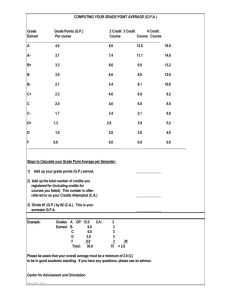
programme catalogue - Cipriani College of Labour & Cooperative
advertisement

PROGRAMME CATALOGUE | 2014 - 2015 Vision Statement With a proud tradition of accessible high-quality education, we aim to exceed the expectations of our students, staff and other stakeholders, as the premier tertiary educational institution in the Caribbean, in areas of Labour, Co-operative Studies and a dynamic range of other specialised training programmes. Mission Statement Our Mission is to increase the capacity and consciousness of the Labour and Co-operative Movements, people based and professional institutions, both locally and regionally, and to empower present and future working people. To do this we will: • Foster and encourage critical thinking; • Provide the highest quality educational and research programmes for our students in physically and intellectually supportive learning environment; • Provide and enable a highly committed, qualified, dynamic and professional staff; and • Be proactive and innovative in meeting the needs of all our stakeholders in a continuously changing and competitive environment. 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 ACADEMIC INFORMATION ON PROGRAMMES 5 LABOUR STUDIES 8 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Programmes������������������������������������������������������� 6 Bachelor’s Degree Programmes������������������������ 6 Admissions Eligibility for Bachelor’s Degrees���� 6 Exemptions��������������������������������������������������������� 7 Associate of Science Degree (AS)��������������������� 7 Admissions Eligibility for Associate of Science Degrees�������������������������������������������� 7 Associate of Arts Degree (AA)���������������������������� 7 Admissions Eligibility for Associate of Arts Degrees�������������������������������������������������������������� 7 Research & Publications������������������������������������ 7 Research Paper/Project������������������������������������� 7 Bachelor of Arts Degree����������������������������������� 36 Associate of Arts Degree���������������������������������� 42 Bachelor of Science Degree����������������������������� 68 Associate of Science Degree��������������������������� 74 Diploma in Project Management���������������������� 79 Certificate in Project Management������������������� 80 2 GENERAL EDUCATION General Education�������������������������������������������� 10 Developmental Education���������������������������������11 3 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES Certificate in Industrial Relations���������������������� 45 Ten-Week Full-Time Programme in Industrial Relations���������������������������������������������������������� 46 6 MARKETING & PUBLIC RELATIONS Marketing and Public Relations������������������������ 48 Diploma in Public Relations������������������������������ 49 Certificate in Public Relations��������������������������� 49 Certificate in Marketing������������������������������������� 49 7 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Arts Degree����������������������������������� 12 Associate of Arts Degree���������������������������������� 17 Certificate in Credit Union Management���������� 20 Online Cert. In Credit Union Management....... 21 Bachelor of Science Degree����������������������������� 52 4 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Certificate in Occupational Safety, Health and the Environment Full Time (new)���������������������������� 62 Bachelor of Arts Degree����������������������������������� 24 Associate of Arts Degree���������������������������������� 29 Diploma in Human Resource Management����� 33 Certificate in Human Resource Management�� 33 2 Diploma in Industrial Relations Practice����������� 45 Associate of Science Degree in Occupational Safety & Health������������������������������������������������ 57 Diploma in Occupational Safety and Health����� 61 Certificate in Occupational Safety and Health�� 62 Associate of Science Degree in Environmental Management���������������������������������������������������� 63 Diploma in Environmental Management���������� 66 Certificate in Environmental Management������� 66 9 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Science Degree����������������������������� 82 Associate of Science Degree��������������������������� 87 Diploma in Security Administration & Management������������������������������������������������� 91 Certificate in Security Administration & Management���������������������������������������������������� 91 Diploma in Emergency Management��������������� 92 Certificate in Emergency Management������������ 93 10 DEPARTMENT OF CONTINUING STUDIES Department of Continuing Studies������������������� 96 Ten-Saturdays Introductory Courses���������������� 97 Specialised Training����������������������������������������� 98 11 TOBAGO CAMPUS Associate Degrees����������������������������������������� 100 Diplomas�������������������������������������������������������� 100 Certificates����������������������������������������������������� 100 12 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS102 QUALITY POLICY STATEMENT T he Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies aims to provide excellent and outstanding service to our internal and external stakeholders. We aim to consistently meet and surpass stakeholder requirements through continuous improvement endeavours. Every individual shares in the ownership of quality within the college and is focused on stakeholder satisfaction. The objectives of Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative studies are to: • Enhance the institution’s effectiveness in teaching and learning; • Encourage research and the dissemination of research results; • Increase the quality of the student experiences; and • Engage with the Labour and the Co-operative movements, people based and professional institutions both locally and regionally. 3 4 1 ACADEMIC INFORMATION ON PROGRAMMES ACADEMIC INFORMATION ON PROGRAMMES | 01 ACADEMIC INFORMATION PROGRAMMES 6 The Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies offers six (6) Bachelor’s Degrees, three (3) Associate of Arts Degrees and four (4) Associate of Science Degrees, which students may pursue for the purpose of completing specific goals. These programmes are the Bachelor of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies, Human Resource Management, Labour Studies, the Bachelor of Science Degree in Occupational Safety, Health and Environmental Management, Project Management and Security Administration and Management. The Associate of Arts Degrees in Labour Studies, Cooperative Studies and Human Resource Management and the Associate of Science Degrees in Occupational Safety and Health, Security Administration and Management, Project Management and Environmental Management are also part of the College’s offerings. In addition, the College offers occupational certificates and diplomas and other educational and training services to provide total educational opportunities for the nation. BACHELOR’S DEGREE PROGRAMMES The Bachelor’s Degree programmes at Cipriani College of Labour and Cooperative Studies are articulated with the Associate Degree programmes within the same discipline and offer students the possibility of entering at different levels. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY FOR THE BACHELOR’S DEGREES There are three categories of eligible students for the Bachelor’s Degree: • Students who have obtained five CXC/GCE passes, with passes in English Language and Mathematics. These students will require four years full-time to complete the degree • Students who are admitted with A Levels may receive exemptions but will have to complete any additional course(s) offered in the first year of the programme • Students who have completed the Associate Degree in their respective disciplines with a GPA of 2.5 or higher will require two years to complete the degree as part of a 2 plus 2 articulation arrangement. They will have to complete any additional course(s) offered in the first year of the programme • Mature persons (25 years and older) with considerable experience in the field will be interviewed by the Admissions Committee with Prior Learning Assessment Committee (PLAC), chaired by the Registrar, to determine at what point/level of the programme they will be admitted. Exemptions, if any, will also be determined by this Committee. 01 | ACADEMIC INFORMATION ON PROGRAMMES EXEMPTIONS ASSOCIATE OF ARTS DEGREE (AA) On the basis of the successful completion of the College’s Associate Degrees, exemptions will be granted for all courses completed in the first two years of the Bachelor Degrees, provided that the student has earned a grade of ‘C’ or higher in the respective courses. The Associate of Arts Degree provides a student with college-credit curricula designed to prepare him/her for a professional level of employment and for advancement in specific fields. At the same time too, the Associate of Arts Degree provides full credit for transfer to other institutions for the purpose of satisfying the requirements for a Bachelor’s Degree. In addition to the above situation, CCLCS Associate Degree students will also receive exemptions for other courses completed in other CCLCS’ degree programmes and which carry the same course number and name/title as those listed in the Bachelor’s Degree programme, provided that the student has received a ‘C’ grade or higher in the respective courses. There will be no exemption given for the Research Paper/Project. All queries on exemptions will be handled by the Registrar. ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE (AS) The Associate of Science Degree is designed primarily to prepare students for immediate employment and/or advancement in their chosen career and for a change in careers. However, credits earned for many courses in these programmes are acceptable to many institutions of higher education should the student decide to continue toward a Bachelor’s Degree. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY FOR THE ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREES A) Students must complete a minimum of sixty (60) credits, including the general education core courses. B) Students must earn at least a 2.0 grade point average in the credits presented for graduation. Students will be allowed to register for a maximum of five years in order to complete the Associate Degree. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY FOR THE ASSOCIATE OF ARTS DEGREES The overall requirements for the Associate of Arts Degree are as follows: • Earn a minimum of 62 credit hours in academic courses • Earn a minimum grade point average of 2.00. Some programmes may have higher grade point requirements • Meet the degree requirements of the specific programme of study in which the degree is to be awarded, including the general education requirements, as detailed in the College’s Catalogue issued in the year in which the degree began, or which was in effect during the academic year of the most recent readmission to the College • Complete the Research Paper/Project wherever this is required. RESEARCH AND PUBLICATIONS Students are advised that a Research Department exists at the College. This Department can be of special assistance to students in the preparation of their research papers and course projects. It is the responsibility of this Department to produce the necessary material to inform students and staff of the accepted style governing research presentations. This Department also assumes the responsibility for the teaching programmes in research and research methodology of the College. It is the intention of the College to begin publication of selected research papers, articles and other projects by staff and students. Students are therefore encouraged to submit works of academic excellence, especially those with practical value to the Head of this Department. RESEARCH PAPER/PROJECT One of the requirements that must be fulfilled to qualify for the award of the Bachelor’s and the Associate Degree is the completion of a satisfactory research paper. Students are advised to give this requirement continuous attention and to observe the deadlines for the completion of all the stages. Students must read the manual on the research paper which they can obtain from the Head of Department or the Deputy Director of Academic Affairs. Students are reminded that they will not be able to graduate unless they have completed their research paper and that paper has been adjudged satisfactory. Research papers completed outside of one (1) year from the completion of the rest of the courses will not be accepted, except in cases of proven emergency or illness. A student who has completed a research project for his/her Associate Degree will not be allowed to submit that project/paper to fulfill the requirement of the research project in the Bachelor’s Degree. There will be no exemption for the research paper/ project. Students at the Bachelor’s Degree will follow the College’s guidelines for the research paper as outlined in its manual. 7 8 2 GENERAL EDUCATION GENERAL EDUCATION | 01 GENERAL EDUCATION The General Education Programme at Cipriani College of Labour and Cooperative Studies teaches students how to think rather than what to think, how to learn rather than what to learn, in an effort to produce graduates who are better able to adapt and respond to the demands of a fast-changing economic and social environment. 10 VALENTINE SMITH Head of Department/Senior Lecturer MPhil., MSc., BSc. At CCLCS, the General Education Programme seeks to provide students with the opportunity to acquire the knowledge, skills and attitude to live fully, and participate effectively in a democratic society and a global community. The goal of the programme is to produce students who can communicate effectively, analyze critically and understand their society and culture. Such students, it is believed, will be able to utilise the knowledge they receive in a more constructive manner, and to make decisions that lead to positive action in the course of daily living. To accomplish the general education goals, all students receiving either an Associate or Bachelor Degree, must satisfy a set of general education requirements in addition to the requirements of their specific programme. To meet the general education requirements for both the Associate and Bachelor Degrees, a student must earn at least 30 credits in courses distributed as follows: Categories Minimum Credit Hours Communication Arts Quantitative Skills Computing Skills Humanities Natural Science Social Science Critical Thinking 6 3 3 6 3 6 3 The College has selected from within each of the categories listed above, those courses which fulfil the general education requirements. These courses are listed below: CAS 130 CIS 100 Systems COM 101 COM 250 ENG 110 ENM 142 HUM 100 HUM 200 HUM 220 LBS 100 LOG 120 MAT100 PSY 100 RES 100 SOC 100 SPN 100 Caribbean Studies Introduction to Computer Information Fundamentals of Communication Effective Communication Fundamentals of Writing Environmental Science I Cultural Studies Comparative Religion Ethics and Moral Values Introduction to Industrial Relations Critical Thinking Mathematics Introduction to Psychology Research Methods and Statistics Introduction to Sociology Introduction to Spanish 3 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES | 03 BACHELOR OF ARTS DEGREE CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES 12 Co-operatives are playing an ever increasingly significant role globally in “facilitating job creation, economic growth and social development in today’s society.’ Co-operatives are becoming complex business entities with increasing members’ demands. Members now have an expanded range of needs to be met which has resulted in societies having an extremely diverse product spread SHELDON SALINO Head of Department/Senior Lecturer MSc., Post Grad., Dip. The Bachelor of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies and the other related levels are all focused on providing students with the contemporary tools to start-up, operate, manage and serve within a global business environment and more specifically the co-operative business model. This business model facilitates entrepreneurial ideas and contributes to maintaining sustainable development in society, and has proven to be quite resilient, if not the most resilient, during turbulent economic times. The Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies sees itself as a stakeholder in the local co-operative sector that is charged with the responsibility for educating, training, developing and undertaking research of the sector. In this regard, our programmes are driven by the needs of the movement, the needs to equip the sector with appropriately qualified persons and the objective to help the sector achieve its fullest socio-economic potential. Students pursuing Co-operative Studies will find themselves exposed to not only the traditional business management concepts, but also to a type of management that is quickly becoming the leading approach adopted by multinational businesses. This approach of value led management is not an artificial addition for the cooperative business model, but is actually part of the co-operative model DNA. Co-operatives are based on a set of universally accepted principles and values, which has influenced its existence since the 1800’s. Co-operative Studies and the co-operative business model is therefore well positioned to become the dominant model for the 21st century and students of this area are already in demand across the globe. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES Graduates of co-operative studies have various career paths which they may choose, these include: • Entrepreneur (Individual / Collective) • Co-operative Officers • Managers • Community Development Officers • Credit Officer • Customer Service Officers • Marketing Officers • Delinquency Control Officers • NGO Management • Lecturing / Teaching • Consultant At the Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies, students are provided with a comfortable and friendly teaching and learning environment. All lecturers in the Co-operative Studies Department are qualified by local and internationally recognized institutions. In addition to their academic qualifications lecturers have significant industry experience which serves to deliver the right balance of theoretical information and practical application. Students also benefit from the strategy of maintaining manageable class sizes which allow for students to receive the adequate level of student – lecturer interaction, which all contributes to ensuring that all students grasp the concepts. Supporting this strategy is the built-in flexibility that students have with respect to their approach to learning, pace of learning and maintaining manageable course loads. 03 | CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY There are five categories of eligible students for the Bachelor’s Degree in Co-operative Studies: • • • • • Students who have obtained five CXC/ GCE passes, with passes in English and Mathematics. These students will require four years (full time) or five years (part time) to complete the degree. Students with GCE A’ level and CAPE would be accepted into the four year programme and their passes at that level would be considered for exemption, where applicable. Students who have completed the Associate Degree in Co-operative Studies with a GPA of 2.5 or higher. These students will require two years (full time) or three years (part time) to complete the degree as part of a 2 plus 2 articulation arrangement with the College’s Associate Degree Programme. Students who have completed any other Associate Degree from CCLCS will also be eligible for entry and relevant exemptions granted, where applicable. Mature persons (25 years and older) with at least five (5) years experience in Co-operative Management, Credit Union Management or a related field will be interviewed by the Prior Learning Assessment Committee chaired by the Registrar, to determine at what point/ level of the programme they will be admitted. Exemptions, if any will also be determined by this Committee. Students who have acquired an Associate Degree from other recognised tertiary institutions. These persons will be interviewed by the Prior Learning Assessment Committee chaired by the Registrar, to determine at what point/level of the programme they will be admitted. Exemptions, if any will also be determined by this Committee. CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES Bachelor of Arts Degree (BA) – 122 credits General Education Courses 33 Credits CAS 130 CIS 100 COM 101 ENG 110 ENM 142 LOG 120 MAT 100 PSY 100 RES 100 SOC 100 SPN 100 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Caribbean Studies Introduction to Computer Information Systems Fundamentals of Communication Fundamentals of Writing Environmental Science I Critical Thinking Mathematics Introduction to Psychology Research Methods and Statistics Introduction to Sociology Introduction to Spanish Programme Concentration 56 Credits COS 110 COS 120 COS 130 COS 150 COS 200 COS 202 COS 220 COS 350 COS 380 COS 410 COS 420 COS 460 ECN 210 MGT 150 MGT 200 MGT 201 MGT 300 MGT 400 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 3 3 3 3 3 3 Co-operative Law and Principles Co-operative Organization and Operations History and Development of the Co-operative Movement Credit Union Management Principles & Practices Communication and Extension I Communication and Extension II Business Law and Credit Unions Internship* Ethics in Decision Making in Cooperatives Co-operative approach to Human Resource Management Current Issues in the Co-operative Movement Research Paper/Project Interpreting Economic and Financial Data Basic Principles of Money Management & Securities Principles of Business Management Financial Management Strategic Management and Leadership for Cooperatives Credit Risk Analysis * Students who have completed COS 250 Internship in the Associate Degree will be exempted from COS 350 in the Bachelor’s Degree Programme. 13 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES | 03 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES Bachelor of Arts Degree (BA) – 122 credits Supporting Courses ACC 100 ACC 210 BUS 300 COM 201 ECN 100 LBS 200 MAR 200 MAT 400 24 Credits Introduction to Accounting Principles of Auditing Principles of Entrepreneurship Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills Introduction to Economics Fundamental Principles of Labour Law Principles of Marketing Quantitative Methods Electives 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 9 Credits Option A ECN 200 LBS 120 The Economy of the Caribbean Region History of Caribbean Labour 3 3 Managing Organizational Change Mediation/Conflict Resolution 3 3 Market Research Introduction to Events Management 3 3 Option B HRM 400 LBS 400 Option C MAR 120 PBR 145 * ONE COURSE TO BE SELECTED FROM EACH OF THE OPTIONS LISTED ABOVE 14 03 | CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies Day Programme (Full-Time) - 122 credits Year I COS 110 ECN 100 ENG 110 MAT 100 SOC 100 Semester I Co-operative Law and Principles Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Writing Mathematics Introduction to Sociology 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year I ACC 100 CIS 100 COS 120 LOG 120 RES 100 Semester II Introduction to Accounting Introduction to Computer Information Systems Co-operative Organizations and Operations Critical Thinking Research Methods and Statistics 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year II COM 101 COS 200 MGT 200 PSY 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Communication and Extension I Principles of Business Management Introduction to Psychology 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year II ACC 210 COS 202 MAR 200 MGT 201 Semester II Principles of Auditing Communication and Extension II Principles of Marketing Financial Management 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year III Semester I CAS 130 Caribbean Studies COS 220 Business Law and Credit Unions SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish COS 130History and /Development of the Co-operative Movement MGT 150 Basic Principles of Money Management & Securities 15 Credits 3 3 3 Year III Semester II 18 Credits BUS 300 Principles of Entrepreneurship 3 COS 150 Credit Union Management: Principles & Practices 3 ENM 142Environmental Science I3 HRM 200 Theories, Concepts and Principles of Human Resource Management3 MGT 300 Strategic Management and Leadership for Co-operatives3 Elective3 Year IV Semester I 20 Credits COM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills 3 COS 350Internship3 COS 380 Ethics in Decision Making in Co-operatives 3 COS 460Research Paper5 MAT 400Quantitative Methods3 MGT 400Credit Risk Analysis3 Year IV Semester II 15 Credits COS 410 Co-operative Approach to Human Resource Management3 COS 420 Current Issues in Co-operative Movement 3 ECN 210 Interpreting Economic & Financial Data 3 LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law 3 Elective3 3 3 15 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES | 03 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 122 credits Year I ECN 100 ENG 110 SOC 100 Semester I 9 Credits Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Sociology Year I Semester II 9 Credits Year II Semester I 9 Credits Year II Semester II 9 Credits 3 3 3 CIS 100Introduction to Computer Information Systems 3 COS 110 Co-operative Law and Principles 3 LOG 120Critical Thinking 3 COS 120 Co-operative Organizations and Operations 3 MAT 100Mathematics 3 PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology 3 ACC 100 COM 101 RES 100 Year III Introduction to Accounting Fundamentals of Communication Research Methods and Statistics Semester I9 Credits COS 200 MGT 200 MGT 201 Communication and Extension I Principles of Business Management Financial Management Year III Semester II 3 3 3 3 3 3 9 Credits ACC 210 COS 202 MAR 200 Principles of Auditing Communication and Extension II Principles of Marketing Year IV Semester I 3 3 3 12 Credits BUS 300 Principles of Entrepreneurship 3 COS 130 History and /Development of the Co-operative Movement 3 MGT 150 Basic Principles of Money Management and Securities 3 CAS 130Caribbean Studies3 16 Year IV Semester II 15 Credits Year V Semester I 15 Credits Year V Semester II 14 Credits COS 220 Business Law and Credit Unions 3 COS 150 Credit Union Management: Principles and Practices 3 ENM 142 Environmental Science I 3 HRM 200 Theories, Concepts and Principles of Human Resource Management 3 MAT 400 Quantitative Methods 3 COS 350Internship3 COS 380 Ethics in Decision Making in Co-operatives 3 MGT 400Credit Risk Analysis3 SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish 3 Elective 3 COM 201 COS 460 ECN 210 MGT 300 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills Research Paper Interpreting Economic & Financial Data Strategic Management and Leadership for Cooperatives Year VI Semester I 3 5 3 3 12 Credits COS 410 Co-operative approach to Human Resource Management 3 COS 420 Current Issues in Co-operative Movement 3 LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law 3 Elective 3 ASSOCIATE OF ARTS DEGREE 03 | CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES This programme is geared to the training and education of Co-operative personnel, Directors, Committee Members, Managers, Supervisors and other staff as well as young persons and workers generally in the management of business enterprises with specific emphasis on the cooperative type of business. The basic aim of the programme is to enhance the management capability of the Co-operative Movement and to make for greater efficiency in the operations of Co-operative Societies. Students read for courses in Co-operative Law, Cooperative Organization, Business Management, Marketing, Accounting and Auditing and in other areas such as Economics, Information Technology, Mathematics, Sociology and Psychology. The aim is to prepare the student to fit into today’s business environment as well as to train prospective entrepreneurs who are interested in operating their own businesses. management of co-operatives, credit unions, and private businesses as well as in the government service. Students may also go on to specialized higher education that would lead on to careers in Accounting, Auditing, Marketing and Information Technology. The Associate of Arts Degree in Cooperative Studies is accepted as the pre-requisite to the Post Graduate Certificate, Diploma and Master’s in Co-operative Management & Organizational Development at the University of Leicester, for which Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies (CCLCS) is the regional tutorial centre. Our graduates pursue occupations such as Cooperative Officer, Community Development Officer and also work as Managers, Supervisors, Credit Officers, Marketing Assistants and Field Officers. Some also acquire jobs in the private sector in Accounting, Marketing and other areas at the middle management levels. The Associate of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies prepares students to pursue careers in the 17 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES | 03 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES Associate of Arts Degree (AA) – 62 credits General Education Courses CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication ENG 110 Fundamental of Writing LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology 21 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration ACC 100 Introduction to Accounting ACC 210 Principles of Auditing COS 110 Co-operative Law and Principles COS 120 Co-operative Organization and Operations COS 200 Communication and Extension I COS 202 Communication and Extension II COS 250 Internship* COS 260 Research Paper MAR 200 Principles of Marketing MGT 200 Principles of Business Management MGT 201 Financial Management RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics 38 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 3 3 3 3 Supporting Courses ECN 100 Introduction to Economics 3 Credits 3 * An internship will be required for those who do not have any working experience in the field. Students who have working experience will be granted an exemption from COS 250. However, they will be required to submit written proof of their working experience. 18 03 | CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies Day Programme (Full-Time)-62 credits PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Arts Degree in Co-operative Studies Evening Programme (Part-Time)-62 credits Year I Semester I 15 Credits Year I Semester I 9 Credits COS 110 ECN 100 ENG 110 MAT 100 SOC 100 Co-operative Law and Principles Introduction to Economics Fundamental of Writing Mathematics Introduction to Sociology 3 3 3 3 3 ECN 100 ENG 110 Introduction to Economics Fundamental of Writing 3 3 SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology 3 Year I Semester II 9 Credits Year I Semester II 18 Credits ACC 100 CIS 100 COS 120 COS 250 LOG 120 RES 100 Introduction to Accounting Introduction to Computer Information Systems Co-operative Organization and Operations Internship Critical Thinking Research Methods and Statistics 3 3 3 3 3 3 CIS 100 COS 110 Introduction to Computer Information Systems Co-operative Law and Principles 3 3 LOG 120 Critical Thinking 3 Year II Semester I 9 Credits COS 120 MAT 100 Co-operative Organization and Operations Mathematics 3 3 PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology 3 Year II Semester II 12 Credits ACC 100 COM 101 COS 250 Introduction to Accounting Fundamentals of Communication Internship* 3 3 3 RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics 3 Year III Semester I 9 Credits COS 200 MGT 200 Communication and Extension I Principles of Business Management 3 3 MGT 201 Financial Management 3 Year III Semester II 14 Credits ACC 210 COS 202 COS 260 MAR 200 Principles of Auditing Communication and Extension II Research Paper Principles of Marketing 3 3 5 3 Year II Semester I 12 Credits COM 101 COS 200 MGT 200 PSY 100 3 3 3 3 Fundamentals of Communication Communication and Extension I Principles of Business Management Introduction to Psychology Year II Semester II 17 Credits ACC 210 COS 202 COS 260 MAR 200 MGT 201 3 3 5 3 3 Principles of Auditing Communication and Extension II Research Paper Principles of Marketing Financial Management NB: Exemptions will be awarded only in cases where the course numbers in the Associate Degree, Certificate or Diploma are the same. Other exemptions will be awarded in accordance with the College’s policy on exemptions. * An internship will be required for those who do not have any working experience in the field. Students who have working experience will be granted an exemption from COS 250 Internship. However, they will be required to submit written proof of their working experience. 