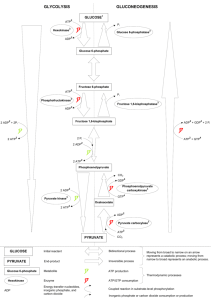
Lecture 16 Glycolysis Glycolysis: oxidative breakdown of glucose to
advertisement

Lecture 16 Glycolysis Glycolysis: oxidative breakdown of glucose to pyruvate with capture of some energy as ATP, NADH (first step in respiration) Themes: sequential, simple enzymatic reactions investment of energy; then recapture control of pathway at key steps: ΔG <<0 production of useful intermediates Glycolysis glucose → pyruvate Subsequent reactions → lactate, CO2 + ethanol, malate → CO2 + H2O Compare respiration to combustion: C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ΔGo’ = -2840 kJ/mol In respiration, including glycolysis, some ΔGo’ (~ 35%) is retained as formation of ATP Phases: priming (-2 ATP/glucose), payoff (+4 ATP, +2 NADH/ glucose) Phase I: 5 reactions 1 2 3 4 glucose → G-6-P → F-6-P → F-1,6-bisP → DHAP + G-3-P ATP → ADP ATP → ADP 5 DHAP → G-3-P Phase II: 5 reactions (note 2 G-3-P substrates per glucose) NAD+ → NADH G-3-P + Pi → 1,3-bisPGA → 3-PGA → ADP → ATP 2-PGA → PEP → ADP → What happens to the pyruvate? Anaerabic conditions: pyruvate → lactate NADH → NAD+ pyruvate → CO2 + acetaldehyde → ethanol NADH → NAD+ pyruvate + CO2 → OAA → malate NADH → NAD+ Aerobic conditions: pyruvate → CO2 + H2O Pyruvate ATP Reaction 1 Note the need for Mg2+ with ATP (common) ΔGo’ =+13.8 kJ/mol = -30.5 -16.7 ΔG’ = ΔGo’ + RTln[P]/[R] = -33.9 Reactions with ΔG<<0 can be regulated Hexokinase is allosterically inhibited by G-6-P, Km ~ 0.1 mM ([glucose] in blood ~ 4 mM) Glucokinase in liver not allosterically inhibited: Km ~ 10 mM Phosphorylation of glucose traps it in the cell Reaction 2 ΔGo’ =+1.67 kJ/mol ΔG’ = -2.92 kJ/mol Near equilibrium: not regulated Reaction 3 ΔGo’ =+16.3 kJ/mol = -30.5 -14.2 ΔG’ = -18.89 ATP is an allosteric inhibitor AMP reverses ATP inhibition (ATP down 8% results in AMP up 4-fold: p. 542) Reaction 4 ΔGo’ =+23.8 kJ/mol ΔG’ = -0.23 kJ/mol Reaction 5 ΔGo’ =+7.56 kJ/mol ΔG’ = +2.41 kJ/mol Overall: glucose + 2 ATP → 2 G-3-P + 2 ADP ΔGo’ =+63.13 kJ/mol −61.0 2.13 (glucose → 2 G-3-P) (2 ATP → 2 ADP) ΔG’ = -53.4 kJ/mol (from relative concentrations in cells) Problem What is the ratio of [DHAP]/[G3P] in the erythrocyte, when ΔG = 2.41 ? ΔG = ΔGo’ + RT ln ([G3P]/[DHAP]) 2,410= 7,560 + (8.31)(298) ln ([G3P]/[DHAP]) ln ([G3P]/[DHAP]) = -2.1 [G3P]/[DHAP] = 0.125 [DHAP]/[G3P] = 8.0 (DHAP useful for making the glycerol in lipids)