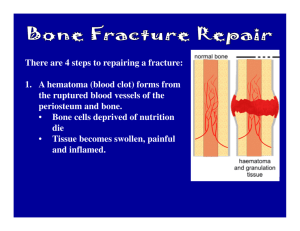
FRACTURE HEALING
advertisement

FRACTURE HEALING Dr. Nuri Aydın, Assoc. Prof. Istanbul University Cerrahpasa School of Medicine Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology nuri.aydin@istanbul.edu.tr • Fracture is a break in the structural conLnuity of the bone GREEN STICK COMPLETE INCOMPLETE Normal Transverse Oblique Spiral Comminuated Avulsion Impacted Fissure GreensLck • Local Signs of Fracture – Pain and tenderness – Deformity – Swelling – Bruising – Loss of funcLon Fracture Mechanism • Single traumaLc event Fracture Mechanism • RepeteLve stress Fracture Mechanism • RepeteLve stress Periosteal reacLon No fracture seen Fracture Mechanism • Abnormal weakening of the bone – MetastaLc bone lesions – Osteoporosis • Senile • Radiotheraphy Inflamma&on Repair SoQ Callus Hard Callus Remodelling STAGES OF FRACTURE HEALING Repara&ve Phase Remodelling Phase INTENSITY OF RESPONSE Inflamma&on Phase 10% 40% 70% INFLAMMATION Hematoma (fibrin clot) Macrophages Inflammatory leukocytes Osteoprogenitor cells HematopoieLc cells secrete growth factors GranulaLon Tissue REPAIR Primary callus response (2 weeks) InflammaLon triggers cell division and growth of new blood vessels (Angiogenesis) SOFT CALLUS Chondrocytes secrete collagen and proteoglycans Creates fibrocarLlage REPAIR Enchondral ossificaLon Bone formaLon SoQ callus turns to hard callus (woven bone) HARD CALLUS Primary CorLcal Healing • Osteonal healing • Resembles normal remodelling • Occurs with rigid immobilizaLon – Plate • Anatomic reducLon Rigid ImmobilizaLon No Visible Callus Secondary CorLcal Healing • Enchondral healing • Closed treatment – Cast • There is movement at the fracture site Periosteal Bridging Callus callus REMODELLING • Begins during the middle of the repair phase • ConLnues up to 7 years • Allows the bone to assume its normal configuraLon • The stresses on the bone is important (Wolff’s Law) Bone Remodelling Cycle REMODELLING • Woven bone replaces with lamellar bone • WOLFF’S LAW – If loading on a parLcular bone increases, • the bone will remodel itself over Lme to become stronger • AdapLve changes happen at the internal architecture of the trabeculae Julius Wolff Newborn Newborn Newborn Newborn Newborn 9 year old Date of Injury Date of Injury Date of Injury Date of Injury AQer 3 months Date of Injury AQer 3 months Date of Injury AQer 5 months Date of Injury AQer 3 months Date of Injury AQer 5 months AQer 12 months Growth Factors of Bone • Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP) • Transforming Growth Factor-­‐beta (TGF-­‐β) • Insulin-­‐Like Growth Factor II (IGF-­‐II) • Platelet-­‐Derived Growth Factor (PDGF) Growth Factors of Bone • Bone Morphogenic Protein (BMP) – OsteoinducLve Mesenchymal cells Osteoblasts • Transforming Growth Factor-­‐Beta (TGF-­‐β) – Induces mesenchmal cells and osteoblasts to produce type II collagen – Regulates carLlage and bone formaLon in fracture callus What influence Fracture Healing? • Biologic Factors – Age – Comorbid medical condiLons – FuncLonal level – NutriLonal status – Nerve funcLon – Vascular Injury – Health of soQ Lssue envelope – Sterility (open fractures) – Smoking – Extent of Bone Loss • Mechanical Factors – SoQ Lssue aiachments to bone – Stability – Anatomic locaLon – Level of energy imparted Endocrine Effects on Fracture Healing Effect Mechanism Growth hormone + Increased callus volume TH/PTH Bone remodelling + Calcitonin +? Unknown Cor&sone -­‐ Decreased callus proliferaLon Systemic Factors Ultrasound and Fracture Healing • Increases mechanical strength of callus • Mechanical energy is transmiied to the cells RadiaLon and Fracture Healing • Decreases the cellularity • Reduces structural integrity Electricity and MagneLc Fields • There are charged molecules on bone and carLlage • Electrical sLmulaLon alters a variety of cellular acLvity • SLmulate bone healing 2011 Healing • StaLc magneLc field increases the radiological callus in the first two weeks • PolarizaLon makes difference in results • No difference in bone mineral density THANK YOU… Dr. Nuri Aydın nuri.aydin@istanbul.edu.tr