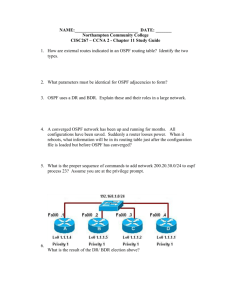
Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses – 2500 Series
advertisement

Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses – 2500 Series Objective • Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. • Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers (BDR) on the multiaccess network. • Configure loopback addresses for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) stability. • Assign each OSPF interface a priority to force the election of a specific router as DR. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, and 2600 or any such combination can be used. Please refer to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in the lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. Perform the following steps on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing. 94 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 1 Configure the routers On the routers, enter the global configuration mode and configure the hostname as shown in the chart. Then configure the console, virtual terminal and enable secret passwords. Next configure the interfaces according and the IP hostnames. Do not configure loopback interfaces and routing protocol yet. If there are any problems configuring the router basics, refer to the lab “Review of Basic Router Configuring with RIP”. Router1 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname LONDON LONDON(config)#enable secret class LONDON(config)#line console 0 LONDON(config-line)#password cisco LONDON(config-line)#login LONDON(config-line)#line vty 0 4 LONDON(config-line)#password cisco LONDON(config-line)#login LONDON(config-line)#exit LONDON(config)#interface ethernet 0 LONDON(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 LONDON(config-if)#no shutdown LONDON(config-if)#exit LONDON(config)#ip host OTTAWA 192.168.1.2 LONDON(config)#ip host BRASILIA 192.168.1.3 Router2 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname OTTAWA OTTOWA(config)#enable secret class OTTOWA(config)#line console 0 OTTOWA(config-line)#password cisco OTTOWA(config-line)#login OTTOWA(config-line)#line vty 0 4 OTTOWA(config-line)#password cisco OTTOWA(config-line)#login OTTOWA(config-line)#exit OTTOWA(config)#interface ethernet 0 OTTOWA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 OTTOWA(config-if)#no shutdown OTTOWA(config-if)#exit OTTOWA(config)#ip host LONDON 192.168.1.1 OTTOWA(config)#ip host BRASILIA 192.168.1.3 Router3 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname BRASILIA BRASILIA(config)#enable secret class BRASILIA(config)#line console 0 BRASILIA(config-line)#password cisco BRASILIA(config-line)#login BRASILIA(config-line)#line vty 0 4 BRASILIA(config-line)#password cisco 95 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. BRASILIA(config-line)#login BRASILIA(config-line)#exit BRASILIA(config)#interface ethernet 0 BRASILIA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 BRASILIA(config-if)#no shutdown BRASILIA(config-if)#exit BRASILIA(config)#ip host LONDON 192.168.1.1 BRASILIA(config)#ip host OTTAWA 192.168.1.2 Step 2 Save the configuration information for all the routers Why save the running configuration to the startup configuration? So that the router will keep the configuration when it is reset. Step 3 Configure the hosts with the proper IP address, subnet mask and default gateway Each workstation should be able to ping all of the attached routers. That is because they are all part of the same subnetwork. Troubleshoot as necessary. Remember to assign a specific IP address and default gateway to the workstation. If running Windows 98, check by using Start > Run > winipcfg. If running Windows 2000, check by using the ipconfig command in a DOS window. Host with gateway IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: London 192.168.1.4 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Host with gateway IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Ottawa 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2 Host with gateway IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Brasilia 192.168.1.6 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.3 Step 4 View the routers configuration and interface information a. At the privileged EXEC mode prompt type: show running-config b. Using the show ip interface brief command, check the status of each interface. c. What is the state of the interfaces on each router? London: Ethernet 0: Up Serial 0: Down Serial 1: Down Ottawa: Ethernet 0: Up Serial 0: Down Serial 1: Down Brasilia: Ethernet 0: Up Serial 0: Down 96 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Serial 1: Down Step 5 Verify connectivity of the routers a. Ping all of the connected FastEthernet interfaces from each other. b. Were the pings successful? Yes c. If the pings were not successful, troubleshoot the router configuration, until the ping is successful. Step 6 Configure OSPF routing on router London a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router London. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. London(config)#router ospf 1 London(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 London(config-router)#end b. Examine the London router running configuration file. c. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes/No d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands. London(config)#router ospf 1 London(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes London(config-router)#end e. Show the routing table for router: London#show ip route f. Are there any entries in the routing table? No g. Why? No other routers have been configured with OSPF. Step 7 Configure OSPF routing on router Ottawa a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router Ottawa. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Ottawa(config)#router ospf 1 Ottawa(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 Ottawa(config-router)#end b. Examine the Ottawa running configuration file. c. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes/No d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands. Ottawa(config)#router ospf 1 Ottawa(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes Ottawa(config-router)#end 97 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 8 Configure OSPF routing on router Brasilia a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router Brasilia. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Brasilia(config)#router ospf 1 Brasilia(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 Brasilia(config-router)#end b. Examine the Brasilia router running configuration file. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes/No c. What did it add? log-adjacency-changes d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands: Brasilia(config)#router ospf 1 Brasilia(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes Brasilia(config-router)#end Step 9 Test network connectivity a. Ping the Brasilia router from the London router. Was it successful? Yes/No b. If not troubleshoot as necessary. Step 10 Show OSPF adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on all routers to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. Is there a designated router identified? Yes c. Is there a backup designated router? Yes d. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor detail for more information. e. What is the neighbor priority of 192.168.1.1 from router Brasilia? 1 f. What interface is Identified as being part of Area 0? Ethernet0 Step 11 Configure the loopback interfaces Configure the loopback interface on each router to allow for an interface that will not go down due to network change or failure. This task is performed by typing interface loopback # at the global configuration mode prompt, where the # represents the number of the loopback interface from 0 2,147,483,647. London(config)#interface loopback 0 London(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.11 255.255.255.255 London(config-router)#end Ottawa(config)#interface loopback 0 Ottawa(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.22 255.255.255.255 Ottawa(config-router)#end Brasilia(config)#interface loopback 0 Brasilia(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.33 255.255.255.255 Brasilia(config-router)#end 98 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 12 Save the configuration information for all the routers After saving the configurations on all of the routers, power them down and back up again. 99 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 13 Show OSPF adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on all routers to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. Is there a designated router identified? Yes c. Write down the router ID and link address of the DR. 192.168.31.33 and 192.168.1.3 d. Is there a backup designated router? Yes e. Write down the router ID and link address of the BDR. 192.168.31.22 and 192.168.1.2 f. What is the third router referred to as? DROTHER g. Write down that Routers ID and link address. 192.168.31.11_and_192.168.1.1 h. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor detail for more information. i. What is the neighbor priority of 192.168.1.1 from router Brasilia? 1 j. What interface is Identified as being part of Area 0? Ethernet0 Step 14 Verify OSPF interface configuration a. Type show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0 on the London router. b. What is the OSPF state of the interface? DROTHER c. What is the default priority of the interface? 1 d. What is the network type of the interface? Broadcast Step 15 Configure London to always be the DR To ensure that the London router always becomes the DR for this multi-access segment, the OSPF priority must be set. London is the most powerful router in the network and so best suited to become DR. To assign the London loopback a higher IP address is not advised, as the numbering system has advantages for troubleshooting. Also London is not to act as DR for all segments to which it may belong. Set the priority of the interface to 50 on the London router only. London(config)#interface ethernet 0 London(config-if)#ip ospf priority 50 London(config-if)#end Display the priority for Interface ethernet 0 London#show ip ospf interface ethernet 0 Step 16 Watch election process a. To watch the OSPF election process restart all of the routers using the reload command. Be sure to save the running config before restarting the routers. As soon as the router prompt is available type: Ottawa>enable Ottawa#debug ip ospf events b. Which router was elected DR? London c. 100 - 577 Which router was elected BDR? Brasilia CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. d. Why? It has the higher Priority. e. To turn off all debugging type undebug all. Step 17 Show OSPF Adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on the Ottawa router to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. What is the priority of the DR? 50 Once the previous steps are completed log off by typing exit and turn the router off. Then remove and store the cables and adapter. 101 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed. 102 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Router Interface Summary Ethernet Ethernet Serial Serial Interface #1 Interface #2 Interface #1 Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) FastEthernet 0/0 2600 FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) (FA0/0) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface. Router Model 103 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Lab 2.3.2 Configuring OSPF with Loopback Addresses – 2600 Series Objective • Configure routers with a Class C IP addressing scheme. • Observe the election process for designated routers (DR) and backup designated routers (BDR) on the multiaccess network. • Configure loopback addresses for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) stability. • Assign each OSPF interface a priority to force the election of a specific router as DR. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the diagram. Any router that meets the interface requirements displayed on the above diagram may be used. For example, router series 800, 1600, 1700, 2500, and 2600 or any such combination can be used. Please refer to the chart at the end of the lab to correctly identify the interface identifiers to be used based on the equipment in the lab. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from 1721 series routers. Any other router used may produce slightly different output. Perform the following steps on each router unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all routers in this lab assignment before continuing. 