Briefs of Leading Cases in Corrections: Anderson, 2008.
0314264159, O’Brien, Edward; Fisher, Margaret; Austern, David T.
Practical Law for Jail and Prison Personnel: West Group, 1987.
Civil Liabilities and Other Legal Issues:
http://nicic.gov/pubs/2001/017068.pdf
• http://www.bls.gov/oco/ocos156.htm
• Do an Internet search for the following:
– Findlaw Turner Safely
– Supreme justia Turner Safely
Copyright © Texas Education Agency 2011. All rights reserved.
Images and other multimedia content used with permission.
44