Page 1 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World
advertisement

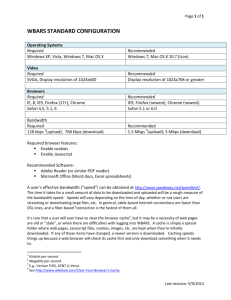
GOALS Understand the differences between the Internet and the World Wide Web Use a web browser to find and open websites Navigate using links, the back button, and the forward button Use bookmarks and browsing history to find favorite sites The Internet, at its most basic level, is simply a network of connected computers. According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the Internet is “a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities, consisting of interconnected networks using standardized communication protocols.” Like personal computers, the Internet exists based on the integration of computer hardware and software. The term Internet is commonly used to describe two basic concepts in computer networking: 1) In terms of computer hardware, the Internet is a physical network of computers and server systems that connect with one another in order to transfer information. 2) In terms of computer software, the Internet is a method of transmitting information across long distances based on a certain set of protocols and programs. The term originated in the 1970s to describe a computer network that combined two or more smaller networks. The Internet as we know it originated with the United States Department of Defense in the late 1960s. ARPANET was developed to facilitate research at government and educational facilities coordinated through the DOD. The first communication over what would become the Internet was sent between UCLA and Stanford University on October 29, 1969. Page 1 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 The introduction of commercial online services from companies like CompuServe and America Online (AOL) expanded the reach of the Internet outside of the academic community in the late 1980s and early 1990s. The World Wide Web was launched in 1991. Through applications such as web browsers, individual computer users can access information that resides on other computers, outside of the information stored locally on their own computers. In this way, the Internet is a fairly simple concept – users join a common network of computers so they can access and share information with other users, organizations, businesses, and governments. Likewise, information sharing across the Internet is a fairly simple concept also – information received from other computers is downloaded to an individual user’s computer, and information sent to other computers is uploaded and distributed across the Internet to a specific destination computer. People commonly use the terms upload and download to refer to sending and receiving specific files across the Internet, such as songs or pictures. In actuality, all information exchanged across the Internet is both uploaded and downloaded. The content of any web page viewed through a web browser is downloaded to an individual user’s computer, and any information transmitted by an individual user us uploaded through the Internet to a specific destination. Today, when most people speak of the Internet, they really mean the World Wide Web (WWW). While the Internet consists of the hardware and software used to transmit and receive information across a global network of computers, the World Wide Web refers to the majority of the information resources available through the Internet. These resources include a vast number of documents, images, and multimedia that form a “web” of information available to users who access shared information through the Internet. The Internet consists of a group of interconnected computers, while the World Wide Web consists of an array of interconnected information. World Wide Web pages, or simply web pages, contain information content that is accessed through the Internet. Page 2 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 One of the most common software applications used on computers is a web browser, which allows you to access the Internet and view web pages. The built-in web browser distributed with Microsoft Windows is called Internet Explorer. This browser is very popular and widely used because of the dominance of the Windows operating system. However, there are several other popular web browsers: Chrome is a free, open-source web browser developed by Google. Firefox is a free, open-source web browser developed by Mozilla. Safari is a free web browser developed by Apple Inc. (available for Macintosh and Windows personal computers) Most web browsers work similarly and operate in a very simple manner through which a website address (or URL) is entered into the address bar of the browser, and web pages are displayed accordingly. Web page links can be followed easily by navigating the mouse pointer to displayed links and buttons, and then clicking on them with the left mouse button. 1 Navigation buttons allow you to move backward and forward through previously viewed web pages. The 2Refresh or Reload button updates the web page to show any recent changes. The 3Home button loads the specified home page (the same page that appears when first opening the browser). 