19 CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES | 03 CERTIFICATE IN CREDIT UNION MANAGEMENT This programme is intended to provide not only certification in credit union management to members of the credit union movement in Trinidad and Tobago, but also training specific to the credit union industry as a whole. It specifically targets the credit union movement as a subset of the wider cooperative movement, credit unions being the most successful and visible type of co-operative in Trinidad and Tobago. The objective of this programme is to provide the students, upon completion, with the necessary skills to function at the middle management level within a credit union. The vision is that holders of this certificate will be able to use it to access job opportunities or promotion within credit unions. This certificate covers a period of one year part-time study (two semesters), with three courses allocated to each semester. Required CoursesCredits Semester I ACC 220 COM 101 COS 165 Credit Union Accounting Fundamentals of Communication 3 History/ Development & Operations of the Credit Union Movement 3 3 Credit Union Management: Principles & Practices Business Law & Credit Unions Basic Principles of Money Management & Securities 3 3 3 Semester II COS 150 COS 220 MGT 150 Total Credits Required18 20 03 | CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES ONLINE CERTIFICATE IN CREDIT UNION MANAGEMENT This Online Certificate in Credit Union Management (OCCUM) provides participants with the necessary skills to function at either the middle management or as an elected officer of a credit union. Similar to the one year Certificate in Credit Union Management, OCCUM is a one year (two semesters) programme, which requires participants to undertake the same six courses that are delivered in the face to face programme. These courses areas are as follows: Required CoursesCredits Semester I Credit Union Accounting 3 Fundamentals of Communication 3 History/Development & Operations of the Credit Union Movement 3 Semester II Credit Union Management 3 Business Law and Credit Unions 3 Money Management & Securities 3 Total Credits Required18 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS 1. What are the ICT requirements to be an online student in this programme? Answer – Access to Computer / Laptop / Tablet with a camera and reliable internet access. 2. How will assessment be conducted? Answer – Assessment will be undertaken in two formats – 1) course work assignments that will be worth 40% and 2) a final examination, valued at 60%. 3. How do I apply for the programme? Answer – The College will accept applications electronically. Completed applications should be scanned and uploaded / emailed to a designated recipient. 4. How can payments be made for the online programme? Answer – Participants can forward payments to the College utilising either wire transfer or bank draft. 21 22 4 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | 04 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT BACHELOR OF ARTS DEGREE “I can’t stand my manager! He doesn’t recognize my contribution to the workplace!” 24 Many people in society have had this thought at some point in time. In fact, according to Forbes who cited a U.S. based study by Accenture, noted that 31% of people did not like their boss; 31% suffered from a lack of empowerment; and 43% indicated there was no recognition from the organisation. These figures contribute to workers feeling undervalued in an organisation. MELISSA BRIDGEWATER Head of Department/Senior Lecturer. M.A., BSc. It is believed that if managers do not value their workers, create opportunities for their personal or professional growth or communicate with them, employees would withdraw from the job-whether it be physically or mentally. Wouldn’t you want to be part of something that gives you the opportunity to develop and empower people to work better for an organisation? If your answer is yes, the Human Resource Management programme is for you! In today’s society, Human Resource Management (HRM) is extremely important since an organisation cannot function effectively without a vibrant workforce. As such, HR practitioners have a responsibility to be aware that they empower and transform the lives of workers, both personally and professionally. Human Resource Management allows organizations to recognize their employees for who they are by developing and managing their talents and abilities, as well as having a conducive work atmosphere for these factors to take place. This helps employees to be not only satisfied in their jobs, but to be productive citizens who are firmly committed to the organisation. The Human Resource Management programme is offered at the Cipriani College of Labour and Cooperative Studies at the Introductory Ten Saturday, Certificate, Diploma, Associate and Bachelor levels. The objectives of this programme are to: • Provide students with an exposure and competencies needed in the field of Human Resources • Equip students with tools needed to develop and utilize a productive and motivated • • workforce, which is a critical factor to organizational success Provide students with the knowledge and understanding of the impact of the creation and maintenance of facilities and a favourable environment in the workplace, which are necessary to sustaining motivated employees Contribute to society by showing students methods to possibly reduce socio-economic ills such as unemployment, income inequalities and wealth distribution, therefore improving the society’s welfare In the HRM programme, students have the best of many worlds as students are allowed a flexible class load to balance their other work/life challenges during a given semester; the classes are small and of an interactive nature; and there are faculty members who are committed to ensuring that students receive a high level of quality education. There are several career paths students who successfully complete the HRM programme can follow. After completion of a degree programme in the field, one can apply for many jobs, including: • HR Manager • HR Specialist • HR Generalist • HR Co-ordinator • HR Officer • HR Assistant • Compensation and Benefits Officer • Recruitment and Selection Officer • Training and Development Officer • Lecturer (Academia) HRM is a field of study that continuously empowers and educates the mind, so be prepared to contribute towards making a difference in society. Thank you for your interest in the programme! I look forward to working with each of you. 04 | HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Arts Degree (BA) - 122 credits General Education Courses 33 Credits CAS 130Caribbean Studies3 CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information System 3 ECN 100 Introduction to Economics 3 ENG 110Fundamentals of Writing3 HUM 220 Ethics and Moral Values 3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 MAT 100Mathematics3 PLS 100Introduction to Politics3 SOC 100Introduction to Sociology3 SPN 100Introduction to Spanish3 RES 100 Research Methods & Statistics 3 Programme Concentration56 Credits HRM 230Strategic HRM3 HRM 300 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures I 3 HRM 301 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures II 3 HRM 304 Personal Self –development for HR Professionals 3 HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I 3 HRM 306 Organizational Behaviour II 3 HRM 312 Corporate & Business Human Resource Management 3 HRM 320Training & Development3 HRM 330Compensation Administration3 HRM 335 Job Evaluation and Compensation Management 3 HRM 340Performance Management3 HRM 350Internship3 HRM 365Organizational Communication3 HRM 370 Human Resource Information System 3 HRM 400 Managing Organizational Change 3 HRM 410 Human Resource Development 3 HRM 420 Comparative Human Resource Management 3 HRM 460Research Project5 25 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | 04 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Arts Degree (BA) - 122 credits Supporting Courses24 Credits COM 250Effective Communication3 LBS 100Introduction to Industrial Relations3 LBS 300Employment Law3 LBS 380Ethics in Decision Making3 MGT 200Principles of Business Management3 OSH 231 Occupational Safety & Health Legislative Framework 3 RES 300Research Methods II3 SAM 280 Workplace Violence Mediation & Conflict Resolution 3 Electives: Three (3) courses from another programme including, but not limited to: 9 Credits ENM 265 Ethics, Morality & Corporate Governance in Environmental Management 3 HUM 100 Cultural Studies 3 HUM 200 Comparative Religion 3 LBS 120History of Caribbean Labour3 LBS 290Applied Collective Bargaining3 LBS 335 The ILO and Labour Management Relations in the Caribbean 3 LBS 390Grievance Process3 OSH 225 Principles of Health and Safety Law 3 PRM 120Fundamentals of Project Management3 PRM 225Quality Management3 PRM 245Events Management3 PRM 420 Project Implementation & Organizational Change 3 PSY 100Introduction to Psychology3 26 04 | HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Arts Degree in Human Resource Management Day Programme (Full-Time) - 122 credits Year ISemester I15 Credits Year III ENG 110Fundamentals of Writing3 HRM 304 Personal Self Development for Human Resource Professionals3 HRM 300 Human Resource Systems Functions & Procedures I 3 LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 MAT 100Mathematics3 CAS 130Caribbean Studies3 HRM 335 Job Evaluation & Compensation Management 3 RES 300 Research Methods II 3 SAM 280 Workplace Violence Mediation & Conflict Resolution 3 SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology 3 Year ISemester II 18 Credits ECN 100 Introduction to Economics 3 HRM 301 Human Resource Systems Functions & Procedures II 3 HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I 3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 MGT 200 Principles of Business Management 3 HRM 350Internship3 Year IISemester I 18 Credits CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems 3 HRM 312 Corporate & Business Human Resource Management 3 HRM 230Strategic HRM3 HRM 306 Organizational Behaviour II 3 RES 100 Research Methods & Statistics 3 Elective 3 Year IISemester II15 Credits Year III Semester I 15 Credits Semester II 12 Credits HRM 365 Organizational Communication 3 LBS 300Employment Law3 LBS 380 Ethics in Decision Making 3 OSH 231 Occupational Safety & Health Legislative Framework3 Year IV Semester I 15 Credits COM 250Effective Communication3 HRM 370 Human Resource Information Systems 3 HRM 400 Managing Organizational Change 3 HRM 410 Human Resource Development 3 PLS 100 Introduction to Politics 3 Year IV Semester II 14 Credits HRM 420 Comparative Human Resource Management3 HRM 460Research Project5 SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish 3 Elective3 HRM 320Training & Development3 HRM 330Compensation Administration3 HRM 340Performance Management3 HUM 220 Ethics and Moral Values 3 Elective3 27 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | 04 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Arts Degree in Human Resource Management Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 122 credits Year ISemester I9 Credits Year IV ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing 3 HRM 304 Personal Self Development for Human Resource Professional3 LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 CAS 130Caribbean Studies3 COM 250Effective Communication3 LBS 380 Ethics in Decision Making 3 SAM 280 Workplace Violence Mediation & Conflict Resolution 3 Year I Semester II 9 Credits HRM 300 Human Resource Management-Systems, Functions and Procedures I3 HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I 3 MGT 200 Principles of Business Management 3 Year II Semester I 9 Credits HRM 301 Human Resource Management-Systems, Functions and Procedures II3 HRM 306 Organizational Behaviour II 3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 Year II Semester I 12 Credits CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems 3 HRM 312 Corporate & Business Human Resource Management3 HUM 220 Ethics and Moral Values 3 RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics 3 Year III Semester II 12 Credits HRM 320 Training & Development 3 HRM 330Compensation Administration3 HRM 340 Performance Management 3 Elective 3 28 Year IV Semester I 9 Credits HRM 335 RES 300 SOC 100 Job Evaluation & Compensation Management Research Methods II Introduction to Sociology 12 Credits Year VSemester I 9 Credits HRM 365 Organizational Communication 3 LBS 300Employment Law3 OSH 231 Occupational Safety & Health Legislative Framework3 Year VSemester II 11 Credits Semester II 12 Credits ECN 100 Introduction to Economics 3 HRM 230 Strategic Human Resource Management 3 HRM 350Internship3 MAT 100Mathematics3 Year III Semester II 3 3 3 HRM 460Research Project5 SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish 3 Elective3 Year VI Semester I 9 Credits HRM 370 HRM 400 PLS 100 Human Resource Information Systems Managing Organizational Change Introduction to Politics Year VI Semester II 9 Credits 3 3 3 HRM 410 Human Resource Development 3 HRM 420 Comparative Human Resource Management3 Elective3 ASSOCIATE OF ARTS DEGREE 04 | HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT The acquisition of human resources management skills will provide students with the requirements necessary to meet the challenges of the on-going process of capturing and optimizing the peoples talents and potential for greater productivity. The Associate Degree prepares students to pursue careers in management of human resource functions in private, public and non-governmental agencies, regional and international organizations. It prepares students for supervisory work in Human Resource Management. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY In addition to the College’s normal requirements for admission the following conditions are required for those seeking entry into the Associate Degree in Human Resource Management: • Applicants must have successfully completed one/two years of a recognized programme in Human Resource Management • Applicants are required to have at least two (2) years’ working experience in a Human Resource environment • All students must be prepared to undergo the internship programme • The selection process may include an interview. Each applicant will be required to submit a personal profile so as to assist the College in determining, his/her readiness for the professional and ethical training in Human Resource Management. TRANSFERS Certificate / Diploma To The Associate Of Arts Degree In Human Resource Management Any student who wishes to transfer from the Certificate Programme in Human Resource Management to the Associate Degree Programme may apply to do so, provided that he/she has obtained at least a 3.0 grade point average. Students who have obtained an overall grade point average of 2.5 will normally be allowed to transfer into the Diploma Programme. From the Diploma Programme to the Associate Degree, an overall grade point average of 2.5 is required. From Associate Degree to Bachelor of Arts Degree a grade point average of 2.0 is required. 29 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | 04 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Associate of Arts Degree (AA) - 65 credits General Education Courses 21 Credits ENG 110Fundamentals of Writing3 MAT 100Mathematics3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information System3 ECN 100 Introduction to Economics 3 RES 100 Research Methods & Statistics 3 LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 Programme Concentration41 Credits HRM 230Strategic HRM3 HRM 300 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures I 3 HRM 301 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures II 3 HRM 304 Personal Self–development for HR Professionals 3 HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I 3 HRM 306 Organizational Behaviour II 3 HRM 312 Corporate & Business Human Resource Management3 HRM 320Training & Development3 HRM 330Compensation Administration3 HRM 340Performance Management3 HRM 350Internship3 HRM 360Research Paper5 MGT 200 Principles of Business Management 3 Electives (select ONE)3 Credits LBS 300Employment Law3 PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology 3 PLS 100Introduction to Politics3 PLS 200 Government and Politics of the Caribbean 3 SOC 100Introduction to Sociology3 30 04 | HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Arts Degree in Human Resource Management Day Programme (Full-Time) - 65 credits Year I Semester I15 Credits ENG 110Fundamentals of Writing3 HRM 300 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures I 3 HRM 304 Personal Self –development for HR Professionals 3 LBS 100Introduction to Industrial Relations3 MAT 100Mathematics3 Year I Semester II18 Credits ECN 100Introduction to Economics3 HRM 301 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures II 3 HRM 305Organizational Behaviour I3 HRM 350Internship3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 MGT 200 Principles of Business Management 3 Year II Semester I15 Credits CIS 100Introduction to Computer Information Systems 3 HRM 230Strategic HRM3 HRM 306Organizational Behaviour II3 HRM 312 Corporate & Business Human Resource Management 3 RES 100Research Methods & Statistics3 Year II Semester II17 Credits HRM 320Training & Development3 HRM 330Compensation Administration3 HRM 340Performance Management3 HRM 360Research Paper5 Elective3 31 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT | 04 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Arts Degree in Human Resource Management Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 65 credits Year I Semester I9 Credits ENG 110Fundamentals of Writing3 HRM 304 Personal Self –development for HR Professionals3 LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 Year I Semester II9 Credits HRM 300 HRM 305 MGT 200 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures I Organizational Behaviour I Principles of Business Management 3 3 3 Year II Semester I9 Credits HRM 301 HRM Systems Functions & Procedures II 3 HRM 306 Organizational Behaviour II 3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 Year II Semester II12 Credits ECN 100 Introduction to Economics 3 HRM 350Internship3 MAT 100Mathematics3 Elective3 Year IIISemester I12 Credits CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems3 HRM 230Strategic HRM3 HRM 312 Corporate & Business Human Resource Management3 RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics 3 Year IIISemester II14 Credits HRM 320Training & Development3 HRM 330Compensation Administration3 HRM 340Performance Management3 HRM 360Research Paper5 32 04 | HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT DIPLOMA IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT CERTIFICATE IN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT This programme is intended for those who have completed the Certificate in Human Resource Management or students who, in the opinion of the College, have training and/or experience equivalent to holders of the Certificate. This one-year Certificate in Human Resource Management is open not only to persons who have five (5) C.X.C. subjects or its equivalent but also to those students who have successfully completed the ten (10) week Outreach Programme in Human Resources Management or Supervisory Management. The objectives of this Diploma are to provide further training in the Human Resource Management subject areas and to further develop an understanding of the concepts and application of human resources principles to other management activities. Practitioners and Technicians in Human Resource Departments and other persons who have an acceptable background of training and/or experience will also be considered. The objective of this programme is to examine the principles and theories associated with contemporary human resource practices as they impact on the behaviour of people in organizations. The programme is also intended to develop in the participants an understanding of the theories, techniques and skills associated with organizational development and change. Required CoursesCredits Semester I HRM 300 Human Resource Management, Functions & Procedures I 3 LOG 120 Critical Thinking 3 PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology 3 Semester II HRM 121 Legal Issues of HRM in Operations HRM 241 Collective Bargaining & Compensation HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I 3 3 3 Total Credits Required 8 Required Courses Semester I ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing HRM 105 Fundamentals of Human Resource Management LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations Semester II COM 101 HRM 200 HRM 210 Fundamentals of Communication Theories Concepts & Practices of Human Resource Management Organizational Behaviour & Development Total Credits Required Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 18 33 34 5 LABOUR STUDIES LABOUR STUDIES | 05 LABOUR STUDIES BACHELOR OF ARTS DEGREE “Understanding Your Power” 36 The Bachelor of Arts Degree in Labour Studies along with all other certificate and training courses offered by the Cipriani College of Labour and Cooperative Studies (CCLCS) aims to fill the need for high-quality academic training for professionals and practitioners in the following fields: Industrial Relations; Labour and Manpower Economics and; Human Resource Managers employed in workers’ organizations, business organizations and the public service. At the end of our programmes the CCLCS produces a more empowered and socially conscious graduate capable of making a contribution to the development of the region and improving the lives of working people. IAN DANIEL Head of Department/Senior Lecturer BSc After forty (40) years of developing and offering programmes in Industrial Relations for workers, trade unions and other people based organizations, the Cipriani College of Labour and Cooperative Studies has taken a qualitative leap with the offering of the Bachelor’s Degree. In doing this we continue to serve the needs of our primary institutional stakeholders, in particular and the working people in general. CCLCS began its programme offerings in Industrial Relations in 1972 with a two year Diploma in Labour Studies. Over the years, a one year Certificate and short courses in Industrial Relations were added to course offerings. The College reached a milestone at the beginning of the Academic year 1998-1999 when it began offering the Associate Degree in Labour Studies, the first in the country and the region. Nine years later, CCLCS achieved the significant milestone of launching the Bachelor of Arts Degree in Labour Studies at the start of Academic year 2007-2008. This would soon be followed by the Diploma in Industrial Relations Practice in 20082009, demonstrating the College’s commitment to constantly revising and improving its academic offerings in relation to contemporary industry and workplace needs. All of the College’s programmes have been developed in consultation with our stakeholders to specifically serve the needs of the country and the region, while at the same time offering our students a level of quality which would allow them to compete globally in their chosen field. Our manageable class sizes and diverse student population creates a dynamic and fulfilling adult learning environment, combining the benefits of youth and experience, theory and practice. Labour Studies prepares you for a range of interesting careers that are meaningful and rewarding. These include areas in: • Law and Policy Making • Education and Training • Organizing, Community Activism and Social Justice • Labour and Employment Relations 05 | LABOUR STUDIES Labour Studies graduates find careers in such organizations as: • Unions and Employee Associations • Government Ministries, Departments, Agencies, Boards and Tribunals • Private Corporations • Labour, Employment Service, and Dispute Resolution and various Management Consulting Firms • University and private Research Centres, Public Service Organizations • NGOs, Social and Community Groups • Universities and Colleges The graduate of this programme would be able to: • Assume a leadership role in a worker’s organization • Represent an individual or organization in Industrial Relations matters • Understand and apply the principles of Grievance Handling, Collective Bargaining and Employment Law • Evaluate and undertake research in Industrial Relations matters 37 LABOUR STUDIES | 05 LABOUR STUDIES Bachelor of Arts Degree (BA) – 122 credits General Education Courses30 Credits CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems 3 COM 101Fundamentals of Communication3 COM 250Effective Communication3 ENG 110Fundamentals of Writing3 LOG 120Critical Thinking3 MAT 100Mathematics3 PSY 100Introduction to Psychology3 RES 100Research Methods & Statistics3 SOC 100Introduction to Sociology3 SPN 100Introduction to Spanish3 Programme Concentration53 Credits LBS 100Introduction to Industrial Relations3 LBS 120History of Caribbean Labour3 LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law 3 LBS 210Grievance Handling and Arbitration3 LBS 220 Principles of Caribbean Labour Law 3 LBS 240Collective Bargaining3 LBS 250Internship3 LBS 270 Caribbean Industrial Relations Systems 3 LBS 280 Trade Union Administration, Organization & Governance 3 LBS 290Applied Collective Bargaining3 LBS 300Employment Law3 LBS 310Women in the Workplace3 LBS 330Industrial Arbitration and Mediation3 LBS 335 ILO and Labour Management in the Caribbean 3 LBS 360Research Paper5 LBS 370 Trade Union Leadership 3 LBS 380Ethics in Decision Making3 38 05 | LABOUR STUDIES LABOUR STUDIES Bachelor of Arts Degree (BA) 122 credits Supporting Courses CC 100 Introduction to Accounting ECN 100 Introduction to Economics ECN 200 Economy of the Caribbean ECN 210 Interpreting Economic and Financial Data ECN 220 Labour Economics HRM 105 Human Resource Management LBS 110 Gender Studies MGT 200 Principles of Business Management OSH 231 Occupational Safety And Health Legislative Framework PLS 100 Introduction to Politics PLS 200 Government and Politics of the Caribbean 33 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Electives (Select two) COS 120 Co-operative Organization and operations HRM 300 HRM Systems, Functions & Procedures I HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I HRM 330 Compensation Administration LBS 295 Comparative Labour Movements PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management SOC 200 Industrial Sociology SOC 210 Social Structure of the Caribbean 6 credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 39 LABOUR STUDIES | 05 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Arts Degree in Labour Studies Day Programme (Full-Time) - 122 credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year III Semester I ECN 200 Economy of the Caribbean Region LBS 270 Caribbean Industrial Relations Systems LBS 280 Trade Union Administration, Organization & Governance COM 250 Effective Communication Elective 15 Credits 3 3 Semester II Introduction to Accounting Human Resource Management Critical Thinking Mathematics Research Methods & Statistics 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year III ECN 210 ECN 220 LBS 110 LBS 250 PLS 200 Semester II Interpreting Economic and Financial Data Labour Economics Gender Studies Internship Government and Politics of the Caribbean 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Semester I Fundamental of Communication Introduction to Psychology Fundamental Principles of Labour Law Grievance Handling and Arbitration Introduction to Politics 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year IV LBS 290 LBS 300 LBS 335 LBS 360 SPN 100 Semester I Applied Collective Bargaining Employment Law ILO and Labour Management in the Caribbean Research Paper/ Project Introduction to Spanish 17 Credits 3 3 3 5 3 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year IV LBS 310 LBS 330 LBS 370 LBS 380 OSH 231 Semester II Women in the Workplace Industrial Arbitration and Mediation Trade Union Leadership Ethics in Decision Making Occupational Safety And Health Legislative Framework 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 ECN 100 ENG 110 LBS 100 SOC 100 Semester I Introduction to Computer Information Systems Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Industrial Relations Introduction to Sociology 15 Credits Year I ACC 100 HRM 105 LOG 120 MAT 100 RES 100 Year II COM 101 PSY 100 LBS 200 LBS 210 PLS 100 Year II Semester II LBS 120 History of Caribbean Labour LBS 220 Caribbean Labour Legislations LBS 240 Collective Bargaining MGT 200 Principles of Business Management Elective 40 3 3 3 3 05 | LABOUR STUDIES PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Arts Degree in Labour Studies Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 122 credits Year IV COM 250 ECN 200 LBS 270 Semester I Effective Communication Economy of the Caribbean Region Caribbean Industrial Relations Systems 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year IV ECN 210 ECN 220 LBS 110 Semester II Interpreting Economic and Financial Data Labour Economics Gender Studies 9 Credits 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year V LBS 250 LBS 280 LBS 300 Semester I Internship Trade Union Administration, Organization & Governance Employment Law 9 Credits 3 Semester II Fundamentals of Communication History of Caribbean Labour Research Methods & Statistics 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year V LBS 310 LBS 330 LBS 370 Semester II Women in the Workplace Industrial Arbitration and Mediation Trade Union Leadership 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year III ACC 100 LBS 200 LBS 210 MGT 200 Semester I Introduction to Accounting Fundamental Principles of Labour Law Grievance Handling and Arbitration Principles of Business Management 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 12 Credits 3 Year III LBS 220 LBS 240 PLS 200 Semester II Principles of Caribbean Labour Law Collective Bargaining Government and Politics of the Caribbean 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year VI Semester I LBS 290 Applied Collective Bargaining LBS 335 ILO and Labour Management in the Caribbean OSH 231 Occupational Safety And Health Legislative Framework Elective Year VI Semester II LBS 360 Research Paper LBS 380 Ethics in Decision Making SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish Elective 14 Credits 5 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 ECN 100 ENG 110 SOC 100 Semester I Introduction to Computer Information Systems Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Sociology 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year I LBS 100 LOG 120 MAT 100 Semester II Introduction to Industrial Relations Critical Thinking Mathematics 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year II HRM 105 PLS 100 PSY 100 Semester I Human Resource Management Introduction to Politics Introduction to Psychology Year II COM 101 LBS 120 RES 100 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 41 ASSOCIATE OF ARTS DEGREE LABOUR STUDIES | 05 The Labour Studies programme of Cipriani College of Labour and Cooperative Studies builds on the disciplines of Sociology, Psychology, History, Political Science and Law to offer a multidisciplinary approach to workers and work. Students take courses in Labour History, Labour Law, Information Technology, Economics, Sociology, Psychology and in other areas such as Mathematics, Critical Thinking and Accounting. The aim is to prepare the student for the widest possible concern and interest of the worker in this globalized environment. The programme is thus designed to be comprehensive. This programme provides the present labour leader, the union member and the non-union worker with the relevant theory, principles, skills and practice necessary for success and/or employment in the field. A Labour Studies Degree prepares students to pursue careers in trade unions, all levels of government and even in the private sector 42 as industrial relations officers. Virtually every individual and organization deal with employees at work and with the growing emphasis on human resource issues, there is an on-going demand for graduates with an understanding and the capabilities in these areas. Our graduates pursue occupations such as Industrial Relations Officer, Human Resources Officer, Union Analyst, Labour Officer and Labour Inspector. An understanding of work, workers and employment issues is also a very valuable asset in other occupations such as journalism, teaching and law. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The graduates of this programme will be able to appreciate the application of the principles of industrial relations, employment law, grievance handling, arbitration and collective bargaining in the workplace. The learner will be able to conduct educational research in the field of industrial relations and also identify and analyze industrial relations and legal issues arising from disputes in the workplace. 