1 Cytoskeleton
advertisement

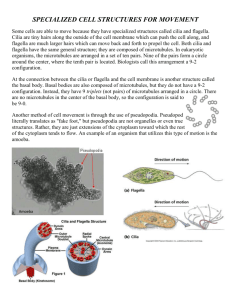
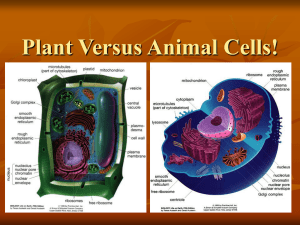
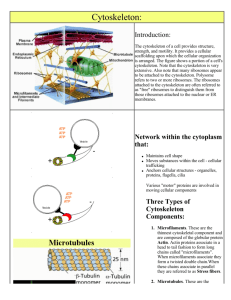
Depat.Anat. Cytology Dr.sarab H. Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton is the supportive structure of the cell. Moreover cytoskeleton of mammalian cell is responsible for cell shape, dynamic organization of cytoplasm, transport of information through the cell and formation of pseudopodia, as well as phagocytosis or exocytosis It includes: 1. Microtubules 2. Microfilaments 3. Intermediate filaments 1-Microtubules They are hollow tubules (cylinders) formed of 13 parallel arranged protofilaments. Each one consists of α- and β- tubulin subunits. Polarity characterizes the microtubules. They have plus end that elongates more rapidly, and minus end attached to microtubule organizing centre (MTOC) in centrosome. Organization: Single microtubules are distributed within the cytoplasm. Also, microtubules are found in form of doublets; two attached tubules as in motile cilia or in group of three tubules forming triplets of centrioles or basal bodies. Functions of microtubules 1-Maintain cell shape. 2-Form mitotic spindle during cell division. 3-Hold the organelles in their places. 4-Form tracks for the movement of intracellular organelles. 5-Form core of motile cilia and flagella for the cell movement. Microtubules Associated Proteins (MAPS): a) Fibrous MAPs: Fibrous MAPs are special type of proteins that cross-link the microtubule. They help in the bundle formation of aggregated parallel microtubules. a) Motors: There are two types MAPs behaving like machines or motors that are able to move along the microtubules: Kinesin and Dynein. These motors use the energy resulted from hydrolysis of ATP to move along the microtubules. Kinesin moves an organelle towards the plus end of microtubule. It attaches to receptor on the organelle, and then walks along microtubule toward the plus end to transport the organelle . 1 Dynein likes the kinesin. It moves the organelle toward minus end of microtubules. Structures are formed of microtubules: a. Centrosome b. Motile cilia c. Flagella Centrosome It is formed of two centrioles . Centrioles A pair of small, cylindrical organelles located at right angles to each other near the nucleus in cytoplasm of animal cells. Functions: Centrioles act as microtubule organizing center (MTOC, MT assembly) and form the mitotic spindle in metaphase of cell division. Ultrastructurally, each centriole is in the form of a cylinder composed of 9 triplets of microtubules (9 x 3) . Centrioles play an important role in the formation of various cellular structures that are made up of microtubules. These include the mitotic spindles of dividing cells, cilia, flagella, and some projections of specialized cells( the axial filaments of spermatozoa). Projections from the cell surface Motile Cilia and Flagella They are cylindrical extensions of plasma membrane provided by core of 9 doublets and 2 central single MT. They are formed by basal bodies (9x3 MT). By help of dynein and ATP hydrolysis they can bend by sliding past each other and results in regular movement of the motile cilia. The free part of each cilium is called the shaft . the region of attachment to the cell surface is called the base . Each cilium is 0.25µm in diameter . It consists of an outer covering that is formed by an extension of the membrane , and an inner core that is made by microtubules arranged in a definite manner. Functional significance of cilia: The cilia lining an epithelial surface move in coordination with one another the total effect being that like a wave . As result fluid , mucous , small solid objects can be moved in a specific direction . Examples: Cilia of respiratory tract (move the mucous secretion over the epithelial surface). In some situation there are cilia-like structures that perform a sensory function.They may be non-motile, but can be bent by external influences. Such cilia present on the cells in the olfactory mucosa of the nose are called olfactory cilia Abnormalities of cilia : Cilia can be abnormal in persons with genetic defects that interfere with synthesis of ciliary proteins . This leads to the immotile cilia syndrome . As secretions are not removed from respiratory passages the patient has repeated and sever chest infections. Women 2 affected by the syndrome may be sterile as movement of ova along the uterine tube is affected . ciliary proteins are present in the tails of spermatozoa, and an affected male may be sterile because of interference with the motility of spermatozoa. Ciliary action is also necessary for normal development of tissues in embryonic life. Migration of cells during embryogenesis is depended on ciliary action , and if the cilia are not motile various congenital abnormalities can result. Flagella These are somewhat larger processes having the same basic structure as cilia . In human body the best example of flagellum is the tail of the spermatozoon. The movements of flagella are different from those of cilia. In a flagellum , movement starts at its base. The segment nearest the base bends in one direction . This is followed by bending of next segments in opposite directions ,so that a wave like motion passes down the flagellum. 2-Microfilaments or Actin filaments They are flexible and solid fibers composed of two intertwined strings of beadlike actin molecules . These are about 5 nm in diameter. They aggregate in form of bundles or network. They attach the cell membrane and zonula adhesion (intercellular junction) and form the apical and basal supporting cell . Functions of microfilaments: 1-Maintain cell shape. 2-Generate movement with myosin in contractile cells like the muscle fibers. 3-Form cleavage furrow in cell division. 4-Form core of bundles in microvilli (they extend or retract of microvilli by their assembling and disassembling). Microvilli and Basolateral folds: Microvilli are finger like projections from the cell surface. Each microvilli consists of an outer covering plasma membrane and core of actin filaments. In the free borders of epithelial cells lining the small intestine appear striated border of microvilli arranged parallel to one another. In some cells the microvilli are not arranged so regularly and give the appearance of a brush border. Microvilli greatly increase the surface area of the cell and are seen most typically at sites of active absorption ,example , intestine, Kidney .Modified microvilli called stereocilia are seen on receptor cells in the internal ear, and on the ep. of the epididymis. In some cells the cell membrane shows deep folds(basolateral folds). Like microvilli, they are an adaptation to increase cell surface area . they are seen in renal tubular cells, ducts of some glands and gut. 3-Intermediate filaments They are non-contractile filaments formed of keratin fibrous protein. These are so called as their diameter(10 nm). They are very stable and tough fibers, concentrated in the terminal web that maintains the cell shape. Their assembling is irreversible. They include cytokeratin 3 (in epithelial cell) of the skin, neurofilament protein (in neuron),desmin( in muscle), vimentin (in many types of cells) Functions of intermediate filaments: 1-Strengthen the cytoskeleton. 2-Stabilize the cell shape. 3-Support cell junctions, particularly the parts under mechanical stress. 4-Disorganization and reorganization of nucleus in cell division. 5-Form nuclear lamina under nuclear envelope to maintain the nuclear form. 4