4 Tabs are a feature included in all newer web browsers. Tabs allow users to open multiple web pages within the same browser window and access the pages by clicking on the corresponding tabs. Google Chrome ❸ Mozilla Firefox Microsoft Internet Explorer Page 3 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 While browsing web pages, you will encounter a variety of hyperlinks (commonly just “links”) that move to other areas of a web page, lead to other web pages, open or activate certain types of visual or audio content, or allow you to upload or download files. The standard format for links is blue, underlined text: www.washoecountylibrary.us. However, the many varieties of web page design are making this standard less common. Also, when graphics and pictures are used as links, it can be difficult to distinguish whether or not certain images on a web page work as links. The good news is that regardless of whether or not there is any visual indication for a link, most web browsers change the mouse pointer icon to a hand with an extended forefinger when the pointer is moved to a link. Most web browsers allow you to save the addresses of websites that you visit for easy retrieval later on. In Internet Explorer, this is called adding a site to your favorites list. In Firefox, this is called bookmarking a page. While on the web page that you would like to save in Internet Explorer, select the Favorites pull-down menu and click on “add to favorites.” In Firefox, while on the web page that you would like to save, select the Adding favorites in Microsoft Internet Explorer Bookmarks pull-down menu and click on “bookmark this page.” Either browser will allow you to alternately use the keyboard shortcut CTRL+D. Adding bookmarks in Mozilla Firefox To retrieve saved website addresses, simply return to the favorites or bookmarks pull-down menu and you will see your saved sites listed. You can also create subfolders to organize your website addresses into separate categories. In Internet Explorer, select organize favorites; in Firefox, select organize bookmarks. Page 4 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 In addition to saving and retrieving web pages through favorites or bookmarks, you can save one or more home page(s), which will be the first website(s) loaded when you launch your web browser. In Internet Explorer, select “Add or change home page” from the Home Page pull-down menu. Alternately, go to the Tools pull-down menu and choose “Internet Options.” This method will open the Internet options dialog box. The first tab is called “General,” and the first section allows you to set a home page. In Firefox, go to the Tools pull-down menu and choose “Options.” This will open the options dialog box. The first tab is called “General,” and the first section allows you to set a home page. Setting a Home Page in Internet Explorer Setting a Home Page in Mozilla Firefox NOTE: Usually, it is easiest to first navigate to the website that you want to set as your home page, then go to the Internet options dialog box (Internet Explorer) or options dialog box (Firefox) and click on the use current or use current page button. It is also possible in most browsers to set a home page by dragging and dropping the current URL (displayed in the address bar) onto the Home Page button. Using the Home Page button’s pull-down menu to set a home page in Internet Explorer Page 5 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 The World Wide Web is truly an amazing resource of vast amounts of information that literally grows each day. Accessing, filtering, and reviewing the information content available from the web is primarily done with the help of a search engine. Search engines are typically accessed through a web portal or web page and allow users to enter keywords that relate to particular items of interest. Search engines are complex programs that perform automatic data mining to return relevant web pages, information, images, and videos that match keyword searches initiated by users. Bing (from Microsoft; formerly MSN), Google, and Yahoo are three of the most popular, although there are many other general and specialized search engines. Typically, users conduct two types of information searches: 1) keyword searches and 2) phrase searches. Keyword searches are accomplished by entering one or more words that relate to a subject area of interest. This is the most common type of search conducted on the Internet. Results from search engines, called hits, are typically ranked so that the most relevant, widely viewed, and/or most popular results are shown first, with subsequent hits listed in decreasing relevance and popularity. Each search engine develops its own algorithms to determine relevance and rank, so the top search results from one search engine will not necessarily being the same on each search engine. A simple search for the word ‘frogs’ on Google (left) and Bing (right) Page 6 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 A search for the keywords ‘frogs,’ ‘life,’ & ‘cycle’ on Google (left) and Yahoo (right) Many search engines use predictive text to suggest common searches related to keywords of interest. For the above search on frogs, Google suggested an array of related keywords, including the multiple keyword search for frogs life cycle: Many Internet users are not aware that exact phrase searches, using quotation marks, can be conducted to help find original sources for things such as poems, books, and lyrics: Page 7 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 Because of the proliferation of Internet crimes, it is important for computer users to evaluate search results to ensure that they are connecting to reputable websites. While most illegitimate websites are linked to through spam and phishing schemes, unfortunately there are many that offer poor quality merchandise and services, charge inflated prices, have very poor return policies, and/or poor customer service. There are several questions you can ask yourself to help determine if you have connected to a legitimate website: Is the site operated by a well-known, reputable government