What is Haptics?
advertisement

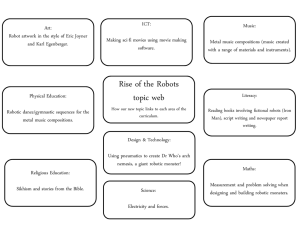
Course Content: A. ADVANCED ROBOTS ● ● What is an Exoskeleton? What is Haptics? Applications of Haptics? B. HAPTIC ARM ● ● ● ● Haptic glove Haptic sensing Applications Advantages C. ACTUATORS ● ● ● ● Types of actuators used in robotics Servo motors Why Servo motors? Servo motor control D. DESIGN CRITERIA ● ● ● ● ● D.O.F. (degree of freedom) Robot workspace Mobile manipulators Selecting an end-effector Motor selection criteria E. SENSORS ● ● ● ● ● Study of different types of sensors Haptic sensor Optical encoder Tactile sensor Hall effect sensor Feedback sensors KNOW YOUR CONTROLLER ● ● ● ● ● Introduction to Embedded C for AVR controllers Using an IDE Features of ATmega16 Programming your controller I/O pins, delay, LCD, Timers COMMUNICATION ● ● ● ● ● ● Wired Communication Wireless Communication (only discussion) HANDS ON Construction of the Robotic arm Construction of the Haptic suite Wired control of the Robotic arm using Haptic Suite/Glove Take away kit involves: 1. ARKDUINO circuit board ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● Micro Controller - ATMEL ATmega 8 Operating Voltage - 5V Input voltage - 6V-20V Digital I/O pins - 14 out of which 6 provide PWM Analog Input Pins - 8 DC Current per I/O pin - 40mA. Flash Memory - 16KB SRAM - 1KB EEPROM - 512Bytes Clock Speed 16 MHz USB-UART converter Proper Indicator LED's USB/ EXT input voltage 5V output supply pins - 3 3.3 V output supply pins - 1 Breadboard Compatibility (dimension of a 40 pin DIP IC) 2. D.C. Motor (3) 3. Potentiometer (3) 4. Robotic arm assembly (1set) 5. Robotic arm base (1set) 6. Haptics suit assembly (1set) 7. Battery for DC supply (3) 8. USB cable for programming (1) 9. Nuts, bolts, screw driver and many more Content developed in association with ARK Technosolutions.