6th Grade Vocabulary
advertisement
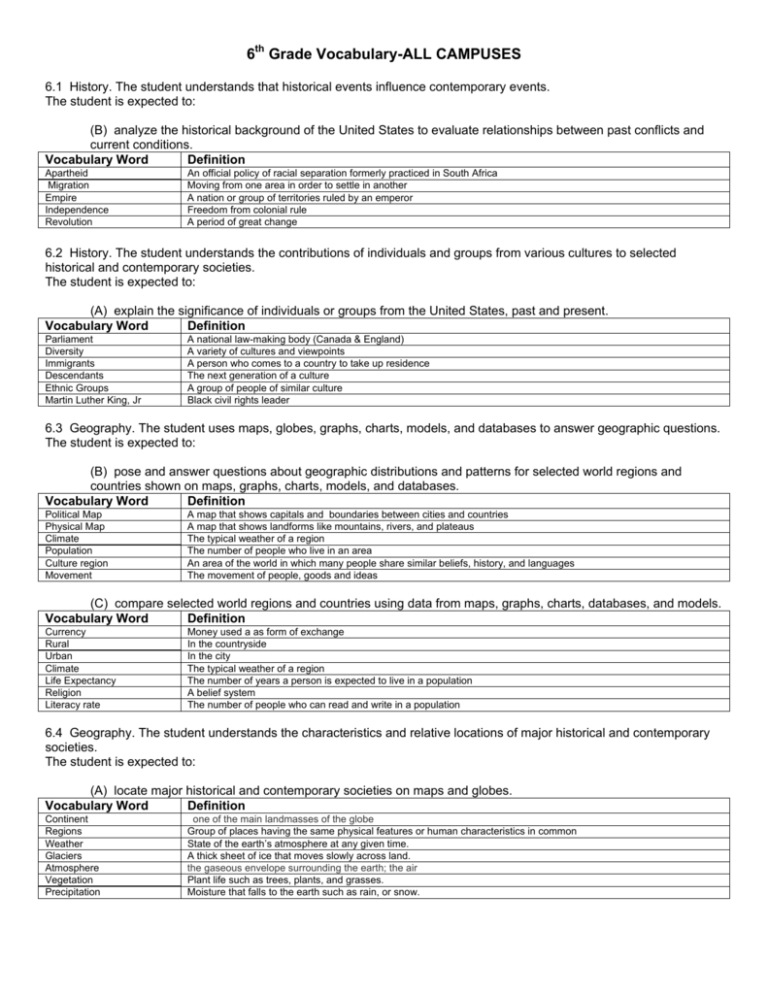
6th Grade Vocabulary-ALL CAMPUSES 6.1 History. The student understands that historical events influence contemporary events. The student is expected to: (B) analyze the historical background of the United States to evaluate relationships between past conflicts and current conditions. Vocabulary Word Definition Apartheid Migration Empire Independence Revolution An official policy of racial separation formerly practiced in South Africa Moving from one area in order to settle in another A nation or group of territories ruled by an emperor Freedom from colonial rule A period of great change 6.2 History. The student understands the contributions of individuals and groups from various cultures to selected historical and contemporary societies. The student is expected to: (A) explain the significance of individuals or groups from the United States, past and present. Vocabulary Word Definition Parliament Diversity Immigrants Descendants Ethnic Groups Martin Luther King, Jr A national law-making body (Canada & England) A variety of cultures and viewpoints A person who comes to a country to take up residence The next generation of a culture A group of people of similar culture Black civil rights leader 6.3 Geography. The student uses maps, globes, graphs, charts, models, and databases to answer geographic questions. The student is expected to: (B) pose and answer questions about geographic distributions and patterns for selected world regions and countries shown on maps, graphs, charts, models, and databases. Vocabulary Word Definition Political Map Physical Map Climate Population Culture region Movement A map that shows capitals and boundaries between cities and countries A map that shows landforms like mountains, rivers, and plateaus The typical weather of a region The number of people who live in an area An area of the world in which many people share similar beliefs, history, and languages The movement of people, goods and ideas (C) compare selected world regions and countries using data from maps, graphs, charts, databases, and models. Vocabulary Word Definition Currency Rural Urban Climate Life Expectancy Religion Literacy rate Money used a as form of exchange In the countryside In the city The typical weather of a region The number of years a person is expected to live in a population A belief system The number of people who can read and write in a population 6.4 Geography. The student understands the characteristics and relative locations of major historical and contemporary societies. The student is expected to: (A) locate major historical and contemporary societies on maps and globes. Vocabulary Word Definition Continent Regions Weather Glaciers Atmosphere Vegetation Precipitation one of the main landmasses of the globe Group of places having the same physical features or human characteristics in common State of the earth’s atmosphere at any given time. A thick sheet of ice that moves slowly across land. the gaseous envelope surrounding the earth; the air Plant life such as trees, plants, and grasses. Moisture that falls to the earth such as rain, or snow. (B) identify and explain the geographic factors responsible for patterns of population in places and regions. Vocabulary Word Definition Elevation Climate Economy Region Agriculture Adaptation Landform the altitude of a place above sea level or ground level A typical weather of a region. The system by which business owners in a region use productive resources to provide goods and services to provide peoples’ wants. Group of places having the same physical features or human characteristics in common Farming In ability to modify, in order to survive in a particular environment A feature of the earth’s surface such as a mountain, valley, or plateau. (C) explain ways in which human migration influences the character of places and regions. Vocabulary Word Definition Immigration Emigration Immigrant The process of moving to a new country to take up residence The process of moving from one country to take up residence in another A person that comes to a country to take up residence (D) identify and explain the geographic factors responsible for the location of economic activities in places and regions. Vocabulary Word Definition Equal opportunity Population density Diversity A guarantee that government and private institutions and will not discriminate against people on the basis of factors such as race, religion, age, or gender. the number of people living per unit of an area (e.g. per square mile); the number of people relative to the space occupied by them A variety of culture and view points. 