05 | LABOUR STUDIES LABOUR STUDIES Associate of Arts Degree (AA) 68 credits General Education Courses CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology 24 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations LBS 120 History of Caribbean Labour LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law LBS 210 Grievance Handling and Arbitration LBS 220 Principles of Caribbean Labour Law LBS 240 Collective Bargaining LBS 250 Internship LBS 260 Research Paper MGT 200 Principles of Business Management 29 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 3 Supporting Courses ACC 100 ECN 100 HRM 105 PLS 100 PLS 200 3 3 3 3 3 15 Credits Introduction to Accounting Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Human Resource Management Introduction to Politics Government and Politics of the Caribbean 43 LABOUR STUDIES | 05 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Arts Degree in Labour Studies Day Programme (Full-Time) - 68 credits PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Arts Degree in Labour Studies Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 68 credits Year I CIS 100 ECN 100 ENG 110 LBS 100 SOC 100 Semester I Introduction to Computer Information Systems Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Industrial Relations Introduction to Sociology Year I CIS 100 ECN 100 ENG 110 SOC 100 Semester I Introduction to Computer Information Systems Introduction to Economics Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Sociology 12 Credits Year I ACC 100 HRM 105 LOG 120 MAT 100 RES 100 Semester II Introduction to Accounting Fundamentals of Human Resource Management Critical Thinking Mathematics Research Methods and Statistics 3 3 3 3 Year I ACC 100 LBS 100 LOG 120 MAT 100 Semester II Introduction to Accounting Introduction to Industrial Relations Critical Thinking Mathematics 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year II COM 101 LBS 200 LBS 210 LBS 250 PLS 100 PSY 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Fundamental Principles of Labour Law Grievance Handling and Arbitration Internship* Introduction to Politics Introduction to Psychology 18 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year II COM 101 PLS 100 PSY 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Introduction to Politics Introduction to Psychology 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year II HRM 105 LBS 120 RES 100 Semester II Fundamentals of Human Resource Management History of Caribbean Labour Research Methods and Statistics 9 Credits Year II LBS 120 LBS 220 LBS 240 LBS 260 MGT 200 PLS 200 Semester II History of Caribbean Labour Principles of Caribbean Labour Law Collective Bargaining Research Paper Principles of Business Management Government and Politics of the Caribbean 20 Credits 3 3 3 5 3 3 Year III LBS 200 LBS 210 LBS 250 MGT 200 Semester I Fundamental Principles of Labour Law Grievance Handling and Arbitration Internship* Principles of Business Management 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year III LBS 220 LBS 240 LBS 260 PLS 200 Semester II Principles of Caribbean Labour Law Collective Bargaining Research Paper Government and Politics of the Caribbean 14 Credits 3 3 5 3 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 15 Credits 3 *Completed during the vacation between the first and second academic year *Completed during the second and third academic year 44 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 05 | LABOUR STUDIES DIPLOMA IN INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS PRACTICE CERTIFICATE IN INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS Cipriani College of Labour & Co-operative Studies (CCLCS) has been offering programmes in Industrial Relations for workers, trade unions and other people-based organizations for the last forty (40) years. As the only institution which has remained focused in the area of Industrial Relations, the College has exercised a profound influence in this area through the quality of graduates which it has produced over the years. This one-year Part-Time Certificate Programme in Industrial Relations is aimed at those who may not want to pursue a higher level programme but still want to attain a certain level of competence in Industrial relations. This programme will focus more on the practical courses of Industrial Relations. The strength of the College lies in its ability to connect the theory of Industrial relations with its practice and it is in this context that CCLCS is seeking to fulfill a critical need for workers, trade unions and other people-based organizations through the development and offering of this Diploma in Industrial Relations Practice. This programme is designed primarily for officials and leaders of trade unions and those who in the shortest time possible wish to acquire the skills necessary for running a union. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES PROGRAMME OUTCOMES At the end of this programme graduates will become more skillful Industrial Relations Practitioners and will be able to apply: a) Mathematical and economic tools; b) Collective bargaining theories when engaging in the process of collective bargaining. The graduates will be able to modify and assess the approaches and styles when presenting evidence and arguments before the Industrial Court of Trinidad and Tobago. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY • Industrial Relations or HR Practitioners with at least five years experience in the field will be considered for entry however candidates MUST provide documentary evidence of experience. Required Courses Semester I COM 250 Effective Communication LBS 130 Caribbean Labour Relations History LBS 205 Industrial Relations Law and Practice Semester II ECN 210 LBS 245 LBS 285 At the end of this programme the learner will be able to remodel his/ her approach to trade union administration and governance, collective bargaining, grievance handling and employment law. At the same time, also, should they wish to move forward to the Associate of Arts Degree, they would be able to use the credits acquired towards the Associate Degree. This will also enhance employment opportunities and promotion. Required Courses Semester I LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law LBS 210 Grievance Handling and Arbitration Total Credits Required 3 3 3 Credits 3 3 3 Semester II COM 101 LBS 120 LBS 240 Fundamentals of Communication History of Caribbean Labour Collective Bargaining Total Credits Required Interpreting Economic and Financial Data Collective Bargaining: Principles, Procedures and Practices Selected Industrial and Labour Relations Issues Credits 3 3 3 18 3 3 3 18 45 LABOUR STUDIES | 05 TEN WEEK FULL-TIME PROGRAMME IN INDUSTRIAL RELATIONS This programme gives a broad introduction to Industrial Relations to members of Trade Unions and Associations. Students will be assessed during and at the end of the programme. Successful completion can be used as entrance qualification for the Certificate or Diploma Programmes in Industrial Relations only. Topics addressed include: 1. Principles of Management 2. Introduction to Industrial Relations 3. Topics in Labour Economics 4. History of the Trade Union Movement 5. Principles of Collective Bargaining 6. Grievance Handling 7. Introduction to Co-operatives 8. Basic Principles of Communication 9. Principles of Accounting & Business Mathematics 10. Introduction to Labour Legislation 46 6 MARKETING & PUBLIC RELATIONS MARKETING AND PUBLIC RELATIONS | 06 MARKETING AND PUBLIC RELATIONS “Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders” (The American Marketing Association). Public Relations “The deliberate, planned and sustained effort to establish and maintain mutual understanding between an organisation (or individual) and its (or their) publics” (The Public Relations Institute of Australia). The Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies introduced Marketing and Public Relations in the academic year 1997/1998 in an effort to provide stakeholders with an opportunity to improve their skills in the areas of relationship building, customer satisfaction and delivery value. SELWYN WALTRESS Head of Department/Senior Lecturer MBA,BA(Econ), CIFC The Marketing programme is offered at the Certificate level only and includes some core courses that give the student a comprehensive understanding of the marketing concept. The courses include Principles of Marketing, Marketing Practice, Marketing Research and Forecasting, Marketing Planning and Control, Sales Techniques and Fundamentals of Communication. These courses are designed within a two semester academic year of teaching and learning. Each course consists of 45 contact hours and carries three credits each for a programme total of 18 credits. A graduate of this Certificate Programme will be equipped with competencies to function as a valuable Marketing Assistant or functionary within a marketing department. In addition, this programme matriculates graduates for a Bachelor of Science level in Marketing. The Public Relations programme has two levels, the Certificate and the Diploma. The Certificate is designed to ensure that a solid foundation is built, whilst at the Diploma level the student will be exposed to the exciting world that joins theory with 48 practice. They are both one-year programmes comprising of six courses each, and 45 contact hours per course, carrying three credits each resulting in 18 credits. The Certificate programme is the foundation, building a practitioner who understands the role and function of public relations within institutions whether they be corporate or social sectors, through the principles of public relations. The ability to write within a demanding public relations world is the primary course; Writing for Public Relation. The role of the media, the impact of public relations in a globalized environment and an introduction to events co-ordination, all prepare the graduate to function in any government or private organizations public relations department. The Diploma builds on the students understanding of public relations and explores the exciting world of advertising within a public relations context as well as studies marketing communications tools that PR Practitioners may employ to achieve success. The Diploma also takes a critical look at the law and ethics of the media, crisis management as it relates to the media and takes events management to yet another level. This diploma prepares the graduate to perform at a junior management level in an Advertising Agency, an Image Consultancy firm or an Events Management company. 06 | MARKETING AND PUBLIC RELATIONS DIPLOMA IN PUBLIC RELATIONS This Diploma Programme is aimed at those who seek entry level jobs in Public Relations, Community or Consumer Relations, Marketing Research, Fund Raising and Organizational Image Building. It provides the student with a more in-depth knowledge of the operations of Public Relations practitioners in the areas of effective writing, media operations and wider promotional opportunities. The Courses in this Programme are: Required Courses Semester I PBR 200 The Role and Function of the Public Relations Practitioner PBR 220 Laws and Ethics of Media PBR 250 Principles of Advertising Semester II PBR 245 Events Management PBR 255 Crisis Management and the Media MAR 115 Integrated Marketing Communications Total Credits Required Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 1 CERTIFICATE IN PUBLIC RELATIONS CERTIFICATE IN MARKETING Although open to all who may have an interest in Public Relations and have the necessary qualifications, this Certificate in Public Relations is also aimed at those who have completed the College’s Introduction to Public Relations course, Public Relations Officers, Teachers, Police Officers, Prison Officers and other personnel in public relations departments. This programme will examine the principles and theories of Public Relations, the contemporary methods and process in Public Relations and will demonstrate the usefulness of Public Relations as an effective tool for growth and development of organizations. There are six Courses in this Certificate Programme: Required Courses Semester I PBR 110 Principles of Public Relations PBR 201 Writing for Public Relations MAR 110 Principles of Marketing Semester II PBR 135 Media Relations PBR 145 Introduction to Events Co-ordination PBR 150 Understanding Global Public Relations Total Credits Required Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 This course aims at providing students with an understanding of marketing concepts, operations, practice and analytical skills. Once these areas are successfully completed, students should be able to recognize and confront marketing problems and seek solutions to deal with these problems. The purpose of this programme is: • To provide an understanding of the role and value of marketing in today’s business environment. • To indicate a knowledge of the management of the marketing function in diverse marketing situations. • To develop the ability to analyze, plan, implement and control a marketing programme. • To enable participants to apply the knowledge gained in marketing principles, communication and the operating environment to the marketing task. Required Courses Semester I COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication MAR 110 Principles of Marketing MAR 121 Marketing Research & Forecasting Credits 3 3 3 Semester II MAR 130 Marketing Practices MAR 140 Marketing Planning and Control MAR 150 Sales Techniques Total Credits Required 3 3 3 18 18 49 50 7 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEGREE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH and THE ENVIRONMENT 52 The BSc Occupational Health Safety and the Environment (OSHE) provides holistic and multiple dimensional training relevant to those involved in areas of occupational health, safety and the environment. As such, the programme embraces an interdisciplinary approach, augmented by practical experiences towards a goal of interdisciplinary and integrative Occupational Health Safety and the Environment educational experiences. The BSc OSHE programme can be completed in a minimum of three years and allows flexible options based on students’ specific needs .However, consistent with the CCLCS’ vision to provide accessible high quality education, the BSc OSHE’s structure affords individuals the opportunity to obtain this pragmatic and relevant degree at their own pace and with the support of a range of excellent student services. This BSc OSHE boasts of capitalizing on the experience of almost 30 years of academic offerings in Health and Safety by the CCLCS. The programme’s evolution is based on consultation and feedback with our stakeholders and driven by the desire to specifically serve the needs of the country and the region while at the same time providing our students with the ability and capacities to compete globally. The CCLCS BSC OSHE graduate is a competent practitioner sought after by all sectors of the community; energy companies, manufacturers, environmental services, protective services in both the private and public sector. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The graduate of this programme will be able to: • Explore the procedures and techniques to develop health and safety policies and safe systems of work • Design, manage and monitor health and safety performance • Manage the process and hazards at work • Access and critically analyze sources of health and safety information • Critically assess the safety and durability of engineering components and structures • Appraise hazard analysis techniques and make recommendations for improving systems reliability • Assess the hazards of electricity and technical and procedures; measures to prevent shocks, electrical fires and explosion • Understand the management of occupational hygiene within an organization • Understand, develop and implement strategies for controlling exposure to health stressors • Evaluate environmental issues from a social, economic and naturalistic perspective and advance practical and effective responses and solutions in context. 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY Those who fulfil the following conditions will be eligible for admission into the Bachelor of Science Degree in Occupational Safety and Health: • Students who possess 5 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics, English and Science) or • Student who have successfully completed the CCLCS Associate Degree in Occupational Safety and Health or its equivalence (GPA = 2.5) • Students who have successfully completed the CCLCS Certificate or Diploma in Occupational Safety and Health with a 3.0 GPA • • Mature students (25 years and older) who have 3 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics and English) and have worked continuously within a Safety environment for at least 5 years. Students who possess the National Examination Board of Occupational Safety and Health (NEBOSH) (UK) Certificate. Because of lack of space, not everyone eligible for admission is guaranteed admission into the programme. OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & THE ENVIRONMENT Bachelor of Science Degree (BSc) – 122 credits General Education Courses CAS 130 Caribbean Studies CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication ENG 110 Fundamental of Writing HUM 220 Ethics and Moral Values LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology RES 100 Research Method and Statistics SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish 30 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration ENM 121 Principles & Theories of Environmental Management ENM 142 Environmental Science I ENM 143 Environmental Science II ENM 148 Alternative Sources of Energy ENM 221 Environmental Risk Assessment ENM 231 Environmental Impact Assessment ENM 235 Environmental Investigative and Impact Assessment Techniques ENM 240 Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management ENM 258 Economics of Environmental Management PHY 100 Introduction to Physics OSH 110 Safety Technology I OSH 120 Safety Management I OSH 141 Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I OSH 210 Safety Technology II OSH 220 Safety Management II OSH 231 Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework OSH 241 Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene II OSH 250 or ENM 250 Internship* OSH 255 Principles of Health and Safety Law OSH 301 Process Management Safety OSH 310 Safety Technology III OSH 320 Safety Management III OSH 341 Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene III OSH 360 or ENM 360 Research Paper 74 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 53 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & THE ENVIRONMENT Bachelor of Science Degree (BSc) – 122 credits Supporting Courses BIO 100 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology CHM 100 Introduction to Chemistry LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations Electives (Select any THREE - Diploma graduates MUST choose a course not previously attempted) EMM 275 Disaster Preparedness Planning HRM 105 Fundamental of Human Resource Management HRM 210 Organizational Behaviour and Development HRM 300 Systems, Functions and Procedures I (Human Resource Management) HRM 305 Organizational Behaviour I LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law OSH 245 Fire Safety OSH 400 Fire Protection and Prevention PRM 120 Fundamental of Project Management SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology 9 Credits 3 3 3 9 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 *An internship will be required for those who do not have any working experience in the field. Students who have working experience will be granted an exemption from OSH 250. However, they will be required to submit written proof of their working experience. 54 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Science Degree in Occupational Safety, Health & The Environment Day Programme (Full-Time) - 122 credits Year I COM 101 ENG 110 MAT 100 PHY 100 PSY 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Fundamentals of Writing Mathematics Introduction to Physics Introduction to Psychology 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 LOG 120 OSH 110 OSH 120 OSH 141 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Critical Thinking Safety Technology I Safety Management I Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year II BIO 100 CAS 130 CHM 100 OSH 210 OSH 231 Semester I Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Caribbean Studies Introduction to Chemistry Safety Technology II Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year II ENM 221 LBS 100 OSH 241 OSH 220 OSH 250 RES 100 Semester II Environmental Risk Assessment Introduction to Industrial Relations Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene II Safety Management II Internship* Research Methods and Statistics 18 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year III ENM 121 ENM 142 ENM 231 OSH 255 Semester I Principles & Theories of Environmental Management Environmental Science I Environmental Impact Assessment Principles of Health and Safety Law ELECTIVE Year III ENM 143 ENM 148 ENM 240 OSH 301 Semester II Environmental Science II Alternative Sources of Energy Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management Process Management Safety ELECTIVE Year IV OSH 310 OSH 320 OSH 341 OSH 360 or ENM HUM 220 Semester I Safety Technology III Safety Management III Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene III 3 360 Research Paper Ethics and Moral Values 5 3 Year IV Semester II ENM 235 Environmental Investigative and Impact Assessment Techniques ENM 258 Economics for Environmental Management SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish ELECTIVE 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 17 Credits 3 3 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 55 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Science Degree in Occupational Safety, Health & The Environment Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 122 credits 56 Year I COM 101 ENG 110 PSY 100 PHY 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Psychology Introduction to Physics 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year IV ENM 121 ENM 142 OSH 255 Semester I Principles & Theories of Environmental Management Environmental Science I Principles of Health and Safety Law 9 Credits Year I MAT 100 OSH 110 OSH 120 OSH 141 Semester II Mathematics Safety Technology I Safety Management I Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year IV ENM 143 ENM 148 OSH 301 Semester II Environmental Science II Alternative Sources of Energy Process Management Safety 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year II CAS 130 LOG 120 BIO 100 Semester I Caribbean Studies Critical Thinking Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year V ENM 231 ENM 258 OSH 310 Semester I Environmental Impact Assessment Economics for Environmental Management Safety Technology III 9 Credits 3 3 3 Semester II 100 Introduction to Chemistry Introduction to Computer Information Systems Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene II Internship* 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Semester II Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management 11 Credits Year II CHM CIS 100 OSH 241 OSH 250 Year V ENM 240 OSH 360 or ENM 360 HUM 220 Research Paper Ethics and Moral Values 5 3 Year III OSH 210 OSH 231 OSH 220 Semester I Safety Technology II Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework Safety Management II 9 Credits 3 Semester I Safety Management III Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene III ELECTIVE 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year VI OSH 320 OSH 341 Year III ENM 221 LBS 100 RES 100 Semester II Environmental Risk Assessment Introduction to Industrial Relations Research Methods and Statistics ELECTIVE 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year VI ENM 235 SPN 100 Semester II Environmental Investigative and Impact Assessment Techniques Introduction to Spanish ELECTIVE 9 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY and HEALTH The degree provides a substantial foundation for the legal, management, behavioural and policy issues affecting Occupational Safety and Health in its broadest sense. The scope of the topics is wide ranging and will be covered in sufficient detail to provide a firm basis for future expansion and application. Among the areas the programme addresses are: PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The graduate of this programme will be able to: • Reduce the effect of exposure to hazards in an organization • Apply that which they learn to their individual career paths • Implement safe systems of work and accident prevention • The historical development of Occupational Safety and Health practice • Communicate effectively with practitioners in the related professions • The updated Heinrich Domino Sequence Model • • Safety Technology • Sources of Incidents /Accidents Apply the leadership and management knowledge necessary to supervise Occupational Safety and Health departments well into the twenty-five century • Hazards-Category, Probability and Controls Toxicity • Function at the senior management level in an advisory capacity • Safety responsibilities of Management • Industrial Relations • Pollution Control Management • The Role of State Agencies • Security Aspects of Safety • Risk Assessment Techniques ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY Those who fulfill the following conditions will be eligible for admission into the Associate of Science Degree in Occupational Safety and Health: • Students who possess 5 GCE or CXC ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics, English and Science) or The Associate Degree programme in Occupational Safety and Health is designed to cover a period of two years full-time and three years of part time study. However, students who receive exemptions or credits for previous work in the field may be able to complete the degree in a shorter period of time. • Student who have successfully completed the CCLCS Diploma in Occupational Safety and Health or its equivalence (i.e. GPA = 2.0) • Students who have successfully completed the CCLCS Certificate in Occupational Safety and Health with a 3.0 GPA The degree consists of credits awarded in the pursuit of courses specific to the discipline as well as college credits based on general education courses and electives. • Mature students (25 years and older) who have 3 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics and English) and have worked continuously within a Safety environment for at least 5 years. The Associate of Science Degree in Occupational Safety and Health requires a total of sixty-five (65) credits for completion. 57 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH Associate of Science Degree (AS) – 68 credits General Education Courses CAS 130 Caribbean Studies CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology 21 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration ENM 221 Environmental Risk Assessments OSH 110 Safety Technology 1 OSH 120 Safety Management 1 OSH 141 Occupational and Industrial Hygiene 1 OSH 210 Safety Technology 2 OSH 220 Safety management 2 OSH 231 Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework OSH 241 Occupational and Industrial Hygiene 2 OSH 250 Internship OSH 260 Research 32 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 Supporting Courses BIO 100 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology CHM 100 Introduction to Chemistry LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations PHY 100 Introduction to Physics 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 *An internship will be required for those who do not have any working experience in the field. Students who have working experience will be granted an exemption from OSH 250. However, they will be required to submit written proof of their working experience. 58 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Science Degree in Occupational Safety & Health Day Programme (Full-Time) - 68 credits Year I BIO 100 COM 101 MAT 100 PHY 100 PSY 100 Semester I Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Fundamentals of Communication Mathematics Introduction to Physics Introduction to Psychology 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 LOG 120 OSH 110 OSH 120 OSH 141 OSH 250 RES 100 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Critical Thinking Safety Technology I Safety Management I Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I Internship Research Methods and Statistics 21 Credits Year II CAS 130 CHM 100 OSH 210 OSH 231 OSH 260 Semester I Caribbean Studies Introduction to Chemistry Safety Technology II Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework Research Paper 17 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year II ENM 221 LBS 100 OSH 220 OSH 241 Semester II Environmental Risk Assessment Introduction to Industrial Relations Safety Management II Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene II ELECTIVE Electives (Select any ONE - Diploma graduates MUST choose a course not previously attempted) EMM 275 Disaster Preparedness Planning LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law OSH 150 Security Aspects of Safety OSH 245 Fire Safety 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 5 NB: Exemptions will be awarded only in cases where the course numbers in the Associate Degree, Certificate or Diploma are the same. Other exemptions will be awarded in accordance with the College’s policy on exemptions. 59 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Science Degree in Occupational Safety & Health Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 68 credits Year I COM 101 MAT 100 PHY 100 PSY 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Mathematics Introduction to Physics Introduction to Psychology 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year I LOG 120 OSH 110 OSH 120 OSH 141 Semester II Critical Thinking Safety Technology I Safety Management I Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I 12 Credits 3 3 3 Year II BIO 100 CAS 130 CHM 100 Semester I Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Caribbean Studies Introduction to Chemistry 9 Credits Year II CIS 100 OSH 241 OSH 250 RES 100 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene II Internship* Research Methods and Statistics 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 *An internship will be required for those who do not have any working experience in the field. Students who have working experience will be granted an exemption from OSH 250. However, they will be required to submit written proof of their working experience. 60 Year III OSH 210 OSH 231 OSH 260 Semester I Safety Technology II Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework Research Paper 11 Credits 3 Year III ENM 221 LBS 100 OSH 220 Semester II Environmental Risk Assessment Introduction to Industrial Relations Safety Management II ELECTIVE 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Electives (Select any ONE - Diploma graduates MUST choose a course not previously attempted) EMM 275 Disaster Preparedness Planning LBS 200 Fundamental Principles of Labour Law OSH 150 Security Aspects of Safety OSH 245 Fire Safety 3 5 Credits 3 3 3 3 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT DIPLOMA IN OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH This one-year Diploma is aimed at those who have either successfully completed the CCLCS Certificate programme in Occupational Safety and Health or persons with NEBOSH qualifications. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The graduates of this programme will be able to: • Identify the common hazards and unsafe practices likely to be found in laboratories, on construction sites and in other workplaces • Know the appropriate preventative and protective measures to be taken in the workplace ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY • Students who possess 5 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics, English and Science) or • Students who have successfully completed the CCLCS Certificate in Occupational Safety and Health with a 3.0 GPA • Mature students (25 years and older) who have 3 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics and English) and have worked continuously within a Safety environment for at least 3 years. Required Courses Semester I LOG 120 Critical Thinking OSH 150 Security Aspects of Safety OSH 245 Fire Safety OSH 265 Construction Safety Semester II ENM 221 LBS 100 OSH 270 PSY 100 Environmental Risk Assessment Introduction to Industrial Relations Laboratory Safety Introduction to Psychology Total Credits Required Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 24 61 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 CERTIFICATE IN OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY & HEALTH This one-year part-time Certificate Programme in Occupational Safety and Health is to develop participants’ knowledge in the field of Occupational Safety and Health. It provides an awareness of the legal ramification with respect to Safety and Health issues and to provide practical guidance on the formulation of clearly defined safety policies and procedures. This programme is aimed at persons who have interest in safety and health at their place of employment or those who intend to pursue a career in Safety and Health. Trade Union personnel and the representatives of non-governmental and community based organizations who are likely to be concerned with health and safety issues at the workplace are also encouraged to apply for admission to this programme. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The graduate of this programme will be able to understand and explain the: 62 • Moral, legal and financial reasons for promoting good standards of health and safety within an organization • Importance of setting policy in health and safety • Concept of health and safety culture and its various components • Identification, evaluation and control of hazards • Hazards and risks from the use of work equipment • Effects of exposure to chemical, biological and physical hazards on health • Basic measures to be taken to minimize the risk • Main mechanical and non-mechanical hazards of machinery ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY PROGRAMME OBJECTIVES Entry to this programme is for persons who have: On completion of this programme, candidates will understand: • Completed the CCLCS 10 Saturdays Introductory course in Occupational Safety and Health, or • • The scope and nature of Occupational Safety, Health and Environment 3 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Mathematics and English) or • The legal framework for the regulation of Safety, Health and Environment At least 3 years’ work experience in the field of Occupational Safety and Health. This Certificate programme covers a period of two semesters with three courses • The legal and financial consequences of failure to manage Safety, Health and Environment • The Health and Safety roles and responsibilities of employers, managers, employees and other relevant parties • The guidelines for developing and applying criteria for human resource needs and assessment for environmental problems • The practices and procedures for sound environmental management planning • • Allocated to each semester. Required Courses Credits Semester I COM 101 OSH 100 OSH 231 Fundamentals of Communication Fundamentals of Occupational Safety and Health Occupational Safety and Health Legislative Framework Semester II OSH 110 OSH 120 OSH 141 Safety Technology I Safety Management I Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I Total Credits Required 3 3 3 3 3 3 18 CERTIFICATE IN OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & THE ENVIRONMENT FULL TIME This programme has been specially designed for trade union members at the request of the movement. The full-time programme incorporates elements of Occupational Safety and Health with basic concepts in Environmental Science and will be conducted over two semesters. Required Courses Credits Semester I COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication 3 ENM 121 Principles & Theories of Environmental Management 3 ENM 131 Environmental Issues 3 OSH 100 Fundamentals of Occupational Safety & Health 3 OSH 231 Occupational Safety & Health Legislative Framework 3 Semester II OSH 110 Safety Technology I OSH 120 Safety management I OSH 141 Occupational Health & Industrial Hygiene I ENM 142 Environmental Science I ENM 160 Environmental Law Total Credits Required 3 3 3 3 3 30 ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT • Persons who have successfully completed the CCLCS Diploma in Environmental Management with a 2.5 GPA The Associate of Science Degree in Environmental Management offers students a programme of studies in the management of the environment as it relates to: • Mature students (25 years and older) who have successfully completed the CCLCS Certificate in Environmental Management with at least a ‘B’ average and have worked continuously within the Environmental setting for at least 5 years. Learning to be assessed by a panel. • Management of social and economic development which oversees human activities that creates a built environment in which ecology, people, natural resources, science and scientific management principles are understood and appreciated. • Planning that over arches sustainability that concerns of future generations • Holistic management as integral to total quality management in which the cybernetic linkages and synergies of anthropocentrism are critical to health and profit all stakeholders • Management of all aspects of waste and pollution with special emphasis on proactive and reactive approaches and control application of technologies that reflect efficiencies, effects and impact analyses on receptors • A management study programme that provides the tools and techniques of decision-making based on environmental aspects analyses ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY Those who fulfill the following conditions will be eligible for admission into the Associate of Science Degree in Environmental Management: • PROGRAMME OUTCOMES Upon Successful completion students will: • Know and appreciate the systems and principles which operate in the social and economic spheres which create unique environmental challenges for management • Possess skills and technical competencies to analyze and tackle environmental issues in context of specific geographical and cultural situation • Demonstrate the ability to be effective practitioners relative to impact assessment risk assessment and environmental management systems • Gain an understanding of the legal and legislative aspects that informs the administration of policies in the environmental sphere • Appreciate the ethical and moral nucleus, which is necessary to analyze specific environmental problems in a diverse yet integrated global village. 5 CXC or GCE ‘O’ Level passes (Maths, English and Science) or 63 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT Associate of Science Degree (AS) – 68 credits 64 General Education Courses CAS 130 Caribbean Studies CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology 21 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration ENM 126 Land Degradation & Rehabilitation / Conservation ENM 136 Environmental & Occupational Sociology ENM 143 Environmental Science II ENM 148 Alternative Sources of Energy ENM 215 Caribbean Geological and Geomorphic Environmental Dynamics ENM 226 Biodiversity & Conservation ENM 235 Environmental Investigative and Impact Assessment Techniques ENM 240 Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management ENM 258 Economics for Environmental Management ENM 268 Research Paper ENM 261 Water Resource Management ENM 262 Internship ENM 265 Ethics, Morality and Corporate Governance in Environmental Management 41 Credits 3 Supporting Courses LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 Credits 3 Electives (Select any ONE) ENM 210 Impact Assessment and Evaluation ENM 221 Environmental Risk Assessment EMM 275 Disaster Preparedness Planning ENM 280 Project Management for Environmental Management 3 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 3 3 3 07 | OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Science Degree in Environmental Management - 68 credits Year I COM 101 ENM 126 ENM 136 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Land Degradation & Rehabilitation / Conservation Environmental & Occupational Sociology 9 Credits 3 Year I CIS 100 ENG 110 ENM 143 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Fundamentals of Writing Environmental Science II 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year II ENM 215 ENM 226 ENM 240 LOG 120 Semester I Caribbean Geological and Geomorphic Environmental Dynamics Biodiversity & Conservation Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management Critical Thinking 12 Credits Year II CAS 130 ENM 262 ENM 235 MAT 100 Semester II Caribbean Studies Internship Environmental Investigative and Impact Assessment Techniques Mathematics 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year III ENM 148 ENM 258 ENM 261 PSY 100 Semester I Alternative Sources of Energy Economics for Environmental Management Water Resource Management Introduction to Psychology 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year III ENM 268 ENM 265 LBS 100 Semester II Research Paper Ethics, Morality and Corporate Governance in Environmental Management Introduction to Industrial Relations 11 Credits 5 Electives (Select any ONE) EMM 275 Disaster Preparedness Planning ENM 210 Impact Assessment and Evaluation ENM 221 Environmental Risk Assessment ENM 280 Project Management for Environmental Management 3 3 3 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 65 OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT | 07 DIPLOMA IN ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT Cipriani College of Labour & Cooperative Studies has been offering training in Environmental Management since 1992. The College has moved from an Introductory Course to Certificate programme because of the environment, which has led us to construct an appropriate Diploma Programme to meet the needs of those who wish to become Environmental Specialists. This one-year part-time Certificate Programme in Environmental Management is open to persons who have completed the CCLCS Ten-Saturdays/Introductory Course in Environmental Management or Occupational Safety and Health. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES PROGRAMME OUTCOMES • Appreciate the complexity of the Caribbean Environment and the challenges faced by the diversity • Provide a basic knowledge of environmental models, terms and definitions • Understand both theory and application of Environmental Impact Assessment and Pollution Control • • Acquire skills and competencies in impact assessment and pollution control Expose participants to guidelines for developing and applying criteria for human resource needs and assessment for environmental problems • Gain an insight into the application and effectiveness of environmental legislation • Examine practices and procedures for sound environmental management planning and • Acquire an understanding of research and gain basic skills in both quantitative and qualitative data analysis. • Examine legal platforms and procedures that address environmental management problems. Field trips and exercises are a part of this programme and may incur additional expenses by the students. Required Courses Semester I ENM 151 Environmental Management Systems and Environment al Audits ENM 200 Caribbean Environments - Profiles & Problems ENM 210 Impact Assessment and Evaluation RES 100 Research Methods & Statistics Semester II ENM 221 ENM 230 ENM 240 Environmental Risk Assessment Pollution Control Management Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management Total Credits Required 66 CERTIFICATE IN ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 21 Required Courses Semester I COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication ENM 121 Principles & Theories of Environmental Management ENM 131 Environmental Issues Semester II CHM 100 ENM 142 ENM 160 Introduction to Chemistry Environmental Science I Environmental Law Total Credits Required Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 18 8 PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEGREE PROJECT MANAGEMENT Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies (CCLCS) was the first tertiary institution in Trinidad and Tobago that offered training in Project Management at the Diploma level. This Programme started in 1998 and the Associate of Science Degree in Project Management was introduced in 2004. In 2008, CCLCS created history by offering the Bachelor of Science Degree in Project Management. RATIONALE Interpret the various tools, techniques, practices and methodologies of Project Management • CCLCS is the frontrunner at the level of study in Project Management by offering the Bachelor of Science Degree in that area. • • It completes the curriculum cycle by adding the Certificate at the beginning and the Bachelor of Science Degree at the end. Analyze the interrelationship among of the various tools, techniques, practices and methodologies of Project Management. • • Trinidad and Tobago is positioned for extensive developmental works as the public and private sectors are engaging in various projects to achieve developed nation status. A Bachelor of Science Degree will empower nationals with the necessary knowledge, skills and attitude to satisfy the growing demand for qualified Project Managers. Develop the practical skills to apply this knowledge to the processes of Project Management to achieve project success within project constraints. • Demonstrate the skills to undertake research in Project Management. • Develop the competencies to satisfactorily complete the Project Management Professional Examination. HATIM ALI Head of Department/Senior Lecturer PMP., MHigherEd., MSc., Post Grad. Dip. • Employment opportunities for graduates are Project Assistant, Project Team Member, Project Team Leader or Project Manager. • CCLCS will be the premier tertiary education institution offering Programmes from the Certificate – Diploma –Associate of Science Degree -to the Bachelor of Science Degree in Project Management in a seamless transition with easy exit points to suit our diverse students’ needs. LEARNING OUTCOMES Upon successful completion of the Bachelor’s Programme students will be able to: • 68 • Describe and explain the functioning of the tools, techniques, principles, practices and methodologies of Project Management, 08 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT CRITERIA FOR ADMISSION In order to be admitted to the Programme applicants will be required to possess at least one of the following: Five (5) or more CXC/GCE passes inclusive of Mathematics and English Language Or Five (5) years of Project Management Experience Or CCLCS Diploma in Project Management (2008 and before can be exempted from courses as indicated below) Or CCLCS Certificate in Project Management will enter in yr 11 of the part time programme Or CCLCS Diploma in Project Management completed in 2009 and later will enter at yr 111 of the part time programme Or CCLCS Associate of Science Degree (Students will enter at year 3 full-time or year 4 part-time) EXEMPTIONS Students who have completed the CCLCS Diploma in Project Management in 2008 and before can be exempted from the following course as follows: Course Code and Description Previous CourseMinimum Code and DescriptionGrade PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management C PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 110 Capital Budgeting PRM 150 Proposal Development C C PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing PRM 110 Capital Budgeting PRM 150 Proposal Development C C PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control PRM 215 Project Monitoring and Control PRM 216 Project Performance and Measurements C C PRM 250 Schedule Application Techniques PRM 251 Advanced Workshop in MS Project or PRM 252 Workshop in Ms Project C C PRM 225 Quality Management PRM 220 Total Quality Management C PRM 260 Research Project PRM 260 Research Project C 69 PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Science Degree (BSc) – 121 credits 70 Core Courses: 60 Credits PRM 115 - Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 - Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 125 - Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 - Proposal Development and Costing PRM 145 - Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 - Project Scheduling PRM 200 - Project Executing and Implementing Strategies PRM 210 - Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control PRM 211 - Procurement for Projects PRM 225 - Quality Management PRM 230 - Managing Project Teams PRM 240 - Risk Management PRM 250 - Schedule Application Techniques PRM 300 - Evaluating Project Results PRM 310 - Contract Administration and Negotiation PRM 320 - Leadership in Project Management Environment PRM 330 - Communication and Stakeholders Management PRM 400 - Project Closure and Post Project Support PRM 410 - Environmental and Social Impact of Projects PRM 420 - Project Implementation and Organizational Change 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 08 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Science Degree (BSc) – 121 credits General Education Courses: 33 Credits ENG 110 - Fundamentals of Writing CIS 100 - Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 201 - Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills LOG120 - Critical Thinking MAT100 – Mathematics PSY 100 - Introduction to Psychology SOC 100 - Introduction to Sociology ECN 100 - Introduction to Economics CAS 130 - Caribbean Studies SPN 100 - Introduction to Spanish MAT 150 - Introduction to Statistics 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits Internship: 3 Credits PRM 255 Internship 3 credits Research: 10 Credits PRM 260 Research Project PRM 460 Research Paper 5 Credits 5 credits Supporting Courses: 15 Credits LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations RES 301 Research Methods MAT 301 Quantitative methods 1 HRM 430 Legal HR Issues for the Project Manager HIS 400 Historical Perspectives of labour and Cooperative Movements in the Caribbean 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 71 PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 PRE-REQUISITES PROGRAMME STRUCTURE PRM 120 is a prerequisite for all other Project Management Courses, must do it in semester 1 before continuing Project Management courses. PRM 145 is a prerequisite for PRM 200 and all courses in years 3 to 5 CCLCS offers a five (5) year part-time and four (4) year full-time Bachelor of Science Degree in Project Management. This programme consists of one hundred and twenty one (121) credits, with thirty (33) credits in general education courses, seventy three (73) credits in the programme concentration, fifteen (15) credits in supporting related courses. PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Science Degree in Project Management (Part Time) Year I Semester I ENG 110 PRM 115 PRM 120 Fundamentals of Writing Management Concepts and Principles Fundamentals of Project Management Semester II PRM 125 PRM 135 COM 201 Project Identification and Selection Strategies Proposal Development and Costing Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills Year II Semester I CIS 100Introduction to Computer Information Systems MAT 100 Mathematics PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 Project Scheduling 72 Semester II PRM 200 PRM 210 LOG 120 PRM 255 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control Critical Thinking Internship Year III Semester I PRM 225 PRM 211 PRM 230 MAT 150 Quality Management Procurement for Projects Managing Project Teams Introduction to Statistics Semester II LBS 100 PRM 250 PRM 240 PRM 260 Introduction to Industrial Relations Schedule Application Techniques Risk Management Research Project Year IV Semester I PRM 300 PRM 310 PSY 100 MAT 301 Evaluating Project Results Contract Administration and Negotiation Introduction to Psychology Quantitative Methods 1 Semester II PRM 320 PRM 330 SOC 100 RES 301 Leadership in Project Management Environment Communication and Stakeholders Management Introduction to Sociology Research Methods Year V Semester I PRM 400 PRM 410 ENC 100 HRM 430 RES 460 Project Closure and Post Project Support Environmental and Social Impact of Projects Introduction to Economics Legal HR Issues for the Project Manager Research Paper (Year Long Course) Semester II PRM 420 CAS 130 SPN 100 HIS 400 Project Implementation and Organizational Change Caribbean Studies Introduction to Conversational Spanish Historical Perspectives of Labour and Cooperative Movements in the Caribbean 08 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Science Degree in Project Management (Full Time) Year 1 Semester I ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems MAT 100 Mathematics Semester II PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 Project Scheduling COMM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills PRM 255 Internship Year II Semester I PRM 200 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control PRM 211 Procurement for Projects LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 150 Introduction to Statistics Semester 11 PRM 250 Schedule Application Techniques PRM 240 Risk Management LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations PRM 230 Managing Project Teams PRM 225 Quality Management PRM 260 Research Project Year III Semester I PRM 300 Evaluating Project Results PRM 310 Contract Administration and Negotiation PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology MAT 301 Quantitative Methods 1 Semester II PRM 320 Leadership in Project Management Environment PRM 330 Communication and Stakeholders Management SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology RES 301 Research Methods 1 Year IV Semester I PRM 400 Project Closure and Post Project Support PRM 410 Environmental and Social Impacts of Projects ENC 100 Introduction to Economics HRM 430 Legal HR Issues for the Project Manager RES 460 Research Paper (Year Long Course) Semester II PRM 420 Project Implementation and Organizational Change CAS 130 Caribbean Studies SPN 100 Introduction to Conversational Spanish HIS 400 Historical Perspectives of Labour and Cooperative Movements in the Caribbean 73 PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE PROJECT MANAGEMENT 74 CCLCS offers the Associate of Science Degree in Project Management. This programme is offered as both full time and part time. The duration of the full time is two (2) years whilst the duration of the part time is three (3) years. CRITERIA FOR ADMISSION In order to be admitted to the Programme applicants will be required to possess at least one of the following: Five (5) or more CXC/GCE passes inclusive of Mathematics and English Language Or Five (5) years of Project Management Experience Or CCLCS Diploma in Project Management (2008 and before can be exempted from courses as indicated below) Or CCLCS Certificate in Project Management will enter in yr 11 of the part time programme Or CCLCS Diploma in Project Management (2009 will enter at yr 111 of the part time programme) EXEMPTIONS Students who have completed the CCLCS Diploma in Project Management in 2008 and before can be exempted from the following course as follows: Course Code and Description Previous Course Code and Description Minimum Grade PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 110 Capital Budgeting PRM 150 Proposal Development C C C PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing PRM 110 Capital Budgeting PRM 150 Proposal Development C C PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control PRM 215 Project Monitoring and Control PRM 216 Project Performance and Measurements C C PRM 250 Schedule Application Techniques PRM 251 Advanced Workshop in MS Project or PRM 252 Workshop in MS Project C C PRM 225 Quality Management PRM 260 Research Project PRM 220 Total Quality Management PRM 260 Research Project C C 08 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT REQUIREMENTS • Demonstrate knowledge of the forms of control used in Project Management CCLCS offers a three (3) year part-time and two (2) year full-time Associate degree in Project Management. • Acquire the tools and strategies necessary for the practical application of the concepts and methodologies towards project management. This programme consists of sixty eight (68) Credits, Fifteen (18) credits in General Education courses, Thirty nine (39) credits in the Project Management concentration, Three (3) credits in Internship, Five (5) credits in the Research Project and Six (3) credits in Supporting Courses • Analyze the importance of managing, allocating and using resources to achieve a given goal for efficient and effective outcomes • Demonstrate the importance of professionalism and integrity in the execution of projects PROGRAMME OUTCOMES • Demonstrate the knowledge and skills which will prepare them for International Certification for Project Management Professionals (PMP). Upon completion of this programme, students will be able to: • Demonstrate how to manage projects. • Explain the importance and effectiveness of controlling systems and mechanisms in a project environment • Develop, use and analyze the tools and strategies for monitoring and controlling projects 75 PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 PROJECT MANAGEMENT Associate of Science Degree (AS) – 68 credits Mandatory Courses to be completed: 76 Core Courses: 39 credits PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 Project Scheduling PRM 200 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control PRM 211 Procurement for Projects PRM 225 Quality Management PRM 230 Managing Project Teams PRM 240 Risk Management PRM 250 Schedule Application Techniques 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 08 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT PROJECT MANAGEMENT Associate of Science Degree (AS) – 68 credits General Education Courses: 18 credits ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics MAT 150 Introduction to Statistics 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits Internship: 3 credits PRM 255 Internship 3 credits Research: 5 credits PRM 260 Research Project 5 credits Supporting Courses: 3 credits LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 credits Pre Requisite PRM 120 is a prerequisite for all other Project Management Courses, must do it in semester 1 before continuing Project Management courses. PRM 145 is a prerequisite for PRM 200 and all PRM courses in the third year of the programme. 77 PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 PROGRAMME OF STUDY ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT FULL TIME 2 YEARS PROGRAMME OF STUDY ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT PART TIME 3 YEARS Year I Semester I ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems MAT 100 Mathematics Year I Semester I ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management Semester II PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 255 Internship COM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills PRM 170 Project Scheduling Year II Semester I PRM 200 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies MAT 150 Introduction to Statistics PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control LOG 120 Critical Thinking PRM 211 Procurement for Projects Semester II PRM 250 Schedule Application Techniques PRM 240 Risk Management LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations PRM 230 Managing Project Teams PRM 225 Quality Management PRM 260 Research Project 78 Semester II PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing COM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills Year II Semester I CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems MAT 100 Mathematics PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 Project Scheduling Semester II PRM 200 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies PRM 255 Internship PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control LOG 120 Critical Thinking Year III Semester I PRM 225 Quality Management PRM 211 Procurement for Projects PRM 230 Managing Project Teams MAT 150 Introduction to Statistics Semester II LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations PRM 250 Schedule Application Techniques PRM 240 Risk Management PRM 260 Research Project 08 | PROJECT MANAGEMENT DIPLOMA IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT CCLCS offers a two (2) year (Part-Time) Diploma in Project Management Entry Requirements: 5 GCE ‘O’ Levels or CXC subjects inclusive of Mathematics and English or 5 years of Project Management Experience or CCLCS Ten Saturdays Introductory Programme in Project Management or CCLCS Certificate in Project Management ( will enter at yr 11) PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 Project Scheduling PRM 200 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits General Education Courses: CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits Major Pathways within the Programme - Where the Programme can lead to different areas of emphasis: Pre Requisite On completion with a minimum GPA of 2.0 students can move from the Diploma to the third year of the Associate of Science Degree. PRM 120 is a prerequisite for all other Project Management Courses, must do it in semester 1 before continuing Project Management courses. PRM 145 is a prerequisite for PRM 200 Targeted Profession / Occupations for Graduates: • Project Assistant • Project Team Member • Project Team Leader Upon completion of this programme, students will be able to: • Describe the basic tools, techniques, principles, practices and methodologies of Project Management • Utilize the tools and techniques of project management relative to the nine knowledge areas (PMBOK) • Identify the financial requirements of a project and explain why these are essential to the successful planning of the project. • Acquire the tools necessary to understand the financial market place and to make decisions on funding requirements and expected returns from project investments. • Identify the tools used for tracking project cost, schedule and quality performance. Mandatory courses to be completed: Core Courses PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits This part time Diploma is conducted over two (2) years and consists of thirty nine (39) Credits as follows: Year I Semester I ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management Semester II PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing COMM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills Year II Semester I CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems MAT 100 Mathematics PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning PRM 170 Project Scheduling Semester II PRM 200 Project Executing and Implementing Strategies PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control LOG 120 Critical Thinking 79 PROJECT MANAGEMENT | 08 CERTIFICATE IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT CCLCS offers a one (1) year (Part Time) Certificate Programme in Project Management. Entry Requirements: • Successful completion of the Introductory Ten-Week Outreach Programme in Project Management. • Persons with acceptable background of training and/or experience in the related field. • 5 GCE/ CXC ‘ O ‘ Level subjects inclusive of Mathematics and English Language Major Pathways within the Programme- Where the Programme can lead to different areas of emphasis: It is expected that students can pursue higher academic courses of study within this and related subject areas and make advancement as follows: • Students on completion of the Certificate programme with a GPA of 2.0 and above can advance to the Diploma in Project Management Targeted Profession / Occupations for Graduates: • Project Assistant • Project Team Member Upon completion of this programme, students will be able to: 80 • Explain the concepts and principles of management. • Explain the basic concepts and principles of Project Management. • Identify the basic project management skills and techniques necessary to plan and manage projects. • Analyze the social, financial and non-financial issues which impact on project development. • Evaluate and apply the methods for selecting projects. • Prepare a winning proposal with appropriate costing and budgeting. Mandatory Courses to be Completed: Core Courses: PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategy PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits 3 credits General Education Courses: ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing COM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills 3 credits 3 credits PRE-REQUISITES PRM 120 is a prerequisite for all other Project Management Courses, must do it in semester 1 before continuing Project Management courses. This one (1) year part time Certificate programme consists of eighteen (18) Credits as follows: Semester I ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing PRM 115 Management Concepts and Principles PRM 120 Fundamentals of Project Management Semester II PRM 125 Project Identification and Selection Strategies PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing COMM 201 Technical Report Writing and Presentation Skills 9 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT | 09 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEGREE SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT 82 This highly respected interdisciplinary programme is aimed at persons who possess experience in Security Administration and Management and wish to pursue a career in that field and draw on that experience to integrate their practice with the theory. JOHN SYLVESTER Head of Department/Senior Lecturer MED., MSc., M.A., BSc. The Bachelor’s Degree in Security Administration and Management offers students a sound foundation in legal procedures, criminal evidence, crime investigation and security risks detection. The areas of concentration offered in the degree will also introduce students to most aspects of loss prevention. As such, the programme will prepare students for the pursuit of security careers in the private and public sectors, equipping them to perform duties in private investigations and risk detection work. To meet the increasingly high demands for qualified security personnel for employment in police and prison services, the military and security firms, students will learn new strategies in the approach to security functions. These strategies will enhance students’ capacity in security administration and management, risk assessment and investigation as required in private law enforcement. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY There are five categories of eligible students for the Bachelor’s Degree in Security Administration and Management: • Students who have obtained five CXC/ GCE passes, with passes in English and Mathematics. These students will require four years (full time) or five years (part time) to complete the degree • Students with GCE A’ level and CAPE would be accepted into the programme and their passes at that level would be considered for exemption, where applicable • Students who have completed the Associate Degree in Security Administration and Management with a GPA of 2.5 or higher. These students will require two years (full time) or three years (part time) to complete the degree as part of a 2 plus 2 articulation arrangement with the College’s Associate Degree Programme. Students who have completed any other Associate Degree from CCLCS will also be eligible for entry and relevant exemptions granted, where applicable • Mature persons 25 years and older with considerable experience in Security Administration and Management. These persons will be interviewed by the Prior Learning Assessment Committee chaired by the Registrar, to determine at what point/ level of the programme they will be admitted. Exemptions, if any will also be determined by this Committee • Students who have acquired an Associate degree from other tertiary institutions. These persons will be interviewed by the Prior Learning Assessment Committee chaired by the Registrar, to determine at what point/ level of the programme they will be admitted. Exemptions, if any will also be determined by this Committee. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The graduate of the Bachelor’s Degree in Security Administration and Management will be able to: • Identify and categorize security related threats to the business environment • Examine the physical vulnerabilities of property and develop appropriate strategies to deter attacks by criminal elements • Supervise and manage medium to large size firms • Point out mitigation measures to stakeholders to reduce crime • Conduct risk assessment for personnel protection • Develop and write response plans to combat criminal activities. 