1. The azide ion, N3 -, is linear with two NN bonds
advertisement
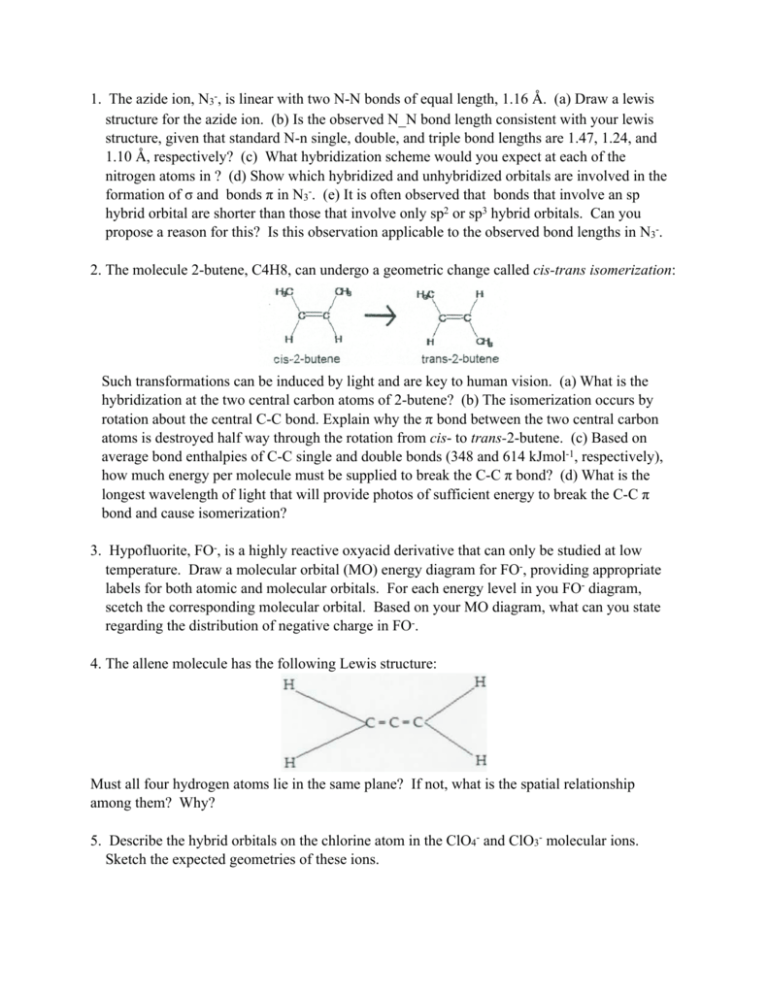
1. The azide ion, N3-, is linear with two N-N bonds of equal length, 1.16 Å. (a) Draw a lewis structure for the azide ion. (b) Is the observed N_N bond length consistent with your lewis structure, given that standard N-n single, double, and triple bond lengths are 1.47, 1.24, and 1.10 Å, respectively? (c) What hybridization scheme would you expect at each of the nitrogen atoms in ? (d) Show which hybridized and unhybridized orbitals are involved in the formation of σ and bonds π in N3-. (e) It is often observed that bonds that involve an sp hybrid orbital are shorter than those that involve only sp2 or sp3 hybrid orbitals. Can you propose a reason for this? Is this observation applicable to the observed bond lengths in N3-. 2. The molecule 2-butene, C4H8, can undergo a geometric change called cis-trans isomerization: Such transformations can be induced by light and are key to human vision. (a) What is the hybridization at the two central carbon atoms of 2-butene? (b) The isomerization occurs by rotation about the central C-C bond. Explain why the π bond between the two central carbon atoms is destroyed half way through the rotation from cis- to trans-2-butene. (c) Based on average bond enthalpies of C-C single and double bonds (348 and 614 kJmol-1, respectively), how much energy per molecule must be supplied to break the C-C π bond? (d) What is the longest wavelength of light that will provide photos of sufficient energy to break the C-C π bond and cause isomerization? 3. Hypofluorite, FO-, is a highly reactive oxyacid derivative that can only be studied at low temperature. Draw a molecular orbital (MO) energy diagram for FO-, providing appropriate labels for both atomic and molecular orbitals. For each energy level in you FO- diagram, scetch the corresponding molecular orbital. Based on your MO diagram, what can you state regarding the distribution of negative charge in FO-. 4. The allene molecule has the following Lewis structure: Must all four hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane? If not, what is the spatial relationship among them? Why? 5. Describe the hybrid orbitals on the chlorine atom in the ClO4- and ClO3- molecular ions. Sketch the expected geometries of these ions. 6. Predict the hybrid orbitals used by the sulfur atom(s) in each of the following. Also predict the molecular structure, including bond angle(s). a. SO2 b. SO3 c. S2O32d. S2O82e. SO32f. SO42g. SF2 h. SF4 i. SF6 j. F3S—SF