6.5 Geography. The student understands how geographic factors influence the economic development, political relationships, and policies of societies. The student is expected to: (A) explain factors such as location, physical features, transportation corridors and barriers, and distribution of natural resources that influence the economic development and foreign policies of societies. Vocabulary Word Definition Diversity Migration Population Density Equal Opportunity Fertile Landform Physical Features A variety of cultures and viewpoints Movement of one area in order to settle in another the number of people living per unit of an area (e.g. per square mile); the number of people relative to the space occupied by them Guarantee against ageist discrimination on basis of race, religion, age or gender Rich in resources and nutrients Feature of the Earth’s surface, such as a mountain, valley, or a plateau landforms, bodies of water, climate, natural vegetation and soil 6.7 Geography. The student understands the impact of interactions between people and the physical environment on the development of places and regions. The student is expected to: (A) identify and analyze ways people have adapted to the physical environment in selected places and regions. Vocabulary Word Definition Region Adaptation Agriculture Renewable Resources Non-Renewable Resources Irrigation Group of places having the same physical features or human characteristics in common In ability to modify, in order to survive in a particular environment the science of cultivating land, raising crops, and feeding, breeding, and raising livestock; farming Resource that can be used and replace over a short period of time Resource that can only be replaced over millions of years The process of bringing water to dry land 6.11 Government. The student understands the concepts of limited governments, such as constitutional and democratic governments, and unlimited governments, such as totalitarian and non democratic governments. The student is expected to: (A) describe characteristics of limited and unlimited governments. Vocabulary Word Definition Limited Government a type of government in which its functions and powers are prescribed, limited, and restricted by law Unlimited Government Type of government in which the leaders have almost absolute power (B) identify examples of limited and unlimited governments. Vocabulary Word Definition Monarchy Constitutional Monarchy Absolute Monarchy Dictatorship Tyranny Democracy Oligarchy Government ruled by a king or queen Government ruled by a king or queen whose power is determined by the nation’s constitution and laws a monarchy that is not limited or restrained by laws or a constitution Government ruled by one person who has complete control over a country’s government r arbitrary or unrestrained exercise of power; despotic abuse of authority Government that receives its power from the people Republic Government in which power belongs to the citizens, who govern themselves through elected representatives Government in which a group of selected individuals, aristocrats, make the decisions (C) identify reasons for limiting the power of government. Vocabulary Word Definition Bill of Rights Amendment Checks and Balances Federal System Citizen Branches of Government a formal statement of the fundamental rights of the people of the United States, incorporated in the Constitution as Amendments 1–10, and in all state constitution an alteration of or addition to a motion, bill, constitution, etc The “checking” of powers of the branches of government National system of government Legal member of a country In the US, consists of the Legislative, Executive, and Judicial branches; separates the power of government (D) compare limited and unlimited governments. Vocabulary Word Definition Germany United States Sparta Athens country controlled in WWII by a dictator country ruled under democracy ruled under an oligarchy one of the first places with a democratic form of government 6.12 Government. The student understands alternative ways of organizing governments. The student is expected to: (B) identify examples of governments with rule by one, few, or many. Vocabulary Word Definition Monarchy Constitutional Monarchy Dictatorship Democracy Republic Oligarchy Government ruled by a king or queen Government ruled by a king or queen whose power is determined by the nation’s constitution and laws Government ruled by one person who has complete control over a country’s government Government that receives its power from the people Government in which power belongs to the citizens, who govern themselves through elected representatives Government in which power belongs to a few citizens called aristocrats (C) identify historical origins of democratic forms of government. Vocabulary Word Definition Athens City-state Polis Developed form of democratic government Central city and it’s surrounding villages that follow the same laws, have one form of government and share culture traits Central city in a city state 6.14 Citizenship. The student understands the relationship among individual rights, responsibilities, and freedoms in democratic societies. The student is expected to: (B) explain relationships among rights and responsibilities in democratic societies. Vocabulary Word Definition Democracy Government Bill of Rights Constitution Individual Rights Citizenship Citizen Republic Political Process Equal Opportunity A government that receives its power from the