09 | SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Science Degree (BSc) – 122 credits General Education Courses CAS 130 Caribbean Studies CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing ENM 142 Environmental Science 1 HUM 220 Ethics and Moral Values LOG 120 Critical Thinking MAT 100 Mathematics PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology RES 100 Research Methods and Statistics SPN 100 Introduction to Spanish 33 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration SAM 100 Introduction to Security SAM 110 Principles of Security Administration SAM 120 History of the Security Industry in T&T and the Caribbean SAM 210 Security Administration SAM 222 Crisis and Risk Management SAM 250 Physical Security and Planning SAM 270 Emergency Planning and Disaster Control SAM 280 Workplace Violence and Mediation SAM 209 Computer Crime SAM 291 Industrial Espionage SAM 292 Conflict Resolution SAM 300 Crisis Intervention SAM 310 Bio- Terrorism SAM 340 Leadership and Security Management SAM 350 Internship SAM 410 Legal Aspects of Security SAM 420 Forensic Investigation SAM 460 Research Paper 56 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 83 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT | 09 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT Bachelor of Science Degree (BSc) – 122 credits 84 Supporting Courses ACC 100 Introduction to Accounting CJT 160 Fundamentals of Criminal Investigation CJT 200 Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence LAW 100 Introduction to Civil and Criminal Law LAW 120 Civil and Criminal Law LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations LAW 310 Legal and Ethical Issues in Security Management OSH 120 Safety Management I SAM 400 Principles of Crime Prevention 27 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Electives: Select any three CJT 220 Criminology CJT 250 Principles of Crime Prevention ECN 100 Introduction to Economics HRM 300 Systems, Functions and Procedures I (Human Resource Management) LAW 320 Crime and Justice in the Caribbean PRM 135 Proposal Development and Costing SAM 271 Disaster Preparedness SAM 275 Principles of Security Information Systems SAM 300 Crisis Intervention SAM 430 Current Issues in Security Administration SAM 450 Monitoring and Evaluation of Security Programmes 9 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 09 | SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Science Degree in Security Administration & Management Day Programme (Full-Time) - 122 credits Year I CAS 130 ENG 110 MAT 100 SAM 100 SAM 110 Semester I Caribbean Studies Fundamentals of Writing Mathematics Introduction to Security Principles of Security Administration 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year III Semester I CJT 200 Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence SAM 222 Crisis and Risk Management SAM 291 Industrial Espionage SAM 310 Bio-Terrorism Elective 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 COM 101 HUM 220 LAW 100 SAM 120 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Fundamentals of Communication Ethics and Moral Values Introduction to Civil and Criminal Law History of the Security Industry in Trinidad & Tobago and the Caribbean 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 15 Credits 3 Year III LAW 310 SAM 250 SAM 292 SAM 340 SAM 350 Year II LAW 120 LBS 100 OSH 120 PSY 100 RES 100 Semester I Civil and Criminal Law Introduction to Industrial Relations Safety Management 1 Introduction to Psychology Research Methods and Statistics 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year IV Semester I SAM 270 Emergency Planning and Disaster Control SAM 400 Principles of Crime Prevention SAM 410 Legal Aspects of Security SAM 460 Research Project Elective 17 Credits 3 3 3 5 3 Year II CJT 160 ENM 142 LOG 120 SAM 210 SPN 100 Semester II Fundamentals of Criminal Investigation Environmental Science 1 Critical Thinking Security Administration Introduction to Spanish 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year IV Semester II ACC 100 Introduction to Accounting SAM 280 Workplace Violence and Mediation SAM 209 Computer Crime SAM 420 Forensic Investigation Elective 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Semester II Legal and Ethical Issues in Security Management Physical Security and Planning Conflict Resolution Leadership and Security Management Internship 3 3 3 3 3 85 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT | 09 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Bachelor of Science Degree in Security Administration & Management Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 122 credits 86 Year I CAS 130 ENG 110 SAM 100 Semester I Caribbean Studies Fundamentals of Writing Introduction to Security 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year I COM 101 LAW 100 MAT 100 SAM 110 Semester II Fundamentals of Communication Introduction to Civil and Criminal Law Mathematics Principles of Security Administration 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year II CIS 100 HUM 220 SAM 120 Semester I Introduction to Computer Information Systems Ethics and Moral Values History of the Security Industry in T&T and the Caribbean 9 Credits Year II LBS 100 PSY 100 LAW 120 RES 100 Semester II Introduction to Industrial Relations Introduction to Psychology Civil and Criminal Law Research Methods and Statistics 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year III CJT 160 OSH 120 SPN 100 Semester I Fundamentals of Criminal Investigation Safety Management 1 Introduction to Spanish 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year III ENM 142 LOG 120 SAM 210 Semester II Environmental Science 1 Critical Thinking Security Administration 9 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year IV Semester I ACC 100 Introduction to Accounting CJT 200 Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence SAM 222 Crisis and Risk Management SAM 291 Industrial Espionage Elective 15 Credits 3 Year IV SAM 292 SAM 310 LAW 310 SAM 250 Semester II Conflict Resolution Bio-Terrorism Legal and Ethical Issues in Security Management Physical Security and Planning 12 Credits 3 3 Year V Semester I SAM 410 Legal Aspects of Security SAM 420 Forensic Investigation OSH 400 Fire Protection and Prevention Elective 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Year V SAM 280 SAM 209 SAM 350 SAM 460 Semester II Workplace Violence and Mediation Computer Crime Internship Research Paper/Project 14 Credits 3 3 3 5 Year VI SAM 270 SAM 340 Semester I Emergency Planning and Disaster Control Leadership and Security Management Elective 3 9 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 ASSOCIATE OF SCIENCE DEGREE 09 | SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT The programme will provide a substantial foundation for the legal, management, behavioural and policy issues affecting security in its broadest sense. Among the areas the programme addresses are: • Personnel Security • Information Technology • Investigation • Protection of proprietary information • Law • Security Management • Crisis Management • Essentials of Risk Management • The Associate of Science Degree Programme in Security Administration and Management is designed to cover a period of two years full-time and three years of part-time study. However, students who receive exemptions or credits for work done previously in the field may be able to complete the degree in a shorter period of time. The degree consists of credits awarded in the pursuit of courses specific to the discipline as well as college credits based on general education courses and electives. The Associate of Science Degree in Security Administration and Management requires a total of sixty-eight (68) credits for completion. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES The Graduate of this programme will: • be prepared to reduce an organization’s exposure to risk • be able to communicate with practitioners in the related professions • have the leadership and management knowledge necessary to operate security organizations and departments well into the twenty-first century • be able to manage the human resource of his/her organization • be able to understand and assess client needs • be able to function at the senior management level in an advisory capacity. ADMISSIONS ELIGIBILITY Those who fulfill the following conditions will be eligible for admission into the Associate of Science degree in Security Administration and Management: • Students who possess five or more CXC/ GCE passes including English and Mathematics with a G.P.A of 2.0 or above or • Students who have successfully completed the CCLCS Diploma in Security Administration and Management or • Mature students (25 years and older) who have at least a GPA of 3.0 and have worked within a Security environment for at least five years with 3 CXC or GCE ‘O’level passes including English and Mathematics. 87 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT | 09 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT Associate of Science Degree (AS) – 68 credits 88 General Education Courses ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication LOG 120 Critical Thinking CAS 130 Caribbean Studies MAT 100 Mathematics CIS 100 Introduction to Computer Information Systems PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology RES 100 Research Methods & Statistics 24 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Programme Concentration CJT 200 Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence HRM 210 Organizational Behaviour and Development LAW 120 Civil/Criminal Law SAM 120 History of the security Industry in Trinidad & Tobago and the Caribbean SAM 100 Introduction to Security SAM 222 Crisis & Risk Management SAM 250 Physical Security Planning SAM 260 Research Paper SAM 255 Internship SAM 291 Industrial Espionage SAM 292 Conflict Resolution 35 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 3 3 3 09 | SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT Associate of Science Degree (AS) – 68 credits Supporting Course LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations 3 Credits 3 Electives: Select any TWO (one from each group) 6 Credits Group A CJT 220 SAM 270 SAM 280 SAM 290 Criminology Emergency Planning and Disaster Control Workplace Violence/ Mediation and Conflict Resolution Computer Crime and Industrial Espionage 3 3 3 3 Group B ECN 100 HRM 300 SOC 100 Introduction to Economics Systems, Functions and Procedures I Introduction to Sociology 3 3 3 89 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT | 09 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Science Degree in Security Administration & Management Day Programme (Full-Time) - 68 credits 90 Year I COM 101 SAM 100 MAT 100 LAW 120 ENG 110 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Introduction to Security Mathematics Civil/Criminal Law Fundamentals of Writing 15 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 LOG 120 CAS 130 RES 100 SAM 120 SAM 255 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Critical Thinking Caribbean Studies Research Methods & Statistics History of the security Industry in Trinidad & Tobago and the Caribbean Internship 18 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year II Semester I HRM 210 Organizational Behaviour and Development SAM 250 Physical Security Planning SAM 291 Industrial Espionage SAM 292 Conflict Resolution Elective 15 Credits Year II Semester II CJT 200 Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations SAM 260 Research Paper PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology SAM 222 Crisis & Risk Management Elective 20 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 5 3 3 3 PROGRAMME OF STUDY Associate of Science Degree in Security Administration & Management Evening Programme (Part-Time) - 68 credits Year I COM 101 SAM 100 ENG 110 Semester I Fundamentals of Communication Introduction to Security Fundamentals of Writing 9 Credits 3 3 3 Year I CIS 100 MAT 100 LAW 120 Semester II Introduction to Computer Information Systems Mathematics Civil/Criminal Law 9 Credits Year II LOG 120 CAS 130 RES 100 SAM 120 Semester I Critical Thinking Caribbean Studies Research Methods & Statistics History of the security Industry in Trinidad & Tobago and the Caribbean 12 Credits 3 3 3 Year II SAM 291 SAM 292 HRM 210 SAM 255 Semester II Industrial Espionage Conflict Resolution Organizational Behaviour and Development Internship* 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Year III Semester I SAM 250 Physical Security Planning PSY 100 Introduction to Psychology SAM 260 Research Paper Elective 14 Credits 3 3 5 3 Year III CJT 200 LBS 100 SAM 222 12 Credits Semester II Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence Introduction to Industrial Relations Crisis & Risk Management Elective 3 3 3 3 09 | SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT DIPLOMA IN SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT CERTIFICATE IN SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT This one-year part-time diploma programme is designed for those persons who have completed the Certificate in Security Administration and Management and for those individuals who hold positions at the administrative level in the protective services whose knowledge and experience equate with the outcomes of the certificate programme. The one-year part-time Certificate in Security Administration and Management is designed for those persons who have completed the 10-Saturday Introductory Programme in Security Administration and Management. Supervisory and management personnel in the protective services would also be considered for entry based on their knowledge and experience in security administration and management. Personnel in other branches of the protective service are also welcome. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES Students completing the Diploma in Security Administration and Management would have gained the competencies for the following: • Participate in the critical problems of loss prevention • Interpret and apply the laws related to private security protection • Conduct risk assessment and make recommendation • Assist in the development of loss prevention planning • Assess risk levels to safety and security of facilities • Recommend physical security measures for employers • PROGRAMME OUTCOMES Students completing the Certificate in Security Administration and Management would have gained competence for the following: • Identify security vulnerability and risks • Assist in coordination of emergency operations • Protect evidence on stakeholders’ premises Conduct in-house investigation and produce written reports • Assist in the deterrence of in-house crimes • Advise employers on the requirement of the OSH Act • Interact with law enforcement on issues affecting employers • Implement strategies in loss prevention plans • Conduct security audits and estimate risk factors to employers. DIPLOMA 24 Credits Required Courses Semester I LAW 120 Civil/Criminal Law SAM 210 Security Administration SOC 100 Introduction to Sociology ENG 110 Fundamentals of Writing Semester 2 LBS 100 CJT 220 SAM 222 SAM 240 Introduction to Industrial Relations Criminology Crisis & Risk Management Security Operational Management Total credits required Credits 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 CERTIFICATE 21 Credits Required Courses Semester I LAW 100 Introduction to Civil and Criminal Law COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication SAM 100 Introduction to Security 3 3 3 Semester 2 OSH 120 Safety Management I LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations CJT 160 Fundamentals of Criminal Investigation SAM 110 Principles of Security Administration Total credits required 3 3 3 3 21 Credits 24 91 SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT | 09 DIPLOMA IN EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT This one-year part-time Diploma Programme in Emergency Management is open to persons who hold the Certificate in Emergency Management as well as practitioners in other fields who have knowledge and experience that is equated with the outcomes of the Certificate in Emergency Management. PROGRAMME OUTCOMES Students completing the Diploma in Emergency Management would have gained the competence for the following: • Represent communities and agencies in discussions on disaster preparedness • Develop and designed disaster mitigation strategies • Advise agencies and communities on risk reduction plans • Participate in multi-agency coordination and management of emergency operations during disasters. • Advise stakeholders on disaster impact expectations to aid their decision-making • Develop and design disaster plans to minimize the threats of terrorism and other man made, technological and natural disasters. DIPLOMA 24 Credits 92 Required Courses Semester I 12 credits COM 221 Incident Report Writing EMM 225 Hazard Mitigation in Disaster Management HRM 210 Organizational Behaviour & Development EMM 150 Introduction to Terrorism Credits Semester II EMM 290 Exercise Design LOG 120 Critical Thinking EMM 255 Introduction to Technology in Crisis & Emergency Management EMM 260 Community Emergency Response Team 12 credits 3 3 Total Credits Required 24 3 3 3 3 3 3 09 | SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT CERTIFICATE IN EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT PROGRAMME OUTCOMES This one-year part-time Certificate Programme in Emergency Management is open to persons who have completed the Introductory Course in Crisis and Emergency Management and to others individuals who have had three years training and background experience in related fields. These individuals would include the following: Upon completion of this Certificate Programme, students will be able to do the following: • • • • • • Conduct hazard analysis • Develop and write disaster plans Risk managers in the private and public sectors as well as those who will be responsible for hazards assessments, OSHA compliance, and emergency response (volunteer agencies included) • Interpret and apply the laws and polices in emergency management • Coordinate emergency management operations • Prepare for and conduct disaster planning meetings Emergency management professionals who will be relied upon to protect the public in the event of major emergencies. This includes professional and auxiliary firefighters, police officers, emergency medical service workers, and private industry safety managers • Advise on the best practices in emergency management • Conduct pre-planning activities for community reliance • Implement the Phases of Emergency Management to disaster management needs • Implement the Principles of Emergency Management in emergencies • Apply the National Incident Management System (NIMS) to disaster management • Advise on the operation of Emergency Organizing Committees (EOGs) Governmental and industrial emergency management planners who must prepare for potential emergencies by designing procedures, purchasing equipment as in some cases where they may have to predict possible disasters Aspiring emergency management professionals seeking a broad-based education in the procedures for coping with daily emergencies and major disasters Emergency management professionals who need additional skills to prepare for management opportunities. CERTIFICATE Required Courses Semester I COM 101 Fundamentals of Communication EMM 100 Introduction to Emergency Management EMM 110 Emergency Operation Policies and Laws EMM 120 Response Agency Preparedness 24 Credits Credits 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Semester 2 EMM 200 Public Preparedness and Awareness EMM 210 Incident Command System EMM 220 Resource Management and Recovery EMM 230 Leadership in Disaster Preparedness 12 Credits 3 3 3 3 Total Credits Required 24 93 94 10 DEPARTMENT OF CONTINUING STUDIES DEPARTMENT OF CONTINUING STUDIES DEPARTMENT OF CONTINUING STUDIES | 10 The Department of Continuing Studies falls under the purview of the Division of Academic Affairs. The Division is headed by the Deputy Director Academic Affairs. The Continuing Studies Department (CSD) oversees the College’s evening programmes at the Valsayn Campus, Pleasantville, El Dorado and Metal Industries Company Satellite Centres. The department also has a functional relationship with its Tobago Campus and ensures that all services, operational, programme and teaching material are in sync with all the other centres. The establishment of this department is also a recognition of the validity of life long learning in a globalized world. All programmes of the College are also offered on evenings and weekends and cater primarily to 96 working adults who are seeking to increase their chances for upward mobility within the workplace or a change of career. The Department functions as the primary coordinating unit for part-time students and faculty and the other departments of the College. The Continuing Studies Department seeks to enhance the experience and success of our students by providing advice, attending to queries raised and utilizing problem-solving measures to alleviate day-to-day issues and concerns. The department liaises with Lecturers to attend to queries and concerns, and provides information to aid their effectiveness. Centre Supervisors/Coordinators monitor and oversee the efficient operations of the classes. 10 | DEPARTMENT OF CONTINUING STUDIES TEN-SATURDAYS INTRODUCTORY COURSES Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies offers outreach courses for a TenSaturdays period, each session being for a fourhour period. These courses are aimed at both specific audiences and the general population. Many of these courses are pre-requisite for other courses and programmes, especially in cases where the participant may not have the traditional qualification to enter into a certificate programme. Most of these courses are of an introductory nature and, as such, they are required before one can move on to a more advanced course in that area. They do not, however, guarantee admission into the more advanced courses. These courses give an overview of the subject area being taught. These courses are generally offered at three venues - Valsayn, San Fernando and Tobago. Following is the list of Ten-Saturdays (Outreach) courses offered by the College: 1. Computer Operations and Applications 2. Co-operative Management 3. Crisis and Emergency Management 4. Environmental Management 5. Events Management 6. Facilities/Building Management 7. Fire Protection Management 8. Human Resource Management 9. Industrial Relations 10. Job Evaluation, Classification & Compensation Systems 11. Marketing 12. Occupational Safety and Health 13. Project Management 14. Public Relations 15. Security Administration and Management 16. Supervisory Management 17. Securities & Investment 97 DEPARTMENT OF CONTINUING STUDIES | 10 SPECIALISED TRAINING The Specialised Training Unit continues to construct programmes that are designed to match the needs of all our stakeholders who desire training and career development for their employees/ members. This Unit falls under the purview of the Director’s Office and has been mandated to analyze the educational and developmental needs of the College’s stakeholders and plan, implement and evaluate specific programmes and/or courses that seek to satisfy their needs. The Specialised Training Department focuses on the businesses, industries, government ministries and departments, credit unions, trade unions, nongovernmental organizations and other public and private institutions across Trinidad and Tobago and the region. The training programmes are tailored to suit the needs of the organization and are conducted within a time frame that fits into the organization’s operations. The College also provides stakeholders with an option as it relates to the venue. Once accommodation is available in-house, the programme would be conducted on site; however, the Valsayn Campus is equipped to provide participants with an enjoyable educational experience. This Unit has over the years gained valuable experience in conducting programmes of different styles for a variety of entities such as the Ministry of Labour and Small and Micro Enterprise 98 Development, Caribbean Safety Products, the Immigration Division of the Ministry of National Security and the Customs and Excise Division of Ministry of Finance, just to mention a few. Working with local and foreign consultants, as well as using trained and qualified in-house resources in specific areas, the Specialised Training Unit has successfully completed programmes in ‘Leadership Training for Trade Unions’, ‘Project Management in the Airline Industry’, ‘The Art of Communicating to the Media’, and other specially designed programmes in Security Administration, Environmental Management, Occupational, Safety and Health and much more. The Unit is extremely proud of its efforts in 2004, when a knowledgeable team of safety practitioners and legal experts journeyed all over Trinidad and Tobago educating various organizations, both private and public sector, in the ‘Understanding of the Occupational Safety and Health Act’. In 2008 the Specialised Training Unit has already conducted a seminar for Trade Unions and their relevance in the Changing Economic Environment and a training workshop for Labour Officers in the Ministry of Labour and Small and Micro Enterprise Development. The Board of Governors and the Executive Management of the College believe that the Specialised Training Unit will provide stakeholders nationally and regionally with an opportunity to train and develop its human resource as they position themselves to confront the global challenges that lie ahead. 11 TOBAGO CAMPUS CIPRIANI TOBAGO CAMPUS 100 The Cipriani College of Labour and Co-operative Studies (CCLCS) is proud to be an active participant in the tertiary education sector in Tobago. The College has been physically present in Tobago since 1999, offering a number of programmes from Certificate to the Associate Degree level. The student population has been steadily increasing every academic year since 1999 and as a result, the Board of Governors, together with the Executive Management Team of the College have been meeting with the Tobago House of Assembly in an effort to establish a new home for the Tobago Campus with more spacious accommodations. DIPLOMAS At present, the Tobago Campus is located at the Tobago Glass Supplies Building, Rousseau Trace, Spring Garden, Scarborough. The administrative operations of the campus are between the hours 12 noon and 8:30pm, while classes are held from 5:30pm to 8:30pm. Apart from the spacious classrooms, the Tobago Campus is outfitted with a computer lab and an up-to-date library. This facility has been be extended to include a lunch/ staff room, a sick bay, upgraded washrooms and air-conditioned classrooms. This facility supports the College’s programme offerings, which are as follows: ASSOCIATE DEGREES • Associate of Science Degree in Occupational Safety and Health • Diploma in Environmental Management • Diploma in Human Resource Management • Diploma in Occupational Safety and Health • Diploma in Project Management CERTIFICATES • Certificate in Environmental Management • Certificate in Human Resource Management • Certificate in Occupational, Safety and Health • Certificate in Security Administration and Management The Ten-Saturdays/Introductory Courses are offered every February, May and October in all the previously mentioned areas as well as: - Computer Operations and Applications - Crisis and Emergency Management - Events Management - Marketing and Public Relations These courses are pre-requisite for other courses and programmes, especially in cases where the participant may not have traditional matriculation for entry into a programme at a higher level. 12 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS PREFIX 102 PREFIX TITLE PREFIX PREFIX TITLE ACCAccounting BIOBiology BUS Business Studies CAS Caribbean Studies CHMChemistry CIS Computer Information Systems CJT Criminal Justice COMCommunication COS Co-operative Studies ECNEconomics EMM Emergency Management ENGEnglish ENM Environmental Management HRM Human Resource Management HUM Humanities LAWLaw LB Labour Studies MARMarketing MGTManagement MATMathematics OSH Occupational Safety and Health PBR Public Relations PLS Political Science PRM Project Management PSYPsychology RESResearch SAM Security Administration and Management SOCSociology SPNSpanish ACCOUNTING (ACC) ACC 100: Introduction to Accounting - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to the principles of financial accounting with focus on the Nature of Business and Accounting; analysis and recording of business transactions; adjusting entries, completing the accounting cycle, preparation of end-of-period spreadsheet, depreciation, inventory valuation and accounting for a merchandising business. ACC 220: Credit Union Accounting - 3 CREDITS Financial accounting for credit unions will be the main focus of this course. Students will be able to process and record transactions, which occur in a credit union. Students will also be able to prepare the final accounts of credit unions. The course also looks at the interpretation of the Pearls ratios and their usefulness as financial health indicators. ACC 210: Principles of Auditing - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the students to the principles and practices of modern auditing theory and practice. Candidates are presented with topics which include the Role of the Auditor, Professional Standards, Professional Ethics, Audit Working Papers, Internal, Operational and Compliance Auditing with Research and Discussion Cases which acquaint students with the process of researching realistic auditing problems. Pre-requisite ACC 100 BIOLOGY (BIO) BIO 100: Anatomy and Physiology - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the student to the study of human anatomy/physiology and its homeostatic principles. It emphasizes the ways in which the human body adapts to external changes and the problems that attend extreme changes in various work environments. 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS BUSINESS STUDIES (BUS) BUS 300: Principles of Entrepreneurship - 3 CREDITS This course will provide students with a general understanding of entrepreneurship and the characters of the entrepreneur. Students will also gain insight into entrepreneurship in Trinidad and Tobago; the Caribbean and the policies that have been implemented locally and regionally. CARIBBEAN STUDIES (CAS) CAS 130: Caribbean Studies - 3 CREDITS This Caribbean Studies course will focus on the skills of writing, research and critical analysis as students explore common geographical, historical, social, cultural, political and economic factors, which have shaped the development of the different countries of the Caribbean region. CHEMISTRY (CHM) CHM100: Introduction to Chemistry - 3 CREDITS The rationale for an Introduction to Chemistry component in a course on Occupational Safety and Health is to provide the student with an awareness and basic knowledge of chemistry in order to understand and appreciate the role and relevance of chemistry in Safety and Occupational Health. The Introduction to Chemistry course is also meant to provide a basic and comprehensive knowledge of chemistry as an academic discipline of its own. COMMUNICATION (COM) COM 101: Fundamentals of Communication - 3 CREDITS This course covers both verbal and non-verbal communication. The nature, principles and tools of communication are the major areas dealt with. Business letters, reports and meetings constitute part of the contents of the course. In addition, the media, the interview, presentation and planning are examined under the tools of communication. COM 201: Technical Report Writing & Presentation Skills - 3 CREDITS This Course is designed through communication, to evaluate and develop the articulation of the students’ potential and ability to develop and present information and project data within an environment for managers of projects and other specialised activities. Candidates will be trained to identify and select preparation and delivery strategies appropriate for reports of engineering, industrial, commercial, political, technological and social development environments. CO-OPERATIVE STUDIES (COS) COS 110: Co-operative Law and Principles - 3 CREDITS This course deals with the basic principles and philosophy of the Cooperative movement. The course also examines Co-operative legislation and the administration of that legislation. Other legal aspects of Cooperatives are dealt with, such as registration, membership and their duties and privileges and the settlement of disputes. Co-operative society regulations and bye-laws form part of this course as well. COM 221: Incident Report Writing - 3 CREDITS To help meet this need for professionals who can empathize with people as well as manage information. Writing in emergency management, provides students with realistic problems in communication so that, on the job, the student can report technical information clearly and persuasively. COS 120: Co-operative Organization and Operations - 3 CREDITS An examination of the structure and functions of Co-operatives together with the types of business conducted by them. The course also explores the various parts that go to make up a co-operative and how those parts function together. Co-operatives and their role within the economy are also looked at. COM 250: Effective Communication - 3 CREDITS This course will take the participants through techniques of effective speaking and writing, and the use of information technology, which facilitate effective presentation in specific areas as they relate to industrial relations practice. COMPUTER INFORMATION SYSTEMS (CIS) CIS 100: Introduction to Computer Information Systems - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the student to the theoretical and practical foundations of information technology. Major topics include computer components, storage, input and output technologies and system software. Students will also be instructed in Windows operating system and the use of word processing package, spreadsheet and database packages. COS 130: History and Development of the Co-operative Movement - 3 CREDITS This course explores evolution of the co-operatives philosophy and the various pioneers that have contributed to the co-operatives movement. The historical development of co-operatives in selected developed and developing countries will also be given significant focus. COS 150: Credit Union Management - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the student to the major principles and practices of credit union management. A major focus will be the examining of the role, function and responsibilities of the Board of Directors and other committees; and how they interact to perform as the management team. The role of the professional manager in an organization built on the principle of volunteerism will also be examined. 