entity, organization, or business? Examples: usa.gov, redcross.org, amazon.com Does the site demonstrate competent web design? Sometimes the signs of illegitimate organizations and scam websites include poor page design, noticeable misspellings, and dead links. Are there few or no pop-up advertisements? Again, many disreputable websites will launch multiple pop-up ads that fill up your screen, causing confusion to entice you into clicking on purchase offers that you do not want or need, or to prevent you from exiting the site. Does the site include standard contact information or a clearly identified way to contact the business or organization? Although some websites operate as web-only businesses, reputable sites should have links such as About Us, Contact Us, or Location(s) that provide an address, telephone number, and/or email contact information. If the site sells goods, services, or subscriptions, is there a clearly identified way to contact customer service and are there links that clearly explain return policies, cancellation, or requests for refunds? If the site provides site-based or subscription services, are there links that explain the terms of services (TOS)? This is especially important for users of free e-mail services, because there are always rules and restrictions for the use of site-based services that should be made accessible to users. The Internet can be accessed in number of ways. Broadband service provided through an Internet Service Provider (ISP) is the most common way home users access the Internet. Users pay a monthly subscription fee to an ISP that provides Internet access through broadband service, and less frequently through a dial-up connection. Dial-up Internet service is often considered an outdated and soon-to-beeliminated approach to Internet access. For many people, however, due to the lack of telecommunication infrastructure in rural parts of the US, dial-up service may be the only option available. Page 8 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 A modem is required regardless of whether you have dial-up or broadband service. A cable modem is an external piece of hardware that enables information to be exchanged across existing cable television infrastructure. A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is an external piece of hardware that enables information to be exchanged across existing telephone lines. There are two primary differences between dialup service and DSL service: 1) Much higher speed is available through DSL service, and 2) DSL modems do not require exclusive access to the phone line, so phone calls can be made and received while accessing the Internet. Similar to a cable modem, the phone line that brings telephone service into a home is attached to the DSL modem, and an Ethernet cable links the DSL modem to the computer or router. In some cases, cable and DSL modems use a USB connection to link the modem to the computer, instead of an Ethernet cable. It is also very common for home broadband subscribers to set up a wireless local area network (LAN) to allow for wireless Internet access inside their home. This requires connecting a cable modem or DSL modem to a wireless router, which makes Internet connections available wirelessly to desktop computers and laptops that are equipped with a wireless network card. Many people access the Internet through free services provided by schools, libraries, and businesses. At schools and libraries, access is typically provided through an existing computer network. Individuals can use computers linked to the Internet which are made available for certain periods of time allowed by the organization. Users who have laptops with a wireless network card can often access the Internet for longer periods of time through schools and libraries because they provide their own equipment. The proliferation of wireless Internet access through businesses has come to be known as Wi-Fi service. Technically, Wi-Fi is a certification given to certain companies whose products meet wireless networking standards that ensure compatibility across the many types of wireless equipment available. However, the term has become broadly used to indicate the availability of wireless Internet access at certain locations, regardless of whether the equipment is certified. Many businesses advertise Wi-Fi hotspots to attract customers to whatever goods or services that they sell. This is very common at libraries, airports, hotels, restaurants, and coffee shops. Users should be careful because occasionally these wireless networks are only available for a fee. Also, the risk of a personal computer security breach is greater at a public location where many unknown users may access the network at any given time. Page 9 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13 www.gcflearnfree.org/Internet101 www.gcflearnfree.org/Internet/module/3 www.bbc.co.uk/webwise/courses/Internet-basics/ www.bbc.co.uk/webwise/accredited-courses/level-one/using-the-Internet www.bbc.co.uk/webwise/topics/using-the-web/ www.gcflearnfree.org/chrome www.gcflearnfree.org/mozillafirefox www.gcflearnfree.org/Internetexplorer8 www.bbc.co.uk/webwise/topics/using-the-web/using-a-browser www.gcflearnfree.org/informationsavvy www.gcflearnfree.org/google/module/8 www.bbc.co.uk/webwise/topics/using-the-web/searching www.gcflearnfree.org/Internetsafety www.gcflearnfree.org/Internetsafetyforkids www.bbc.co.uk/webwise/accredited-courses/level-one/keeping-safe-online Page 10 | Basic Computer Skills Series: The Internet and the World Wide Web Content based on: Zeiser, A. (2009). Introduction to Internet. Reno, NV: AZ Consulting. REV 2/13