104 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 1 Configure the routers On the routers, enter the global configuration mode and configure the hostname as shown in the chart. Then configure the console, virtual terminal and enable secret passwords. Next configure the interfaces according and the IP hostnames. Do not configure loopback interfaces and routing protocol yet. If there are any problems configuring the router basics, refer to the lab “Review of Basic Router Configuring with RIP”. Router1 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname LONDON LONDON(config)#enable secret class LONDON(config)#line console 0 LONDON(config-line)#password cisco LONDON(config-line)#login LONDON(config-line)#line vty 0 4 LONDON(config-line)#password cisco LONDON(config-line)#login LONDON(config-line)#exit LONDON(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 LONDON(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 LONDON(config-if)#no shutdown LONDON(config-if)#exit LONDON(config)#ip host OTTAWA 192.168.1.2 LONDON(config)#ip host BRASILIA 192.168.1.3 Router2 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname OTTAWA OTTOWA(config)#enable secret class OTTOWA(config)#line console 0 OTTOWA(config-line)#password cisco OTTOWA(config-line)#login OTTOWA(config-line)#line vty 0 4 OTTOWA(config-line)#password cisco OTTOWA(config-line)#login OTTOWA(config-line)#exit OTTOWA(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 OTTOWA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 OTTOWA(config-if)#no shutdown OTTOWA(config-if)#exit OTTOWA(config)#ip host LONDON 192.168.1.1 OTTOWA(config)#ip host BRASILIA 192.168.1.3 Router3 Router>enable Router#configure terminal Router(config)#hostname BRASILIA BRASILIA(config)#enable secret class BRASILIA(config)#line console 0 BRASILIA(config-line)#password cisco BRASILIA(config-line)#login BRASILIA(config-line)#line vty 0 4 BRASILIA(config-line)#password cisco 105 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. BRASILIA(config-line)#login BRASILIA(config-line)#exit BRASILIA(config)#interface fastethernet 0/0 BRASILIA(config-if)#ip address 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 BRASILIA(config-if)#no shutdown BRASILIA(config-if)#exit BRASILIA(config)#ip host LONDON 192.168.1.1 BRASILIA(config)#ip host OTTAWA 192.168.1.2 Step 2 Save the configuration information for all the routers Why save the running configuration to the startup configuration? So that the router will keep the configuration when it is reset. Step 3 Configure the hosts with the proper IP address, subnet mask and default gateway Each workstation should be able to ping all of the attached routers. That is because they are all part of the same subnetwork. Troubleshoot as necessary. Remember to assign a specific IP address and default gateway to the workstation. If running Windows 98, check by using Start > Run > winipcfg. If running Windows 2000, check by using the ipconfig command in a DOS window. Host with gateway IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: London 192.168.1.4 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 Host with gateway IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Ottawa 192.168.1.5 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2 Host with gateway IP Address: Subnet mask: Default gateway: Brasilia 192.168.1.6 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.3 Step 4 View the routers configuration and interface information a. At the privileged EXEC mode prompt type: show running-config b. Using the show ip interface brief command, check the status of each interface. c. What is the state of the interfaces on each router? London: FastEthernet 0: Up Serial 0: Down Serial 1: Down Ottawa: FastEthernet 0: Up Serial 0: Down Serial 1: Down Brasilia: FastEthernet 0: Up Serial 0: Down 106 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Serial 1: Down Step 5 Verify connectivity of the routers a. Ping all of the connected FastEthernet interfaces from each other. b. Were the pings successful? Yes c. If the pings were not successful, troubleshoot the router configuration, until the ping is successful. Step 6 Configure OSPF routing on router London a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router London. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. London(config)#router ospf 1 London(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 London(config-router)#end b. Examine the London router running configuration file. c. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes/No d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands. London(config)#router ospf 1 London(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes London(config-router)#end e. Show the routing table for router: London#show ip route f. Are there any entries in the routing table? No g. Why? No other routers have been configured with OSPF. Step 7 Configure OSPF routing on router Ottawa a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router Ottawa. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Ottawa(config)#router ospf 1 Ottawa(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 Ottawa(config-router)#end b. Examine the Ottawa running configuration file. c. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes/No d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands. Ottawa(config)#router ospf 1 Ottawa(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes Ottawa(config-router)#end 107 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 8 Configure OSPF routing on router Brasilia a. Configure an OSPF routing process on the router Brasilia. Use OSPF process number 1 and ensure all networks are in area 0. Brasilia(config)#router ospf 1 Brasilia(config-router)#network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 Brasilia(config-router)#end b. Examine the Brasilia router running configuration file. Did the IOS version automatically add any lines under router OSPF 1? Yes/No c. What did it add? log-adjacency-changes d. If there were no changes to the running configuration, type the following commands: Brasilia(config)#router ospf 1 Brasilia(config-router)#log-adjacency-changes Brasilia(config-router)#end Step 9 Test network connectivity a. Ping the Brasilia router from the London router. Was it successful? Yes/No b. If not troubleshoot as necessary. Step 10 Show OSPF adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on all routers to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. Is there a designated router identified? Yes c. Is there a backup designated router? Yes d. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor detail for more information. e. What is the neighbor priority of 192.168.1.1 from router Brasilia? 1 f. What interface is Identified as being part of Area 0? fastethernet0/0 Step 11 Configure the loopback interfaces Configure the loopback interface on each router to allow for an interface that will not go down due to network change or failure. This task is performed by typing interface loopback # at the global configuration mode prompt, where the # represents the number of the loopback interface from 0 2,147,483,647. London(config)#interface loopback 0 London(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.11 255.255.255.255 London(config-router)#end Ottawa(config)#interface loopback 0 Ottawa(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.22 255.255.255.255 Ottawa(config-router)#end Brasilia(config)#interface loopback 0 Brasilia(config-if)#ip address 192.168.31.33 255.255.255.255 Brasilia(config-router)#end 108 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 12 Save the configuration information for all the routers After saving the configurations on all of the routers, power them down and back up again. 109 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Step 13 Show OSPF adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on all routers to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. Is there a designated router identified? Yes c. Write down the router ID and link address of the DR. 192.168.31.33 and 192.168.1.3 d. Is there a backup designated router? Yes e. Write down the router ID and link address of the BDR. 192.168.31.22 and 192.168.1.2 f. What is the third router referred to as? DROTHER g. Write down that Routers ID and link address. 192.168.31.11 and 192.168.1.1 h. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor detail for more information. i. What is the neighbor priority of 192.168.1.1 from router Brasilia? 1 j. What interface is Identified as being part of Area 0? fastethernet0/0 Step 14 Verify OSPF interface configuration a. Type show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0 on the London router. b. What is the OSPF state of the interface? DROTHER c. What is the default priority of the interface? 1 d. What is the network type of the interface? Broadcast Step 15 Configure London to always be the DR To ensure that the London router always becomes the DR for this multi-access segment, the OSPF priority must be set. London is the most powerful router in the network and so best suited to become DR. To assign the London loopback a higher IP address is not advised, as the numbering system has advantages for troubleshooting. Also London is not to act as DR for all segments to which it may belong. Set the priority of the interface to 50 on the London router only. London(config)#interface Fastethernet 0/0 London(config-if)#ip ospf priority 50 London(config-if)#end Display the priority for Interface fastethernet 0/0. London#show ip ospf interface fastethernet 0/0 Step 16 Watch election process a. To watch the OSPF election process restart all of the routers using the reload command. Be sure to save the running config before restarting the routers. As soon as the router prompt is available type: Ottawa>enable Ottawa#debug ip ospf events b. Which router was elected DR? London c. 110 - 577 Which router was elected BDR? Brasilia CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. d. Why? It has the higher Priority. e. To turn off all debugging type undebug all. Step 17 Show OSPF Adjacencies a. Type the command show ip ospf neighbor on the Ottawa router to verify that the OSPF routing has formed adjacencies. b. What is the priority of the DR? 50 Once the previous steps are completed log off by typing exit and turn the router off. Then remove and store the cables and adapter. 111 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Erasing and reloading the router Enter into the privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. If prompted for a password, enter class. If that does not work, ask the instructor for assistance. Router>enable At the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command erase startup-config. Router#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files! Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete Now at the privileged EXEC mode, enter the command reload. Router#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. In the first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the router has reloaded the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started! Press Enter. Now the router is ready for the assigned lab to be performed. 112 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Router Interface Summary Ethernet Ethernet Serial Serial Interface #1 Interface #2 Interface #1 Interface #2 800 (806) Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) 1600 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 1700 FastEthernet 0 (FA0) FastEthernet 1 (FA1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) 2500 Ethernet 0 (E0) Ethernet 1 (E1) Serial 0 (S0) Serial 1 (S1) FastEthernet 0/0 2600 FastEthernet 0/1 (FA0/1) Serial 0/0 (S0/0) Serial 0/1 (S0/1) (FA0/0) In order to find out exactly how the router is configured, look at the interfaces. This will identify what type and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all of the combinations of configurations for each router class. What is provided are the identifiers for the possible combinations of interfaces in the device. This interface chart does not include any other type of interface even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in IOS command to represent the interface. Router Model 113 - 577 CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v 3.1 - Lab 2.3.2 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.