103 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 COS 170: Co-operative Organization and Operations - 3 CREDITS This course will look at the development of the credit union movement in the Caribbean. Particular attention will be paid to factors contributing to both decline and also growth. The course also entails an investigation into trends in the credit union movement and projections for the future. COS 200: Communication and Extension I - 3 CREDITS This course examines the extension concept, philosophy and process of Co-operatives. It also looks at the concept and principles of community development. The nature, principles, history and techniques of Adult learning are also covered in this course. COS 202: Communication and Extension II - 3 CREDITS This course is a sequel to COS 200. It focuses on the management and administration of Adult/Extension programme. It looks at topics such as course planning and design, leadership, group interaction, teaching techniques, audio-visual aids and public relations. COS 220: Business Law and Credit Unions - 3 CREDITS The main objective of this course is to introduce students to ethical values, principles, philosophies, business practices and applicable legislation incidental to the operations of Credit Union and Co-operatives in Trinidad and Tobago. COS 380: Ethics in Decision Making in Co-operatives - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the students to the different moral theories as well as the relevance in applying ethical principles in organizational decision making. The course will also provide participants with an indepth understanding of guiding principles which they should possess to manage a co-operative. Finally, the challenges that decision makers experience in acting 104 COS 410: CJT 200: Co-operative Approach to Criminal and Civil Procedure and Evidence Human Resource Management - 3 CREDITS - 3 CREDITS The course will prepare participants to manage in the context of membership based organizations and a people-centered approach to business as compared to a business that is driven by profit and views human resources as a tool to increasing profitability ethically will also be explored. This course is intended to provide students with the planning and analytical tools that are necessary to manage crises. An in-depth approach to risk assessment to identify areas vulnerable to hazards and the costs of losses to businesses and industry will be taught to students taking this course. Students will also be guided to explore the programmes that have been developed for the management of the risks that impact facilities and their environments. The understanding of the concepts and theories of risk management are introduced to allow students to attain the security professionalism to develop plans to protect organizations from problems they face in security operations. COS 420: Current Issues in the Co-operative Movement - 3 CREDITS This course will explore the numerous global, regional and national issues that affect the Co-operative movement. Co-operatives like any other business types are affected by a variety of areas but also have some issues that are unique to the movement, which will be explored. Students will also gain a detailed understanding of the global, regional and national cooperative structure and the relevance of each of these parts and how they support the overall system. CRIMINAL JUSTICE (CJT) CJT 120: Criminal Law - 3 CREDITS This course examines the nature of criminal law, the general principles of liability, defences, arrest and search, specific offences like assaults and woundings, larceny, breaking offences and praedial larceny and other offences as contained in several acts such as the Dangerous Drugs Act No 38/91, the Trespass Act, Firearms Act, Trade Dispute and Protection of Property and the Summary Offences Act. CJT 160: Fundamentals of Criminal Investigation - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to train the student in investigative procedures and techniques. Students are exposed to a conceptual, analytical and practical approach with the aim of improving their critical thinking and skill investigation. CJT 220: Criminology - 3 CREDITS This course will assist the student in understanding issues relating to the definition, measurement, portrayal, and control of the phenomenon we call crime. It will also look at the theories and the various explanations of crime which are predominantly based on societal influences. ECONOMICS (ECN) ECN 100: Introduction to Economics - 3 CREDITS This course provides the student with a thorough understanding of the basic principles of economics. Topics include the nature of economics, the price system, markets and pricing, national income and fiscal policy, money and banking, unemployment and inflation, and international trade. ECN 120: Introduction to Labour Economics - 3 CREDITS This course seeks to introduce students to the basic concepts in economics. It covers topics such as demand and supply, competition policy, factor markets, analysis and measurements of labour force statistics, wage determination and trade unionism. The course also looks at some contemporary issues in labour 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS economics such as government policy and the effect of globalization on the labour market. ECN 200: The Economy of the Caribbean Region - 3 CREDITS The sub-title of the course is - A Development Perspective. The focus is on the growth and development performance of the Anglophone states of the Caribbean region against the background of the discourse on the economics of developing countries. The examination starts with perspectives on economic development: how is development to be defined; the problem of measuring development; and the critical factors in development as identified and analyzed in the literature on the subject. A survey of development theory in general is followed by an outline of the theory particularly with reference to the Caribbean economy. This leads to an exploration of the problems facing these economies and the strategies geared to the solution of these problems. Key sectors and problem areas of the Caribbean economy are examined in some detail. Special attention is given to petroleum and natural gas sector in Trinidad and Tobago. The analysis of the petroleum and natural gas sector highlights the implications of a development thrust driven by a depletable natural resource. The pre-requisites for this course are Level I courses in Economics, Mathematics and Statistics, or courses of equivalent content. ECN 210: Interpreting Economic and Financial Data - 3 CREDITS This course provides students with an understanding of the basic tools, concepts and techniques for (a) assessing trends in key economic variables and phenomena, such as, national income, inflation, unemployment, productivity, real wages and earnings and profits; and (b) interpreting and evaluating business data as presented in financial and accounting statements of business and state enterprises. are applied to the examination of a particular kind of market, i.e. the labour market. This examination is done with appropriate modifications of received theory to take account of the characteristics of the labour markets and labour market institutions of developing countries such as those of the Caribbean. Analysis of pay determination under market and institutional forces leads to consideration of various versions of national wage policy. The key aspects of manpower policy are analyzed in some detail, including human capital theory, the economics of education and the contribution to economic growth of qualitative development of human resources. Major related issues, including unemployment, income inequality and poverty are also analyzed. EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (EMM) EMM 100: Introduction to Emergency Management - 3 CREDITS This course explores the issues relevant to emergency management and focuses on the four elements that are necessary for the effective management of emergencies, whether man made or technological. The course is intended to give students a thorough understanding of these four elements. EMM 110: Emergency Operation Policies and Laws - 3 CREDITS The primary goal of this course is to reintroduce students and active respondents to operational policies and the laws that provide for the contingencies of their roles in emergency management. This course will provide students with the need to know about the Standard Operation Guides (SOGs) for police, fire, EMS and other emergency workers who are required to respond to emergencies and disasters. Their protection under the law from civil liability and from prosecution for use of private, public properties and resources to deal with eventualities are also addressed. EMM 120: ECN 220: Labour Economics - 3 CREDITS In this course, basic principles of economic theory Response Agency Preparedness - 3 CREDITS This course exposes students to the strategies and practices which response agencies deploy in emergency response. Practices associated with drill frequencies, equipment testing, Emergency Support Function (ESF) radio communication and interoperability, interagency and resource coordination, method of mission requests, mutual aid and manpower use are studied as pro-active pre-planning measures to be developed in Standard Operation Guides (SOGs) of the agency’s emergency management plans. EMM 150: Introduction to Terrorism - 3 CREDITS This course focuses students’ attention on the activities that terrorists who operate as individuals or groups carry out to achieve radical changes nationally and around the world. Topics to be covered in the course include the identification of terrorist groups, who are willing to kill masses of people or destroy state or private property, by the use of explosives, weapons, and other violent means. Students will conduct research that will provide them with the most contemporary measures that governments must use to counter terrorism. This course will give students a clear understanding of what terrorism really is in the world today. EMM 200: Public Preparedness and Awareness - 3 CREDITS This course identifies the strategies and practices used around the world to make the public more alert and responsive to their own care and well being for the first few hours of an emergency before quantitative and qualitative assistance are brought to bear upon the emergency by state responders. Students will focus on public outreach programmes, method of public education and training and evaluating the benefits of self-taught brochures and pamphlets. EMM 205: Current Trends in Emergency Management - 3 CREDITS This course provides students with an in-depth knowledge of Emergency Management and the philosophy of emergency planning for community, business and industry. Students will get a management perspective on issues and concerns for the constraints to effective emergency management that responders 105 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 must think about today. The course allows students to explore the levels of emergency management planning that in current undertaken locally and in the Caribbean region in order that they may determine the emphasis that the private, commercial, industrial, state and local governments place on emergency and/or disaster and management to save lives and protect property in case disaster strike. EMM 210: Incident Command System - 3 CREDITS This course explores the efficiency of the Incident Command System (ICS) in emergency management and its methods of deployment at emergencies and disasters. All the attributes of the ICS involving command, operation, planning, logistics and finance are covered along with new additions to the System such as human services. EMM 220: Resource Management and Recovery - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on the issues of managing resources needed for the recovery stage in emergency management. The management of food, shelter, evacuation, mass care, alternative housing and business continuity will be analyzed to give students a clear understanding of their importance to the recovery effort. EMM 225: Hazard Mitigation Disaster Management - 3 CREDITS This course provides the definitions for natural, manmade and technological hazard mitigation and their role in disaster management. Students will analyze past and current government and private sector programmes. They will also examine new approaches structural verses non-structural actions; roles of the natural environment in mitigating natural hazards and prevention/preparedness for reducing the impacts of future disastrous events. EMM 230: Leadership in Disaster Preparedness - 3 CREDITS 106 This course explores the strategies and practices to be deployed from leadership positions in disaster preparedness. The course introduces contingent readiness in case of emergencies. Students are taught the conceptual approaches to preparedness that include training and education, tabletop exercises, functional and full scale drills, public outreach education, planning, facilitation, coordinated management, workplace safety and evacuation so as to give them an understanding of their impact on disaster preparedness. actions. The course describes information management procedures based on the nature of crises, emergencies, and disasters. Simulation and emerging hardware capabilities such as remote sensing, high performance computing, communications and GPS, GIS, GDSS, DSS, EIS are explored. EMM 260: Community Emergency Response Team - 3 CREDITS EMM 240: Politics and Policy in Emergency Management - 3 CREDITS This course deals with issues associated with the politics and disasters and primarily what politics has to do with emergency management. Students will be made aware of the political impacts that disasters have on a representative democracy. The course allows students to explore the roles that elected officials play in all phases of emergency management, their concerns about disasters and the manner in which they should undertake to prepare for and respond to disasters. Students will seek to find out whether disaster policies are the same or different from other government policies and what criteria are used to decide on matters of disaster mitigation and recovery. An examination will be conducted on how governments develop disaster policies and implement them as well as how state and local legislation affect emergency management. This course provides instructions to emergency coordinators in the private sector or state and local government sectors to train volunteers in communities who are likely to respond to major emergencies or disasters when the formal emergency services are not able to respond immediately to and sufficiently support communities needs. Students must complete nine topics that include disaster preparedness, fire, medical operations, search and rescue, organization, communications, operations, personal readiness and equipment, and terrorism recognition that Community Emergency Response Team (CERT) members in communities must learn before they are allowed to safely respond to emergencies or disasters. The instructions in the course stress the importance for CERT members not to consider themselves as an alternative to the formal response agencies. EMM 275 : Disaster Preparedness Planning - 3 CREDITS EMM 255: Information Technology for Crisis and Emergency Management - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to the application of appropriate information technology to crisis and emergency management as a national and international priority. Students will be instructed to focus on the unique nature of management and decision making in the high velocity, complex, and unstructured environment created by crises and disasters. This course also provides for students to begin thinking as emergency and crisis managers to take actions and make critical decisions, under great stress and time pressure, with incomplete and contradictory information. Students will learn about the effective management of information, which is critical to the success of these decisions and This course deals with emergency preparedness for communities with a focus on hazard identification to minimise human and economic losses. Act No. 1 of 2004 requirements for organizations’ emergency, evacuation and fire prevention planning is also examined. The course also enables students to advise stakeholders on impact of man-made, natural and technological disasters. EMM 290: Exercise Design - 3 CREDITS This course teaches students how to lead and influence others, particularly formal and informal responders in emergency management situations, by increasing their capacity and skills in conflict management, 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS group dynamics and leadership abilities. Students will plan and develop exercise programmes to conduct tabletops, functional and full-scale drills and exercise within facilities and communities. Planning for the development of drills and exercises will also include areas of consideration by students for packaging and advertising the drills and exercises before they are actually conducted by emergency co-ordinators in the private sectors and at the state and local levels of government. This course addresses amongst other issues land degradation and explores the increasing challenge to find productive land in the context of an increasing population. ENM 131: ENG 110: Fundamentals of Writing - 3 CREDITS ENM 136: This course is designed for students who need instruction in grammar and punctuation, sentence construction, paragraph development and essay writing. It will also attempt to develop good habits of Expository Writing - informative writing which could be found in hand books and non-fiction articles in magazines and scientific journals. The Expository Skills of Definition, Comparison and Contrast, Cause and Effect, Process/ Analysis will be examined in detail. Environmental and Occupational Sociology ENM 100: Introduction to Management - Non-Credit Course Environmental This course provides students with a basic understanding of the concepts and applications of Environmental Management. It covers topics such as environmental principles and hazards, the value of environmental resources, the legal framework of environmental management and the principles of environmental management. ENM 121: Principles and Theories of Environmental Management - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to facilitate an analysis and synthesis of the theories and principles of environmental management and an exploration of some practical tools and methods employed therein. ENM 126: Land Degradation and Rehabilitation/Conservation - 3 CREDITS Environmental Management Systems Environmental Audits - 3 CREDITS and This course is designed to translate the theoretical to practical applications as the commitment to sound environmental practices evolve. Environmental Issues - 3 CREDITS This course identifies and explores contemporary environmental concerns and highlights those that are relevant to the Caribbean region. ENGLISH (ENG) ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT (ENM) ENM 151: - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to create an appreciation of diverse views and culture with respect to environmental values and to appreciate their significance in the quest for sound environmental management practices ENM 142: Environmental Science I - 3 CREDITS Environmental Science 1 is an introduction to the fundamentals of the physical and natural science and its facilitation of biological processes that constitutes the living earth. It is fundamental to environmental understanding and by extension management. ENM 143: Environmental Science II - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the dynamism of the biosphere and the interactions and evolutionary processes that are critical to the interdependence of species that inhabit the earth. ENM 148: Alternate Sources of Energy - 3 CREDITS This course is specific to energy needs and evaluates the traditional fossil fuels and takes on the critical challenge of alternate options in contemporary and future development. ENM 160: Environmental Law - 3 CREDITS Environmental Law seeks to explore the development of law from common law as it applies to civil society and to target, in a general way, torts and applications that are relevant to environmental issues. The course will also explore the Environmental Management Act and other pertinent legislations in Trinidad and Tobago. ENM 200: Caribbean Environments’ Profiles & Problems - 3 CREDITS This course explores the challenges of small islands states in the context of globalization and the imperative of equity and quality of life to the survival of small island states. ENM 210: Impact Assessment and Evaluation - 3 CREDITS This course adopts a cost-benefit analysis approach in assessing and evaluating the impact on the environment. It also exposes the student to geographical information systems approach, land suitability and landscape analysis approaches and audits site assessment approaches. ENM 215 : Caribbean Geologic & Geomorphic Environmental Dynamics - 3 CREDITS The earth’s dynamic systems are continuously bringing about changes to our geologic and geomorphic topographical environments. The Caribbean Basin Region is no exception to these impacts. In coastal regions that are extremely fragile, these impacts can be devastating. This course addresses these concerns as an outcome management need of environmental management. 107 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 ENM 218 ENM 235: Management of Tropical Marine Environments Environmental Investigative & Impact Assessment Techniques - 3 CREDITS ENM 218 explores the physical and biological processes necessary for the understanding of the Tropical Marine Environment. It analyses the causes of degradation and deterioration of this natural resource. In doing so it underscores the interaction of demographic, economic, social and political factors in determining how the resource is used and managed. It offers options for mitigation and conservation in a range of unique Tropical Marine Environments. By advancing sound principles and practices of management it challenges and encourages students to be better stewards of the Tropical Marine Environment. ENM 221: Environmental Risk Assessment - 3 CREDITS Ecological risk assessment focuses on the identification and analysis of environmental risk. It is essential to stewardship in economic development as it provides a critical understanding of and a platform for effective management strategies toward the goal of quality life. ENM 226: Biodiversity and Conservation - 3 CREDITS Course Description: Conservation of biodiversity is necessary as the cascading effects of species endangerment throughout the ecosystem create threats to its healthy functions. This course creates opportunities to address this positively by exploring options in conservation. ENM 230: Pollution Control Management - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to create awareness of critical pollution issues and introduces and evaluates methods and tools available for the prevention and control of pollution. ENM 231: Environmental Impact Assessment - 3 CREDITS Environmental impact assessment is geared toward creating a fundamental understanding of the EIA process. It equips the student with the necessary skills to be an effective practitioner of EIA. 108 Environmental quality problems, their root causes and resource use relationships are identified in this course. Techniques to so do are assessed and appropriate investigative strategies in the context of field sampling strategies are studied. ENM 240: Legal and Legislative Framework of Environmental Management - 3 CREDITS This course applies the common law and Caribbean Environmental Legislation as a management tool with a view to abating industrial and domestic practices which impact negatively on our environment. ENM 245: Economics of Coastal Zone Resource Use - 3 CREDITS Environmental Coastal zone resource use is critical to the sustainable economic development of the Caribbean. Development planning focuses on macroeconomic principles whilst neglecting those of Environmental and Resource Economics. This course introduces this neglected aspect of economic appraisal and assessment both from the Institutional Allocation Approach for market and non-market purposes. ENM 258: Economics for Environmental Management - 3 CREDITS This course approaches economic concepts and theories as a practical tool in environmental management and analyses the application of regulations and fiduciary strategies towards the goal of sustainability. ENM 268: Research Paper - 5 CREDITS The Research Report involves both desk and field studies. The report is assessed by submission of a research proposal (20%) and a 5,000 word written report (80%). All research topics are subject to approval by the Research Committee before supervisors are assigned. The research paper is designed to harness the student’s knowledge, and skills to analyze and offer solutions that can be successfully implemented to an environmental problem. ENM 261: Water Resource Management - 3 CREDITS This course facilitates the new approach that is imperative to address the critical problem of clean fresh water. It not only explores root causes of scarcity but initiates ideas and practical solutions to alleviate the plight of polluted water and deprivation especially of vulnerable sectors of the community. ENM 265: Ethics, Morality & Corporate Governance Environmental Management - 3 CREDITS in This course contextualises the principles of environmentalism within the Caribbean. It focuses on the ethical and moral questions of power, law, rights, justice and responsibility of governments and institutional managers towards sustainable economic development. ENM 280: Project Management for Environmental Management - 3 CREDITS In this course, it is shown that Project Management principles are applicable to all aspects of environmental management. Students are exposed to these applications especially in the spheres of EIA and EMS development. HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM) HRM 105: Fundamentals of Human Resource Management - 3 CREDITS This course covers some of the fundamentals of Human Resource Management within the organizational structure, such as its origins and values, the role of management, recruitment and selection, compensation, evaluation, management-labour relations, the role of the supervisor and the benefits of employee wellness 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS programmes. HRM 230: HRM 304: - 3 HRM 121: CREDITS Personal Self Development for Human Resource Professionals - 3 CREDITS Legal Issues of Human Resource Management in Operations - 3 CREDITS This course examines the concepts of Strategic Human Resource Management, strategic management elements, environmental analysis and diagnosis, environmental forecasting and strategic formulation and implementation. This course gives the student an opportunity to learn behaviour skills appropriate to professional operating in a Human Resource Development and Management environment. The course also offers an understanding of the effects of individual behaviour on others in the workplace. It further seeks to demonstrate the effectiveness as a group member in the work environment. Strategic Human Resource Management This course is an introduction to the law both in terms of its definitions and procedure as it relates to the business of human resource management. The course will provide you with an overview of the main components of the legal system and the special areas of concern to the human resource practitioner. You will also be made aware of the legal definitions of different categories of employed persons and the law as it relates to the private and public sectors of the economy. You will be able to identify legal issues in various human resource / industrial relations scenarios. You will be able to provide some level of advice to your organization in these areas by applying the relevant law. HRM 241: Collective Bargaining Management - 3 CREDITS and Compensation The student will examine the principles and practices of collective bargaining and compensation management to develop expertise and skills necessary for the H.R. Function. HRM 300: HRM 200: Human Resources Management Theories, Concepts and Principles of Human Resource Management - 3 CREDITS Systems, Functions & Procedures I - 3 CREDITS This course seeks to examine several theories and concepts of Human Resource Management and the principles and their implementation in the practice within the organizational structure. Pre-requisite: HRM 105 HRM 210: Organizational Behaviour and Development - 3 CREDITS This course is designed as the introduction to organizational behaviour. It will expand on those Human Resource topics covered previously and introduce the environment within which HR operates. There are three levels of analysis in organizational behaviour – the individual, groups and the organization itself. This course will help students make sense of behaviour in organizations by examining the context and dynamics of these environments and the influence of this organizational environment on the individual within its borders. In this course, students will learn the key functions, procedures and systems for efficient and effective Human Resource Management in organizations. They will also identify the skills necessary to be a manager. This course will also deal with union management practices in Trinidad and Tobago. It will identify the human resource factors in organizations and the importance of operating them for effectiveness and productivity. HRM 301: Human Resource Management Systems, Functions and Procedures II - 3 CREDITS This course will further build on the systems and functions studied in HRM 300. It will also assist the student in implementing at a managerial level the major knowledge and skills learnt. The course will identify and develop skills for operations along the Human Resource Management portfolio. The course will deal with the effective utilisation of people in organizations. HRM 305: Organizational Behaviour I - 3 CREDITS This course deals in depth with the issues of Organizational Behaviour Concepts in the area of the individual, the group and the organizational structure. It also covers the theories and concepts of Organizational Behaviour at all levels of the organization. HRM 306: Organizational Behaviour II - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to teach the student how the design of the organizational structure impacts on behaviour. It further examines the issues of power, conflict, politics and new areas in the field of leadership, as well as managing diverse employees. HRM 312: Corporate and Business Human Resource Management - 3 CREDITS This course deals with the major role played by top executives and divisional heads with respect to overall planning, policy formulation; decision making; restructuring merges; acquisitions and technological advances in Human Resource Management. There will be specific references to the measurement of the contributions of the Human Resource element to the profitability of an acquisition using standard normal dollar. Also how to measure the effective use of competition domestically and internationally. 