people The people and groups within a society that have the authority to make laws, to make sure they are carried out, and to settle disagreements about them. Ten amendments to the US Constitution that list specific freedoms guaranteed to every US citizen the system of fundamental principles according to which a nation, state, corporation, or the like, is governed, and the document which outlines them. The status of a citizen, which includes certain duties and rights A legal member of a country A nation in which power belongs to the citizens, who govern themselves through elected representatives Legal activities through which a citizen influences public policy A guarantee that government and private institutions will not discriminate against people on the basis of factors such as race, religion, age, or gender 6.19 Culture. The student understands the relationships among religion, philosophy, and culture. The student is expected to: (A) explain the relationship among religious ideas, philosophical ideas, and cultures. Vocabulary Word Definition globatlization Culture Cultural trait Value Multi-lingual Civilization Migration Diversity Spreading around the world The belief, customs, laws, art, and ways of living that group of people share. The food, clothing, technology, beliefs, language, and tools that the people of a culture share. A principle or ideal by which people live. The ability to speak more than one language. an advanced state of human society, in which a high level of culture, science, industry, and government has been reached Movement from one area in order to settle in another. Variety of cultures and viewpoints. 6.20 Science, technology, and society. The student understands the relationships among science and technology and political, economic, and social issues and events. The student is expected to: (A) give examples of scientific discoveries and technological innovations, including the roles of scientists and inventors. Vocabulary Word Definition Revolution Capitalism Industry Labor force Scientific revolution Irrigation Technology A fundamental change in the way of thinking about or visualizing something An economic system in which the factories and business that make and sell goods are privately owned and the owners make the decisions about what goods to produce. Any area of economic activity. A pool of available workers. th th A period of great scientific change and discovery during the 16 and 17 centuries. The process of bringing water to dry land. Tools and equipment made through scientific discovery 6.21 Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of sources including electronic technology. The student is expected to: (A) differentiate between, locate, and use primary and secondary sources such as computer software; interviews; biographies; oral, print, and visual material; and artifacts to acquire information about selected world cultures. Vocabulary Word Definition Primary Sources Secondary Sources Artifact Archaeology A first hand account or document of an event or time Sources that interpret, analyze or summarize primary sources a handmade object, as a tool, or the remains of one, as a shard of pottery, characteristic of an earlier time or cultural stage, esp. such an object found at an archaeological excavation the scientific study of historic or prehistoric peoples and their cultures by analysis of their artifacts, inscriptions, monuments, and other such remains, esp. those that have been excavated. (B) analyze information by sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions. Vocabulary Word Definition (C) organize and interpret information from graphs, charts, timelines, and maps. Vocabulary Word Definition Latitude Longitude Scale Political Map Physical Map Thematic Map Compass Rose Cardinal Directions Intermediate Directions Population Density Distribution Map Elevation Coordinates Absolute Location Relative Location Map Projection Equator A measure of distance north or south of the equator A measure of distance east or west of a line called the prime meridian A tool used for measuring distance A map showing the political boundaries between countries A map showing the landforms and physical features of an area A map that focuses on a specific idea or theme a circle graduated to degrees or quarters and printed on a chart to show direction The four primary points of the compass: north, east, south, and west. compass directions located halfway between the cardinal directions the number of people living per unit of an area (e.g. per square mile); the number of people relative to the space occupied by them A map shows dispersed population How far above or below sea level an area is The numeric location of a place based on longitude and latitude The exact spot on Earth where a place is found The location of one place in relation to other places One of the difference ways of showing Earth’s curved surface on a flat map a great circle of the earth or a celestial body that is everywhere equally distant from the two poles and divides the surface into the northern and southern hemispheres