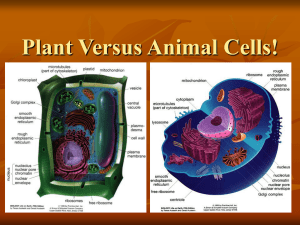
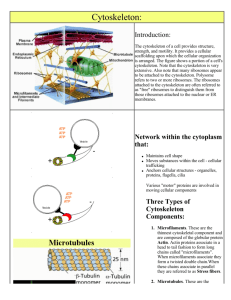
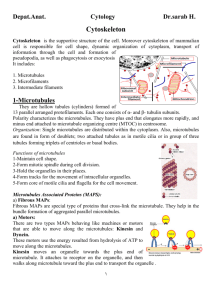
Cytoskeleton
advertisement

Cytoskeleton Burnside, Glenn, Vanscoy, White, Conrad Actin Filaments Actin Filaments Main Function: to help the contraction of cells Found in: eukaryotic cells only If Actin filaments were not present: myosin molecules would be scattered throughout the cell, and the cell would very disorganized and mishaped. Analogy:the actin filament is like an old mp3 player. It has a specific function and is limited. The intermediate filament is like an iPod. It has its specific function and is more dynamic . This analogy works because: Actin filaments • Thin, flexible fibers that occur in bundles or mesh like networks • Each actin filament contains 2 chains of globular actin monomers twisted around each other Intermediate filaments • A rope like assembly of fibrous polypeptides • Give great mechanical strength to skin cells • Several types of these filaments How Actin filaments work together with other organelles Networks of Actin filaments are found beneath the cell cortex which is the meshwork of membrane-associated proteins that support and strengthen the plasma membrane INTERMEDIATE FILAMENTS The intermediate filaments are generally strong and rope like and they play an important role as the structural and functional elements of cytoskeleton. They function as tension bearing elements to maintain cell shape and to anchor other organelles. Intermediate filaments are found in eukaryotes (plant and animal cells) and fungi Diseases Desminopathy: A disease that begins with muscle weakness in the lower body and moves upwards. Malfunctions in keratin also cause many skin diseases Is similar to 1. The intermediate filaments help create the structure of a cell. The base of the boat creates its structure so that it can function properly. 2. The intermediate filaments anchor down other organelles, like how the anchor of a boat anchors down the boat in the water. 3. These things work together as the intermediate filaments functions. Just like how a boat and an anchor work together. CENTRIOLES CENTRIOLES Centrioles organize mitotic apparatus which consists of asters and spindle fibers which help in division of chromosomes. Found in only animal cells. Centrioles are like spindles or nails. 1. like a nail in old times was used to hold information the centrioles acts as an organizing center 2. Has a rod shape like a spindle 3. keeps cells be more efficient DISEASES Centrioles are barrel-shaped structures that are essential for the formation of centrosomes, cilia, and flagella. Deregulation of centrosome numbers has been connected to genome instability and tumor formation, also mutations in centrosomal proteins have recently been genetically linked to microcephaly and dwarfism. Centrioles is an area in the cell where microtubles are produced. The two centrosomes move to opposite ends of the nucleus, and from each centrosome, microtubules grow into a "spindle" which is responsible for separating replicated chromosomes into the two daughter cells. Microtubules organelles function - responsible for various kinds of movement in cells - main structural component of cytoskeleton - provide structure and rigidity, determine shape - directionally transport vesicles and proteins within cytoplasm through transport proteins Microtubules type of cell found in ALL eukaryotic cells Microtubules diseases caused if the organelle malfunctions 1. Parkinson's 2. Alzheimer's Microtubules how the organelle works with other cells the flagella and cilia are composed of microtubules Microtubules analogy a microtubule is similar to railroad tracks Microtubules analogy explained 1. microtubules provide structure to the cell, just like the railroad tracks provide structure to the train 2. microtubules directionally transport vesicles and proteins, just like how the tracks provide the train with direction and allows the train to travel and transport materials 3. microtubules transport proteins called kinesins and dyneins, which act just like the railroad cars FLAGELLA AND CILIA Cilia and Flagella • Formed from specialized groupings of microtubules called basal bodies. • Have a core composed of microtubules connected to the plasma membrane Function: • If there are several along the surface of the cell, they are called cilia, in only one or very few, then they are called flagella. • Cilia and flagella move liquid past the surface of the cell • In single celled organisms, such as sperm, then it is used to swim Type of Cell it is Found in: • Found in most prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells – Eukaryotes tend to have cilia while prokaryotes such as bacteria have flagella Diseases in Organelle malfunctions • ulcer-causing Helicobacter pylori, which uses multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium. • General effects of malfunctioning flagella and cilia: – Developmental defects that cause internal organs to be misplaced or malformed – A disease that results in numerous cysts developing in the kidneys which damage the kidneys – Degeneration of the retina and loss of sight in diseases like retinitis pigmentosa – Bardet-Biedl syndrome, a relatively rare disorder associated with a variety of health problems including retinal degeneration, obesity, kidney malformations, polydactyly, and learning disabilities – Defects in brain development (hydrocephalus) – Male infertility due to immotile or poorly motile sperm, Reduced female fertility due to immotile oviductal cilia Analogy: Flagella are like the wings of a hummingbird. 1) They aid in the mobility of the cell 2) They propagate bends down their length like the muscles in a bird’s wings 3) They move so fast that they cannot be seen by the human eye. Cilia are like the legs of a water spider. 1) There are multiple. 2) While in water, they are used to propel and move around. 3) They control the water flow around the main body. How organelle works with other organelles: • This organelle works with the cell membrane by transporting the cell. By transporting, the flagella or cilia can help the cell get away from harmful toxins or to get closer to a food source. Cilia also help the cell propel water around the cell membrane to help aid in diffusion.