109 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 HRM 320: HRM 350: Training and Development3 credits Internship - 3 CREDITS This course will focus on the theory and practice of the training and development function in organizations. It will also provide students with a comprehensive overview of the issues that may occur in the function from local, regional and international contexts. This course is an eight week on the job practicum in a formalized setting in an organization where students will be provided with application strategic in situational areas of HRM, under supervision. HRM 330: Compensation Administration - 3 CREDITS This course educates the student on how to develop a system that administers compensation to workers. It will focus on the nature, functions and administration of compensation. Along with this, the course deals with preventative measures for conflict and conflict resolution in compensation administration. HRM 335: Job Evaluation and Compensation Management - 3 CREDITS The course consists of two related parts - Job Evaluation Systems and Compensation Management. The job evaluation segment deals with the tools and techniques for evaluating jobs (with a concentration on the Hay Method), setting up salary structures and comparing salaries on the basis of job scores. The compensation sections deals with techniques of comparing salaries of “external market” comparators with those of an evaluated group. In this context, the principles of salary surveys are presented and there is some discussion of pay policy. HRM 340: Performance Management - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to the management and administration of effective performance management systems that enhance overall organizational efficiency, increases profitability and develops employees to work at maximum potential. This course will also provide a comprehensive knowledge of performance management strategies and appraisal systems used within contemporary organizations. 110 and develop its employees by improving their skills, knowledge, abilities, and competencies. The goal is to develop individual and organizational efficiency and productivity as well as personal career growth. HRM 420: Comparative HRM - 3 CREDITS HRM 365: Organizational Communication - 3 CREDITS Organizations create their own culture through the use, interpretation and meanings they place on symbols, events and things as communicated and shared by their employees.? This course will share how the organization’s image, character, and climate are created through and by communication. HRM 370: HRM procedures and processes are dictated by the countries in which they operate. In this course, students will be exposed to the impact of culture, socio-legal, political systems and economies, as they affect Human Resource application. LABOUR STUDIES (LBS) LBS 100 Introduction to Industrial Relations - 3 CREDITS HR Information Systems can significantly improve the efficacy of an organizations operation, manage and track reports and facilitate HR in engaging in strategic Human Resource Management. This course will expose students to the use of software and its applications that assist HR to integrate its organizational functions. This course deals with the theory and practice of industrial relations. Special emphasis will be placed on the development of industrial relations as a discipline as well as the main actors and how they relate with each other. The course also examines the development of new issues in the external environment and how they impact on industrial relations practice at the micro and micro levels in Trinidad and Tobago. HRM 400: LBS 120 Human Resource Information Systems - 3 CREDITS Managing Organizational Change - 3 CREDITS This course will offer a practical and culturally relevant approach to understanding the approach to planning, managing and implementing organizational changes through people. It will share the framework within which organizational change can be successfully achieved, analyze the environmental context within which change occurs, plan appropriately and use change management techniques to minimise the organizational barriers and resistance to change. HRM 410: Human Resource Development - 3 CREDITS HR Development is concerned with the development of people, mostly in organizational environments. Its focus is on providing programs which orient, train, History of Caribbean Labour - 3 CREDITS This course reviews and analyses the history of the Caribbean in the broad periodic separations of early Colonialism, Slavery and the Sugar Revolution, Emancipation and Indentureship, 1830’s to the 1930’s, the era of self-determination and Independence and the contemporary period of essentially the last half century. These periods are purely for academic convenience and do not represent neat separations in our regions history. They allow us only a loose framework from which to map several historical continuities and divergences of interest to us as we look at the role and significance of Labour, the Labour Movement and Trade Unions in the development of our societies. Of central concern to us is the continuous role of global economic and political developments in shaping the development the Caribbean Labour Movement and Caribbean Societies. 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS LBS 130: LBS 210: LBS 270: Caribbean Labour Relations History - 3 CREDITS Grievance Handling and Arbitration - 3 CREDITS Caribbean Industrial Relations Systems This course surveys the development of labour relations in the Caribbean, mostly with reference to Trinidad and Tobago. It focuses for the most part on the phase of organised labour, but with some attention to precedent phases’ Apprenticeship, Indentureship and working people’s movements. From the perspectives of the participants in labour relations (trade unions, business, the colonial administration and the independence administration), the course will examine organizational objectives and strategies and tactics adopted in pursuing objectives. The use of grievance procedures to deal with problems at the workplace and administer the collective bargaining agreement. The course also seeks to focus on relevant Labour Legislation and its impact upon grievance decisions. - 3 CREDITS LBS 140: Introduction to Human Resource Management and Industrial Relations - 3 CREDITS This course examines the various aspects of human resource management such as recruitment, selection, interviewing, performance appraisal, manpower planning and development and the relationship of all of these to the Industrial Relations environment. LBS 200: Fundamental Principles of Labour Law - 3 CREDITS This course deals with the fundamental Principles of Labour Law such as the definition of employment, terms of contract employment, collective agreement and implied terms, constructive dismissal, unfair dismissal and redundancy, the law relating to strikes and other types of industrial actions, tortuous liabilities of trade unions, the legal status of a trade union, the rights of trade union members, wrongful expulsion and natural justice. LBS 205: Industrial Relations Law and Practice - 3 CREDITS This course examines the following topics: Principles of Law; the Industrial Relations Act and other important labour relations statutes; Law of Evidence; Advocacy; Legal Ethics; Rules of Procedure including Directions preparation and filing of documents, judgments and orders of the Court. LBS 220: Principles of Caribbean Labour Law - 3 CREDITS This course examines the essential statutes in Labour Law within the Caribbean such as the Factory Act, Retrenchment and Severance Benefits Act and statutes dealing directly with various essential services (e.g. police service, teaching service, prison service, fire service and the civil service). The course also covers the industrial relations act, the road motor vehicle act, tortuous liability of professional bodies and the liability of employers. LBS 240: Collective Bargaining - 3 CREDITS This course looks at the process of collective bargaining such as preparing proposals and counter proposals, costing proposals, wage determination. It also looks at the theories and principles of collective bargaining, along with the roles played by unions, employer and Government. LBS 245: Collective Bargaining: Principles, Procedures and Practices - 3 CREDITS This course examines philosophies, strategies and tactics of trade unions and employers in the three phases of the collective bargaining process, preparation, negotiation and contract administration. The implications of major items in the collective bargaining agreement will be critically examined. Given the importance of the State as an employer in the Caribbean region, the course will include an analysis of public sector collective bargaining. LBS 270 are an advanced Industrial Relations course dealing with labour relations in the Caribbean. The course examines the systems of industrial relations in the Caribbean in terms of the influence British public policy on industrial relations in the Caribbean, the practice of industrial relations in the public sector. The course also analyses the responses of the actors of industrial relations to the changes of industrial relations in the Caribbean. LBS 285: Selected Industrial and Labour Relations Issues - 3 CREDITS This is a capstone course which draws on the material in other courses to develop in-depth analyses of salient issues like: the wages-prices-profits-productivity nexus; job evaluation and compensation systems; minimum wage policy; the economy of safety and health standards in the workplace; and enterprise framework agreements. LBS 290: Applied Collective Bargaining - 3 CREDITS This course consists of a framework for analyzing collective bargaining by taking into account the role of the environment. It also deals with the strategies and structures adopted by management, the patterns of collective bargaining set by management during the 1980s, 1990s, and 2000 and beyond. The course also addresses issues such as productivity bargaining, disclosure and the different models of joint consultations, as well as different models representing collective bargaining, together with a profile on collective bargaining in different countries. LBS 300: Employment Law - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on legislative aspect of employment law which concentrates on areas such as Collective bargaining, redundancy, transfer undertaking and trade union administration and management as well as the ILO’s and Human Rights perspective. 111 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 LBS 330: LAW 100: LAW 320: Industrial Arbitration & Mediation - 3 CREDITS Introduction to Civil and Criminal Law - 3 CREDITS Crime and Justice in the Caribbean - 3 CREDITS This course is designed specifically to provide skills and knowledge in Industrial Arbitration. It focuses on the principles of arbitration in both the public and private sectors and examines the institutions of arbitration and the legal frame work in which arbitrators must work. It introduces the theories and principles of alternative dispute resolution as well as treaties and ILO Conventions and Recommendations. Industrial Arbitration has been proven to be an effective means of resolving industrial relations problems. This course introduces the student to the substantive criminal law and aspects of civil law relevant to the security industry and its management. It provides information on the structure and jurisdiction of the various aspects of the legal system. A brief outline of the civil and criminal procedure in the courts and rights of parties is included. Students are also introduced to the law of evidence, what evidence is, its various forms, burden and standard of proof and the rule against hearsay. This course explores the institutional arrangements devised by societies in responding to crime in the Caribbean. It provides an overview of the criminal justice system in the region emphasizing the operational similarities within the context of the reductionist theory of crime causation, crime adjudication and penal punishment all within the framework of law enforcement and societal control in the Caribbean. LBS 370: LAW 120: Trade Union Leadership - 3 CREDITS Civil and Criminal Law - 3 CREDITS This course deals with leadership, the exercise of power and the understanding of human nature. It adopts a theoretical approach to examine the nature and quality of social interaction. Special emphasis is placed on the role of transformational and transactional leadership in trade unions and other modern-day organizations. Students are introduced to the substantive criminal and civil law relevant to the security industry and its management of risks reduction in the preservation of lives and property. This course provides information on the structure and jurisdiction of the various aspects of the legal system. An outline of the civil and criminal procedure in the courts and rights of parties are LBS 380: explored briefly. Students will be exposed to aspects of the laws governing evidence, and its various forms, the burden of proof, hearsay and the rules of conduct against the use of the hearsay, arrests, searches and seizures. Ethics in Decision Making - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the different moral theories and looks at the relevance of applying ethical principles in organizational decision making. It provides a correlation between ethical decision making and the principles of justice, human dignity, interpersonal relationship and the respect for employee’s privacy. The course also examines the ethical challenges decision makers experience in acting ethically. A critical analysis is made of leadership and unethical behaviours in trade unions, the private sector and governmental institutions. LBS 390: Grievance Process - 3 CREDITS This course deals with the grievance process including structure, administrative procedures and how to improve them. The rights and responsibilities of management and employees and the impact of environmental factors on the behaviour of parties to a grievance are examined. LAW (LAW) 112 LAW 310: Legal and Ethical Issues in Security Management - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on some of the ethical, legal and professional issues that security personnel face in their day to day decision making. It allows the student to clarify a value system and establish a framework for ethical decision making while simultaneously exploring the application of those decisions to a wide variety of professional dilemmas faced by the security industry. The students, in their discussions and research of the topic, will come face to face with controversial issues existing or anticipated in the security field and the laws that govern the industry. LOGIC (LOG) LOG 120: Critical Thinking - 3 CREDITS This course deals with a variety of complex, cognitive activities such as problem solving, generating and organizing ideas, forming and applying concepts, designing systematic plans of action, constructing and evaluation arguments exploring issues from multiple perspectives, applying knowledge to new situations, critically evaluating the logic and validity of information, developing evidence to support views, carefully analyzing situations and discussing subjects in an organised way. MARKETING (MAR) MAR 100: Introduction to Marketing Non-Credit Course This course is designed to expose students to a practical approach to marketing. The course provides participants with the concepts and practices of marketing and teaches the student how to establish and maintain mutual understanding between the organization and its publics. MAR 110: Principles of Marketing - 3 CREDITS This course explores the role of marketing as an organizational function today in society. It covers the nature of markets; the concepts of marketing and their application in both profit and non-profit entities. Customer satisfaction is also explored in relation to new product development. 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS MAR 115: Integrated Marketing Communications - 3 CREDITS This course expands on PBR 250 and develops the students understanding of Advertising as a promotional tool within the Public Relations environment. It also introduces the student to other promotional options such as Sales Promotions, Exhibitions, Selling and Sales Management, Direct Marketing, etc. MAR 121: Market Research and Forecasting - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on the role of marketing information and intelligence; the scope and purpose of marketing research; the research process - collection and analysis of primary and secondary data; quantitative and qualitative data; and reporting, sales forecasting and measurement of market demands. MAR 130: Marketing Practices - 3 CREDITS Investigation and analysis of buying behaviours and competitors’ behaviour is studied in informing students’ exploration of strategies towards competitive advantage. This course also covers, levels of market segmentation, selection of target markets, managing distribution systems and development and management of communication systems. MAR 140: Marketing, Planning and Control - 3 CREDITS The application of strategic thinking to the marketing process and assessment and analysis of business performance is explored. This course looks also at pricing objectives and strategies; product line, brand and packaging; marketing plan; organizational culture and strategies for controlling marketing activity. MAR 150: Sales Techniques - 3 CREDITS Selling and Sales Management is a critical element within the marketing process and is vital to the overall success of any organization. The student will gain a more than an adequate appreciation of the technique and methods employed in the selling process and will learn how it integrates into the marketing management of an organization. MAR 200: Principles of Marketing - 3 CREDITS This course aims at providing students with the concepts practices and analytical techniques in marketing, throughout. The marketer’s approach will be emphasized and adopted. Once the fundamentals are fully understood, the students will then be trained to recognise and confront problems and to seek out solutions to deal with these problems. MAT 150: Introduction to Statistics - 3 CREDITS Students are introduced to the use of statistics in business decision making. This course provides the analytical tools needed for making informed business decisions using data. The focus is on decision making using the tools of statistics. Topics include graphical and numerical summaries of data, probability distributions, hypothesis tests of mean and proportion, the chisquared test of statistical independence and simple linear regression. MAT 300: Advanced Statistics - 3 CREDITS MAR 220: Marketing and Merchandising - 3 CREDITS This course seeks to provide the student with the concepts, practices and analytical techniques in marketing. Throughout, the marketer’s approach is emphasized and adopted. The course also deals with the recognition and solution of marketing problems. This course provides students with a strong knowledge of the principles and applications of statistics. MAT 301: Quantitative Methods - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to provide students who have not done Mathematics for several years or students with a weak foundation in Mathematics with the understanding of elementary mathematics and to expose them to some of the basic skills required to perform mathematical tasks competently within their different disciplines as well as in their everyday activities. This course provides the fundamental quantitative knowledge necessary for managers to use the results of analyses to enhance the decision-making process. This course will enhance students’ ability to perform the quantitative analyses necessary, understand the usefulness and limitations of the methods, recognize situations where the methods can be applied beneficially and issues involved when utilizing the results of analyses. Coverage is topical and will include basic statistical principles such as probability distributions, inferential statistics (sampling), regression analysis, decision trees, utility theory, and simulation. The introduction of concepts via cases in decisionmaking related to operations and strategies is preferred whenever appropriate. MAT 100: MAT 400: Mathematics - 3 CREDITS Quantitative Methods - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to provide a sound understanding of infinite mathematics and application which will enable students to process problems in disciplines and situational which require the application of mathematical fundamentals. This course provides students with selected procedures of quantitative techniques that are required to affect statistical analysis relevant to business (with specialized forms as Co-operatives) and economic situations which include Risk and Return analysis, Investment Appraisal, Capital Budgeting, Forecasting - Time series analysis and Inventory Control. MATHEMATICS (MAT) MAT 001: Fundamentals in Developmental Mathematics Non-Credit Course 113 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 MANAGEMENT (MGT) characteristic of planning and also introduce aspects of leadership and leadership in co-operatives. MGT 110 : Introduction to Financial Accounting - 3 CREDITS Management and The objective of this course is to provide students with an introduction to financial decision making. Students will be exposed to introductory level accounting and provided with a theory based and relevant understanding of financial decision-making. Topics covered include financial forecasting, planning and budgeting, and the evaluation of the organization’s financial performance and cash-flow. Credit Risk Analysis - 3 CREDITS MGT 150: OSH 100: Students are instructed in the principal concepts of credit risk analysis with focus on the lenders expertise, subjective judgment and the weighting of certain key factors such as net present value and financial leverage as determinants in granting credit. OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH (OSH) OSH 150: Security Aspects of Safety - 3 CREDITS This course seeks to establish the link between safety and security within organizations, giving a clear picture of the overall organizational safety structure, individual responsibilities and the importance of bringing safety and security hazards to light. OSH 210: Safety Technology II - 3 CREDITS Basic Principles of Money Management & Securities Fundamentals of Occupational Safety and Health An introduction to marketable securities, personal financial planning; analysis of financial statements and the decision-making process in securities investments. This course is intended to provide the base on which all future studies in the field of Occupational Safety and Health will rest. This module provides a knowledge and utilisation of: the need for, and factors involved in, the provision and maintenance of safe places of work; safe working practices associated with work in confined spaces; structural safety of workplaces; and the criteria for the selection of work equipment that is safe and without risk to health. MGT 200: OSH 110: OSH 220: - 3 CREDITS Principles of Business Management - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to instruct students in the Role and Environment of Business Management. Topics include the Functions of Securities business planning, analysis and interpretation of Financial Statements, Time Value of money, marketing principles, business ownership and ethics. MGT 201: Financial Management - 3 CREDITS A study in Managerial Finance with an emphasis on Financial Statements and Analysis, Cash Flows and Financial Planning, Time Value of Money, Risk and Return, Capital Budgeting Techniques and The Cost of Capital. Pre-requisite ACC 100 MGT 300: Strategic Management and Leadership in Cooperatives - 3 CREDITS The course will introduce Strategic Management in relation to the voluntary sector. It would also explore the strategic management process, the purpose and 114 MGT 400: epidemiology. - 3 CREDITS Safety Technology I - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to machinery safety, electrical safety and mechanical safety. Other topics include construction safety, lifting machinery and equipment and dangerous substances. OSH 120: Safety Management I - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to the basic principles of Safety management and other related aspects such as its methodology and applications. It also emphasizes an integrated or systems approach to safety, which includes the physical, managerial and behavioural aspects. OSH 141: Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene I - 3 CREDITS This course deals with the effects of work on health. It examines issues such as lighting, stress factors, radiation and dust, OEL, MAC and TLV Standards, hygiene audit and general principles of field measurements and Safety Management II - 3 CREDITS This module provides the knowledge and utilization of: reasons for managing health and safety; a framework for health and safety management; theories of loss causation; statistical and epidemiological analysis; purposes of, and procedures for, reporting, recording and investigation of incidents of injury, ill-health and other loss events. OSH 230: Law Relating to Occupational Safety and Health - 3 CREDITS This course exposes the student to the legal issues involved in Occupational Safety and Health. It examines the limbs of the common law such as Negligence, Vicarious Liability and Nuisance which are the foundation of our local legislation such as the OSH Act 2004, Minerals Act and Explosives Act. Other areas addressed include contract of employment, employer’s liability and insurance and compensation. 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS OSH 265: OSH 231: Occupational Safety and Framework - 3 CREDITS Health Legislative This course exposes the students to legal issues involved in OSHA 3/2006. It explains the statutory obligations for Safety and Health imposed on an organization and individuals by the Act. It also advises managers on the powers of inspectors, different types of enforcement action and their implications. OSH 241: Construction Safety - 3 CREDITS This course summarizes the essential health and safety requirements for developing a safe system of work. It helps the participants to identify health and safety hazards found on many sites and advises on how to control the risks that can arise. Information is given on protecting those who are directly employed to do the work, others working on the site, visitors to the site and members of the public who could be affected. Occupational Health and Industrial Hygiene II - 3 OSH 270: CREDITS Laboratory Safety - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to equip students with the knowledge and skills required to identify, evaluate and prevent or control health hazards in the workplace. Major emphasis is placed on the essential elements of such areas as toxicology, ergonomics, particulates and hearing conservation so as to develop the competence of students to manage the hazards arising in or from the workplace that may cause sickness, impaired health and discomfort among workers. This course will provide the framework of workplace Hazardous Materials Information System to assess laboratory procedures and reagents, evaluate the hazards, and modify procedures to incorporate proper safety precautions. OSH 245: Fire Safety - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to provide students with an understanding of the concepts of fire safety. This course will identify the causes, impacts and results of fire on structures including buildings, institutions, and the agricultural, residential and industrial environment. It provides instruction in the reduction and elimination of fire safety hazards in all local environments, and equips the student with the skills for the collection, interpretation and dissemination of knowledge on fire safety to organizations, employees and the general community. OSH 255: Principles of Health and Safety Law - 3 CREDITS This course provides the knowledge and understanding of the sources and types of law, the burdens of proof and standard defences available; absolute and qualified duties; and the detailed relationships at common law between employers/ occupiers of premises and employees, customers, visitors, contractors and others. OSH 301: Process Management Safety - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to assist in the management of process hazards. It is intended to help prevent the occurrence of or minimise the consequence of catastrophic releases of toxic or explosive materials. The course also addresses the management of process hazards in design, construction, start-up, operation, inspection, maintenance, and modification of facilities. It applies specifically to processes and facilities with a potential for catastrophic release. OSH 310 Safety Technology III - 3 CREDITS This course describes and reviews the causes of and methods of preventing or minimizing the severity of accidents, fires and explosions with structures, plant and processes. OSH 320: Safety Management III - 3 CREDITS This course addresses the criteria and methodologies for effective health and safety and environment management, and the contribution of proactive strategies and legislation to achieve this. It also looks at the control of substances hazardous to health, and the uses for personal protective equipment. OSH 341: Occupational Safety and Industrial Hygiene III - 3 CREDITS This course describes the process of managing occupational hygiene in the workplace and critically evaluates strategies for eliminating and controlling exposure to health stressors. OSH 345: Health Care Workers’ Safety - 3 CREDITS This course will enable health care workers to identify the hazards that they all face in health care facilities. It will provoke workers to be suspicious of their environment and its hazards, to ask questions and get information, to use their own basic knowledge of their work to propose solutions and to see that the Occupational Safety and Health Act 1/2004 is complied with in their workplace. OSH 400: Fire Protection and Prevention - 3 CREDITS This course prepares the student to meet the workplace safety needs for Fire Protection and Prevention, Exits and their requirements, Plans related to fire and other emergencies, and First Aid requirements. This course includes OSH Act recent amendments and its new approach to what the OSH Act requires for workplace safety. The course also designed to give students a clear understanding of the principles and limitations of fire suppression and detection systems. This also covers the history and philosophy of fire prevention, challenges of fire prevention education and public education. PUBLIC RELATIONS (PBR) PBR 100: Introduction to Public Relations No Credit Course This course introduces students to the world of Public Relations, from understanding its definition to appreciating its responsibility. Students are exposed to communication for public relations, the tools of Public Relations, defining targets, setting goals and objectives. The course is also aimed at defining the role and function of a Public Relations practitioner. 115 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 PBR 110: PBR 200: Principles of Public Relations - 3 CREDITS The Role and Function of the PR Practitioner This course examines the purpose of Public Relations, its responsibility, objectives and mission. Students are taught how to plan, effect and evaluate a Public Relations campaign, how to define and set objectives, how to plan and prepare budgets, manage images, massage information and public behaviour and ethics. - 3 CREDITS This course seeks to clearly identify the role and function of the PR Practitioner within the organizational framework. The student will gain both theoretical and practical knowledge of the Public Relations in the organization and learn how effective this management tool can be to the success of any organization. PBR 135: Media Relations - 3 CREDITS PBR 201: This course is aimed at providing students with the structure, behaviour, language and etiquette of primary media as they interface with different audiences and target groups that comprise a society. The student is exposed to the strength, weaknesses and characteristics of primary media, as well as an understanding of the concept of secondary media, as well as analysis of the various audiences attracted to and influenced by them, along with the role, function and responsibility of media to society. Writing for Public Relations - 3 CREDITS PBR 145: Introduction to Event Co-ordination - 3 CREDITS Any event is a valuable technique used in the execution of effective Public Relations and Marketing Plans. This course is design to introduce the participant to the fundamentals of events co-ordination from the analysis of the event to the stages of events planning and implementation. This course is aimed at developing an understanding of the role writing plays in Public Relations, the fundamentals of writing in Public Relations, as well as some of the issues surrounding the use of different writing tools. PBR 220: Laws and Ethics of Media - 3 CREDITS Legal and ethical values are ‘brought to bear’ on the Public Relations Practitioner and this course is designed to ‘flesh’ out the parameters within which the officer must function. The freedom of information and the framework for the dissemination of it will be the focus of this course as the student learn in proper procedure to interact with Media. PBR 245: Events Management - 3 CREDITS PBR 150: Understanding Global Public Relations - 3 CREDITS Public Relations seek to promote goodwill as it strives to build relationships between an organization and its publics. The Public Relations Practitioner gains an appreciation of globalization within a Public Relations framework and understands the role PR plays in the global village. The participant will also learn useful techniques that can build international image and effective global Public Relations Plans. 