Ancient Near East 900 – 500 BC More monarchy and empire
advertisement

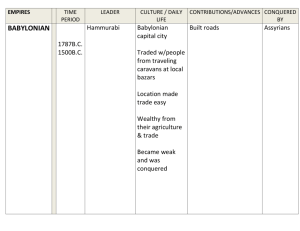
Ancient Near East 900 – 500 BC New Assyria New Babylon Persian Empire More monarchy and empire Crisis of 1200-1000 BC Sea peoples Systems collapse Near East Empires rise and fall Search for more territory, more wealth 1 New Assyria 900 BC – reemergence of Assyria Desire for metals, land, sea trade routes Militaristic Foot soldiers more important Technology – siege towers, battering rams Chariot archers Conquered peoples – annual tribute Raw material, luxury goods Incense, wine, dyed linens, glass, ivory Assyrian culture Male-dominated Sennacherib r. 704-681 BC Lion hunt Irrigation equipment Metal casting Rebellion Medes and Chaldeans destroyed Nineveh 612 BC 2 LION GATE CHALDEANS Neo-Babylonians Nebuchadnezzar II 4 605-562 BC Defeated Egyptians Carchemish 605 BC Chief god – Marduk 3 Ishtar Gate Rise of Persia Cyrus r. 559-530 BC Defeats Medes Babylon 539 BC Religious tolerance Darius I r. 522-486 BC Extends empire Satraps Courier system 4 Persepolis today 5 Zoroastrianism Prophet Zarathustra Dualism Good and evil Humans decide between purity – impurity Salvation or damnation Hebrews Hebrew Monotheism c. 1000-539 BC History of the Hebrews unclear Abraham from Ur to Palestine Joseph – Egypt 1600-1400 B C Moses c. 1250 BC Covenant – obedience led to safety and prosperity, disobedience punished’ Ten commandments After 1000 BC – fully developed monotheism Solomon – r. c. 965-928 BCE No social differentiation No vicarious punishment Trade Temple Monarchy splits – Israel and Judah 6 Israel and Judah Israel conquered by Assyrians in 722 BC Nebuchadnezzar II conquered Judah 597 BC Babylonian captivity Cyrus Return to Palestine Rebuild temple Judaism Influence on Christianity and Islam Importance of scripture Required ritual and ethical purity with regulation of all aspects of life Jews retained identity through religious observance 7