116 The implementation of ‘seamless’ events is the concentration of this course. Participants will gain indepth knowledge of events planning and will be called upon to actually execute an event within the course content. PBR 250: Principles of Advertising - 3 CREDITS This course examines the concept, tasks and responsibility of advertising. The course will also look at the various methods used in modern advertising, both by primary and secondary media. The course also presents the student with the opportunity to conceptualise, plan and design advertising, while at the same time, understanding media planning and implementation as part of the Public Relations process. POLITICAL SCIENCE (PLS) PLS 100: Introduction to Politics - 3 CREDITS This course deals with the basic political concepts such as the nature of politics, pressure groups, political parties, the structure of government, comparative systems of government, electoral systems and voting behaviour. PLS 200: Government and Politics of the Caribbean 3 credits This course is designed to cover systems of government, and constitutional and political development of the region. It discusses Caribbean politics from the 1970s to the present, radical constitutional change and Caribbean politics in the context of global changes. PROJECT MANAGEMENT (PRM) PRM 100: Introduction to Project Management No Credit Course The course introduces the student to the Project Life Cycle concept and enable participants to grasp a sound understanding of project management and to identify and demonstrate appreciation for and importance of the tools applied to the project management process. This course is designed for persons who are seeking to become involved, or who are already engaged in the management and execution of projects. PRM 115: Management Concepts and Principles - 3 CREDITS The central theme in management is the pervasiveness of turbulent change and its impact on organizations. This course focuses to help project managers find innovative solutions to the problems that plague organizations. Managing projects in these turbulent times require a greater application of skills and capabilities. It covers 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS the major management processes such as planning, organizing, leading and controlling, in order to effectively accomplish major goals and objectives.. PRM 120: Fundamentals of Project Management - 3 CREDITS This course introduces the basic concepts and principles of Project Management. It covers concepts such as projects and project management; describes the differences between projects, programmes and portfolio management; discusses the role of the project, programme and portfolio manager. Project integration, project organizations, project stakeholders, life cycle analysis and project management processes and skills of project managers are also introduced. PRM 125: Project Identification and Selection Strategies - 3 CREDITS The course focuses on utilizing the strategic planning process in identifying projects to support business strategies of organizations. In addition, it teaches some of the strategies that managers can utilise to select projects and includes both financial and non-financial criteria. PRM 135: Proposal Development and Costing - 3 CREDITS The course focuses on the methodologies for developing and presenting the project proposal to financial agencies or other relevant stakeholders. In addition, it demonstrates the importance of chartering, preliminary scope statement, scope definition and cost estimating and budgeting for a particular project. PRM 145: Fundamentals of Project Planning - 3 CREDITS This course teaches the basic components of a good project plan, the basic steps in planning and key planning tools used in the project management profession. It focuses on using historical data, archived information, personal information, personal expertise, institutional memory, organizational knowledge and project scope statement to predict resource expenditure, total cost and duration. PRM 170: Project Scheduling - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on that part project management that is concerned with the defining the scope and schedule of the project. There must be an understanding of how the project scope is broken down into smaller components. It also includes defining the project activities, ordering the activities in their logical sequence, estimating the effort and duration of each activity, building the overall project schedule and schedule control. The course exposes students to time management which includes managing the schedule once the project is underway. PRM 200: Project Executing & Implementing Strategies - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on those activities needed to complete the work defined in the project management plan. It involves developing the skills that coordinate people, resources, performing organizations and the integration of the various activities of each project phase according to the project plan to produce the project deliverable. Students should have thorough knowledge of producing project management plans. This course builds on PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning and runs simultaneously with PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control and fits within the project execution phase of the project life cycle within which CCLCS project management programmes were developed. PRM 210: Fundamentals of Project Monitoring & Control - 3 CREDITS Theory and experience confirm that Monitoring and Control is essential if a project is to succeed. This course equips project managers and team members to develop and implement a system to monitor and control the performance of projects in order to increase the chance that the given project will be successful: on target, on schedule, on budget, according to requirements, satisfying the customer and relevant stakeholders. PRM 211: Procurement for Projects - 3 CREDITS This course is covering the Procurement Knowledge area as defined in PMBOK® Guide [fourth edition] and puts emphasis on the decisions if, when and how to procure, the management of the procurement processes and the practical application of the learned topics via examples and scenario based analysis. The students will hereby also be introduced to the basic legal aspects of contract management, fundamentals of contract negotiation and decision making tools. PRM 215: Project Monitoring and Control - 3 CREDITS The actual determination of future project cash flows. Project cash flow elements- investment, working capital, debt repayment scheduling, and the weighted average cost of funds. Translation of a project’s operational impact into cash flows. Sensitivity Analysis. Brief evaluation of non-quantitative evaluative criteria. PRM 216: Project Performance Measurement - 3 CREDITS The assessment of a project’s operational impact. Identification and development of important measurement indicators including productivity, efficiency, quality and resource utilisation. Target setting and evaluation. PRM 225: Quality Management - 3 CREDITS This course teaches the science of Quality Management with emphasis on its application in Project Management. It explores the history and constructs of quality management; benefits of a quality focus; primary approaches and methodologies of Quality Management; and tools and techniques which may be used to incorporate quality into Project Management activities toward supporting overall Project success. PRM 230: Managing Project Teams - 3 CREDITS Project managers face the challenges of operating in project environments characterized by high levels of uncertainty, cross-cultural teams, and global competition for competent human resources. To meet 117 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 these challenges and to make the most effective use of the people involved with the project, as project managers, you can develop a clear understanding of human resource management skills. No Project can succeed without an effective team. In this course participants will learn the techniques, principles and principles to select, develop, manage, assess and retain project team members. This course exposes students to the intricacies of the project team to ensure the goals, objectives and outcomes of the project are successful. It addresses the environment, the team and the organization the team must work from to make certain of project success. PRM 235 Project Integration & Professional Development 1 - 3 CREDITS This course is designed to provide a framework for students to use and manipulate coordinating strategies in the execution of projects, while ensuring that the use of ethical and professional developmental attitudes are involved in these strategic processes. Students will be trained to perform and excel in a global environment of project management and test their capability to ensure transparency, independence and high levels of integrity for the management of stakeholders capital and resources, while meeting the demands of its clients. PRM 240: Risk Management - 3 CREDITS This course teaches about managing the project’s uncertainties, which manifest themselves in both negative risks (threats) but also positive risks (opportunities). The student is exposed to the tools and techniques, which under consideration of the risk management process inputs, are utilized to create the process outputs viz. risk register, risk response plan and others. Active risk management accompanies the project team throughout the complete project life cycle. Practical work and examples will aid in mastering the theme. PRM 245 Change Management - 3 CREDITS The need for change, the importance of change, the 118 identification and management of change and the factors which influence and impact on changes in all activities or working environments will be emphasized in this course. The Project Manager or Project Practitioner being regarded as the ultimate change agent must be and will be taught, assessed and prepared to exist in an environment knowing that this phenomenon is inevitable and can be managed for the good of the organization, its stakeholders, clients and providers of capital. Students will be trained using practical case studies that have been tried and tested and those that initiate change in the various operational environments. PRM 250: Schedule Application Techniques - 3 CREDITS The course Schedule Application Techniques is based on MS Project 2007 and Primavera P6 and is designed to impart basic knowledge of MS Project and Primavera P6 applications up to the level of optimizing and reporting in the context of dynamic scheduling supported by practical exercises in the computer lab. PRM 255: Internship - 3 CREDITS This component is aimed specifically at those with little or no experience in project management. Students will be provided with a level of support from the College to afford them the opportunity to create and develop alliances through attachments in the workplace, while improving their project management skills. At the end of the internship students will be able to: 1. Develop an appreciation for job visibility through the work that he/she undertakes 2. Develop new skills and knowledge which allows the intern to perform better on the job. 3. Develop hands -on/practical experience in the discipline of project management. 4. Develop professional work habit. 5. Demonstrate the achievement of the expected learning outcomes of the project management department. 6. Develop capacity for critical thinking and transferable project management skills. PRM 260: Research Project - 3 CREDITS The research project represents the student’s knowledge, appreciation and ability to integrate all project management methodologies, tools and techniques in developing a project that can be successfully implemented. PRM 295: Research Project & Portfolio Presentation - 5 CREDITS This research project represents the culmination of the Associate Degree programme and should reflect the student’s comprehension and internalization through application, of the knowledge, skills and abilities, he or she has acquired during the program of study. It is an individual exercise which involves periodic consultations with lecturers, employers, work colleagues, relatives, associates and many other stakeholders, with whom they come in contact. This project, being a design and ‘custom made product’ of the student, engages their daily living activities and requires input from these diverse sources. It therefore validates and legitimizes the philosophy of the programme, while at the same time it prepares the project person for the global marketplace. PRM 300: Evaluating Project Results - 3 CREDITS This course focuses on the key components of results oriented evaluations conducted during and after the life of the project. The course will explore the various evaluation tools, techniques and frameworks used in conducting formative, summative and post impact evaluations. This course builds on PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning and runs simultaneously with PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control and fits within the project execution phase of the project life cycle within which CCLCS project management programmes were developed. 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS PRM 310: Contract Administration & Negotiation - 3 CREDITS This course builds on PRM 211 and looks at the development and administration of contracts. It includes a look at typical problems faced by clients and contractors and how they can be managed and resolved. PRM 320: Leadership in Project Management Environment - 3 CREDITS Projects are executed within a dynamic and unforgiving business environment by diverse individuals and teams. This reality has created the need for the demonstration of effective leadership skills by project managers. As a result, this course exposes students’ to the various leadership theories, business communication strategies and other interpersonal skills required in the project environment for project success. The course addresses the Human Resources, Communication and Risk Management Knowledge areas of PMBOK. PRM 330: Communication & Stakeholder Management - 3 CREDITS Stakeholder management can mean the difference between project success and failure. This course builds the communication skills of participants and explores tools and techniques to manage all stakeholders, including the development and distribution of reports. PRM 400: Project Closure & Post Project Support - 3 CREDITS No professional project manager ignores project closure. This course explores the importance of project closure and what is involved in proper project closure and the techniques to be employed in providing clients or customers that post project support. This course focuses on the processes involved in the final stages of project execution. This course builds on PRM 145 Fundamentals of Project Planning and runs simultaneously with PRM 210 Fundamentals of Project Monitoring and Control and fits within the project execution phase of the project life cycle within which CCLCS project management programmes were developed. change within an organization. In addition it focuses on the management of change within the project. PRM 410: PRM 460: Environmental & Social Impacts of Projects Research Paper - 5 CREDITS - 3 CREDITS PSYCHOLOGY (PSY) This course examines the means of anticipating the environmental effects of a proposed action. While many projects impact on our society and our environment, many project managers fail to effectively assess the impact. The results of this oversight range from stakeholder dissatisfaction to project abandonment and sunk costs. This course is geared to give participants a working knowledge of tools and techniques to assess, apply and manage the environmental and social impact of projects. PRM 420: Project Implementation & Organizational Change - 3 CREDITS As students approach the culmination of their course of study in preparation for taking their places in the Project Management Profession, the need for recognizing, appreciating and setting parameters for managing ‘change’ within their own organizations and professional responsibilities, becomes critical. The importance and strategies for managing change and the factors which influence and impact on changes in all activities and working environments will be emphasized in this course, particularly as the country is heading into a ‘developed world’ status. The Project Manager or Project Practitioner being regarded as the ‘ultimate change agent’ must be, and will be taught, assessed and prepared to exist, survive and advance in an environment of transition – knowing that this phenomenon is inevitable and can be managed for the good of the organization, its stakeholders, clients and providers of Capital, particularly as the organization approaches maturity. Students will be trained using practical case studies that have been tried and tested and those that initiate change in the various operational environments. All change management initiatives are projects. This course looks at the application of project management principles to effect organizational change. It also looks at the organization impact of any project and examines strategies to effectively implement PSY 100: Introduction to Psychology - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to give the student an introduction to the basic concepts and perspectives in psychology. It also introduces the student to some of the central issues in social psychology where they will be able to use their critical thinking skills. RESEARCH (RES) RES 100: Research Methods and Statistics - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to fundaments of qualitative and quantitative research candidates will present a research proposal on a topic related to the discipline of pursuit which can be (but not mandatory) the genesis of their Research Report. Pre-requisite MAT 100. RES 300: Research Methods - 3 CREDITS This concept advances the concepts and strategies developed in RES 100 with a focus on practical methodologies essential to a research report. Prerequisite RES 100. RES 301: Research Methods - 3 CREDITS This course aims to introduce students to the assumptions underlying and differences between different methodologies for performing research in the social sciences. The focus is on interpretive and positivist methods. The course attempts to give students the conceptual and methodological resources needed to think and converse as researchers and scientists in organizations and to develop a certain level of competence in at least one research methodology. This 119 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 is accomplished through the generation of a research proposal in a field of interest to the student and critiques of methodological approaches found in the academic literature. RES 460: Research Paper - 5 CREDITS A research paper is an investigative report or expanded essay that presents your own interpretation or evaluation or argument. It is a formal report that answers a question through exploration of a problem or an original idea that sheds new light on a known topic. The student collects information about a specific issue or topic, analyzes the information, and presents all the collected information in a report. The research paper analyses and assesses a perspective or argues a point, which represents students’ own thinking backed up by others’ ideas and information. The purpose is to find and compile data, to participate in an exploration of the data, to make original observations, to show relationships between data, and to make evaluations on a subject. It may mean hours spent in the library, more hours toiling with notes and drafts, and the tasks of dealing with the rules of documentation. SECURITY ADMINISTRATION & MANAGEMENT (SAM) SAM 100 circumstances that informed the development of the security industry over the period from emancipation to present day focusing on the economic, political sociological and administrative policies that circumscribe the shape and culture of organizations that comprise the Security Industry. SAM 210: Security Administration - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to broaden the scope and appreciation of students in analyzing management issues in the security industry. Emphasis will be placed on understanding the bureaucracy and its principles as it relates to Security Organization. The human factor in organizations will be explored so that issues of development can be better understood. SAM 222: Crisis and Risk Management - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to provide the student with the tools necessary to manage crises and to develop programmes for the management of general conditions that will impact upon the organization. Students will be exposed to such as the principles of accident prevention, management leadership in crisis management, hazard recognition and casual factors in accidents, theories of accident/crisis causation and accident and their effects investigations and management. Introduction to Security - 3 CREDITS This course exposes students to the evolution of private security as an SAM 230: industry in the Caribbean region and its functions in to provide protection of assets that public police had no longer been to protect. Particular focus is placed on the private security industry in Trinidad and Tobago in light of the mounting commercial and industrial development taking place. The powers possess by the private security officer is compared to that of the Police Officer in their performance of duty. The demand for private security officers in other areas of protection will be explored by students in the course. - 3 CREDITS SAM 120: History of the Security Industry - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to expose students to the 120 Risk Management , Protection of Business Assets This course is designed to provide the student with tools of analyses, methodologies and typologies in the art and science of protecting and preserving business assets. Elements of risks and vulnerabilities are identified and assessed critically, together with other elements of criticalities and measures proposed to reduce and/ or eliminate to an acceptable level any threat that may have been identified. SAM 240: Security Operational Management - 3 CREDITS The student will be exposed to modern management theories of security management that will provide a theoretical working background that will demonstrate the skills, knowledge and competencies that are require of a practitioner to be effective and efficient in the industry. The course will focus its attention on security planning, auditing, recruiting, organization of resources and negotiating conflicts and resolving grievances. SAM 250: Physical Security and Planning - 3 CREDITS This course will utilise the conceptual foundations of Physical Security and Planning as a basis for analyzing and diagnosing operation risk performance. A primary focus will be understanding and applying diagnostic models and frameworks to assess physical security and planning. In addition to becoming familiarized with different interventions and development technologies, heavy emphasis will be placed on applying various diagnostic models. SAM 270: Emergency Planning and Disaster Control - 3 CREDITS This course teaches the history of the prevalence of crisis disaster and emergency episodes in the Caribbean. It focuses on the various skills regarding crises, disasters and emergencies, including virus attacks on the Information and Communication technology systems of an institution. It prepares the student to pursue further studies in the various specialist field that comprise the teaching areas addressed here. SAM 271: Disaster Preparedness - 3 CREDITS This course teaches the student the essential concepts for and approaches to the preparation of a facility to resist the impact of a natural or human-induced disaster, the minimisation of loss during impact, and the steps to be taken to restore the facility to productive use and function after impact. 12 | COURSE DESCRIPTIONS SAM 280: Workplace Violation and Mediation - 3 CREDITS This course will seek to broaden the scope of the participant’s appreciation of the nature of work place violence, the causes and means of managing, reducing and resolving incidents, and their occurrence. It will also seek to heighten the awareness of the participants of the roles and the functions of the security practitioners in work place violence and conflict resolution and mediation. It will also seek to identify the benefits of mediation as a management tool in solving human relations problems in organizations. SAM 290: Computer Crime - 3 CREDITS This course is intended to help the student to distinguish assess and define the elements of computer crime, and to prepare a report on a case involving computer crime and evaluate some areas of vulnerability and critically and prescribe from as security perspective, risk reduction solutions. SAM 291: Industrial Espionage - 3 CREDITS This course provides a framework for understanding and protecting against industrial espionage. It reviews the history of industrial espionage, current methods of information elicitation, and explores counterespionage options to defend organizations. Students will also learn how companies place their proprietary and protected information at risk as well as how to prevent unwanted information disclosure. The laws regulating espionage and operational counterintelligence measures will be covered. The purpose of the course is to teach how to recognise and neutralise serious threats to both business and government entities. SAM 292: Conflict Resolution - 3 CREDITS This course teaches that conflict is no more than a byproduct of growth, change or innovation. Students are exposed to learning that in today’s rapidly changing work environment, managers, supervisors, and staff must address organizational change in an atmosphere of technological change, diversity, and conflicting modes of communication which tend to produce toxic results. Therefore, the course will allow students to explore conflicts and help them develop mediation and conflict resolution skills to address emergency workplace problems. That is, students will discover how to discuss issues reasonably and how to find common ground and learn that it takes a lot less energy and makes for a much more positive environment. SAM 300: Crisis Intervention - 3 CREDITS This course is an introduction to individual crisis intervention touching upon concepts and application of crisis intervention techniques and skills. It is applicable to those who perform peer support and professional counseling and therapeutic interventions with persons exposed to critical incidents. Supervisors and mangers will benefit from the course material in that they will be able to better able to communicate, understand and asses their workers and improve decision making about operational effectiveness and safety and the need for critical incident stress management (CISM) interventions. SAM 310: Bio-Terrorism - 3 CREDITS This course explores the incidence and threats of terrorism and an investigation of the security and law enforcement measures needed to combat it. Topics such as assassination, kidnapping, hijacking, extortion, sabotage, bomb threats/ searches, hostage negotiations, victims’ survival, and medical/tactical reaction teams will be discussed as they relate to executive protection and terrorism. SAM 340: Leadership in Security Administration - 3 CREDITS This course will provide students with a practical perspective of leadership. It’s about integrating theory and practice and creating a model and a set of related perspectives and concepts about how one can become a better leader. When combined with readings and research this course will serve as a pioneer effort to discuss leadership as applied to public and private security. SAM 350: Internship - 3 CREDITS This is a course in which students receive practical world of work experiences in the workplaces that are aligned with their field of studies. The components of the practical session will include: information session, workplace policies and procedures, workplace safety, business etiquette and ethics and actual work task performed at the place of internship. Students, are not only able to demonstrate proficiency in technical areas but also get opportunities to learn interpersonal skills and the basic understanding of business practices in their disciplines. A written report on the student’s performance during the internship will prepared and submitted to the College by the student’s supervisor or coordinator from which a grade will determined for the course. In addition, all interns will participate in general discussions with their Department Head on their internships. SAM 400: Principles of Crime Prevention - 3 CREDITS This course is concerned with crime prevention through opportunity reduction strategies in the physical environment and immediate situations in which crimes occur. The approach is seen as complimentary to other crime prevention strategies. The course begins by reviewing the field of situational crime prevention that has developed from rational choice and routine activity theories of crime. Close attention is paid to Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) and the creation of defensible space. The section reviews the theory and research related to these approaches, and examines a series of case studies of successful prevention projects. Students will also explore the concepts of situational prevention and CPTED to commercial and institutional settings from a security management perspective. Students will develop practical skills in the management of safety and loss prevention in private and public settings, centred on risk management procedures. They will conduct security risk assessments and developing a loss reduction and safety plan. SAM 410: Legal Aspects of Security - 3 CREDITS This course introduces students to the history on the 121 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS | 12 development of private security and the law. The students will explore the sources of authority which give the security professional powers to carry out his/her functions in saving lives and protecting assets. Areas of interest to the students in respect to their authority that will be taught will include state regulations, licensing, registration and training and matters pertaining to private law enforcement. Those areas of the law which prohibits the security professionals to act will be identified and discussed. SAM 420: Forensic Investigation - 3 CREDITS This course will provide the fundamental concepts of the application of science to criminal investigation and the role of science in the criminal justice system. Actual case histories will be discussed and students will learn how forensic science has impacted the ‘Crimes of the Century.’ Up-to-date technologies, such as DNA profiling and crime scene investigation: including the collection/recovery of forensic evidence from physical crime scenes, victims and suspects, the processing of evidence in the crime lab, and preservation of evidence for presentation in the courtroom will be discussed in detail. SAM 450 Monitoring and Evaluation of Security Programmes - 3 CREDITS The course is designed to equip students with the technical knowledge and application required to plan, designed to equip students with the technical knowledge and application required to plan, design and implement an effective result-based monitoring and evaluation system within any security organization. Deadlines assessment, development evaluation, performance indicators, data gathering, outcome measurement, and expectation gathering will from the principal focal points, within the contrast of security administration and management, of this course. SAM 460 Research Project - 5 CREDITS This course will provide students with the knowledge and skills to design an action research project related to the area of degree specialization. Students will examine methods of research in education in the social 122 sciences, research design and will include qualitative and quantitative approaches. Students will learn the steps and protocol associated with action research and will be required to design an action research proposal. SOCIOLOGY (SOC) SOC 100: Introduction to Sociology - 3 CREDITS This course intends to introduce the student to the discipline of sociology, its major theories and their relevance within contemporary society. It will also provide an array of conceptual tools as pre-requisites for insightful and rigorous analysis of the social world. SOC 110: Introduction to Industrial Sociology 3 credits A sociological study of industrial phenomena. It focuses on the analysis of industrial work organization and an understanding of their structure and function and the consequence for patterns and processes of interpersonal relationships at the work place. SPANISH (SPN) SPN 100: Introduction to Spanish - 3 CREDITS This course develops basic competencies in reading, writing, speaking and listening. The course seeks also to foster an appreciation of Hispanic culture. Students will learn words and phrases which would allow them to function in both a social and work setting. The course will be executed along thematic lines. Students will learn how to tell time, describe the weather, say something about oneself and one’s immediate family, career interests, and future goals. EXECUTIVE MANAGEMENT Professor Denise-Margaret Thompson, Director Ph.D., MSc., BSc., Ms. Eudine Job-Davis Manager Tobago, MBA Dr. Joseph Mills Deputy Director Student Services, D.Ed., MSc., BSc. Hezron Veerasammy MSc., BSc, M.E.T. Manager, Information & Communication Technology Mr. Curtis Daniel, Manager Human Resource & Administration Msc., Bsc., Mr. Brian-Anthony David, Manager, Quality Assurance BA, PGrad. Dip., ASQ-CMQ/OE 123 BOARD OF GOVERNORS 124 Mr. Lennox Marcelle Chairman Ms. Cecilia Greaves-Smith Board Member Mr Anand Tiwari Board Member Mr Aynsley Matthews Board Member Mr Trevor Johnson Board Member Mr. Karyl Adams Board Member Mr Michael Annisette Board Member Ms. Amarra-Lisa Ali Board Member