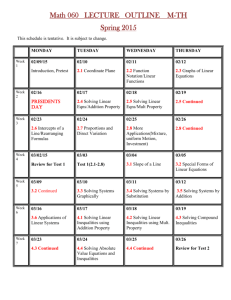
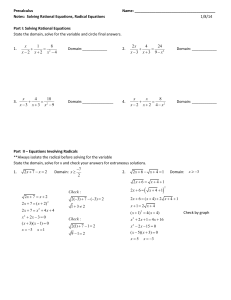
PRECALCULUS Semester I Exam Review Sheet Chapter Topic P.1
advertisement

PRECALCULUS
Semester I Exam Review Sheet
Chapter
P.1
Topic
Real Numbers
{1, 2, 3, 4, …}
Natural (aka Counting) Numbers
{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}
Whole Numbers
{…, -3, -2, -2, 0, 1, 2, 3, …} Integers
Can be expressed as p/q where p and q are integers (q 0)
Rational Numbers
Can not be expressed as p/q such as above
Irrational Numbers
P.2
Exponents and Radicals
Properties of Exponents
Scientific Notation
Addition, Subtraction – break from std form to make exponents the same
Then add or subtract coefficients, adj to std form.
Multiplication, Division – multiply coefficients then add/subt exponents
Radicals and their Properties
Simplifying Radicals
Rationalizing
Rational Exponents
P.3
Polynomials and Factoring
Polynomials
Definitions
Coefficient
Degree
Leading coefficient
Constant term
Monomial, binomial, trinomial, polynomial
Standard form
Polynomial Operations
Addition/Subtraction
Multiplication
General (mult every term in 2nd poly by every term in 1st poly)
FOIL
Special Products
Sum and Difference of Same Terms (Conjugates Pairs)
(ax + b)(ax – b) = a2x2 – b2
Square of a Binomial
(ax + b)2 = a2x2 + 2ab x + b2
(ax - b)2 = a2x2 - 2ab x + b2
Cube of a Binomial
u3 + v3 = (u + v)(u2 – uv – v2)
u3 - v3 = (u - v)(u2 + uv – v2)
Factoring
Definitions
Prime
Irreducible (over reals, over rationals, over integers)
Removing Common Factors
Factoring Special Polynomial Forms
Difference of Two Squares
Perfect Square Trinomial
Sum or Difference of Two Cubes
General Factoring of Trinomials with Binomial Factors
Leading Coefficient is 1
Leading Coefficient is not 1
Factoring by Grouping
P.4
Rational Expressions
Domain of an Algebraic Expression
Simplifying Rational Expressions
Operations with Rational Expressions
Multiplying Rational Expressions
Dividing Rational Expressions
Adding/Subtracting Rational Expressions
Find Common Denominator (LCD?)
Examples 6 and 7, Pg. 40,41
Complex Fractions (Pg. 42: Examples 8, 9, 10, 11)
Simplifying
Factoring Common Quantities with Different Rational Exponents
Difference Quotients
P.5
Solving Equations
Identity – an equation that is true for all x
Conditional equations – an equation that is true for some (or no) x
Solving Conditional Equations
Linear Equations (Pg. 50: Ex. 1-3) Also, see ex 3 for extraneous solutions
Extraneous Solutions may occur when multiplying or dividing by
a variable quantity
Quadratic Equations
Factoring
Square Root Principle
Completing the Square
Quadratic Formula
Polynomial Equations of Higher Degree (Some Cases)
Factoring
Factoring by Grouping
Radical Equations (Check for Extraneous Solutions)
Involving Rational Exponent
Isolate Rational Exponent Term
Raise both sides to reciprocal of exponent
Involving One Radical
Isolate the radical
Square both sides
Solve for x
Verify solutions
Involving Two Radicals
Isolate one radical
Square both sides
Isolate 2nd radical
Square both sides again
Solve for x
Absolute Value
Isolate Absolute Value (on left side)
Create two non-absolute value equations
Set expression inside absolute value equal to the
other side of the equation
Set expression inside absolute value equal to the
opposite of the other side of the equation
Solve both equations for x
P.6
Solving Inequalities
Inequality solutions are sets or intervals and are called the solution set.
Solution sets may be Bounded or Unbounded Intervals
Properties of Inequalities
Two inequalities with the same solution set are equivalent.
Properties of Inequalities
Transitive
a < b and b < c then a < c
Addition of Inequalities
Addition of a Constant
Multiplication by a Constant
a < b and c < d then a + c < b + d
a < b then a + c < b + c
For c > 0, a < b then a·c < b·c
For c < 0, a < b then a·c > b·c
Linear Inequalities
Single Inequality Form
3x + 1 > 5x - 4
Double Inequality Form
5 < 4x – 3 < 7
Absolute Value Inequalities
Isolate Absolute Value quantity on left side
If Inequality is Less Than type:
Determine if inequality has No Solution or is True For All x
If not, then:
Set expression inside absolute value < right side
Set expression inside absolute value > opposite of left side
Solve both of these inequalities to find solution set
Other Types of Inequalities
Polynomial Inequalities
Move all terms to one side of inequality so other side is zero
Find the zeros of the polynomial which are called Critical Points
“n” Critical Points divide number line into “n+1” intervals
Select one convenient Test Point from each Critical Point interval
Evaluate polynomial at each Test Point
Solution is set of all Critical Point intervals that satisfy inequality
Rational Inequalities
Find the Domain of a Square Root Function (Square Root Inequality)
P.7
Errors and the Algebra of Calculus
Algebraic Errors to Avoid
(See Examples in Blue Boxes in Text)
Errors Involving Parentheses
Errors Involving Fractions
Errors Involving Exponents
Errors Involving Radicals
Errors Involving Dividing Out
Some Algebra of Calculus (See Examples in Blue Boxes in Text)
Unusual Factoring
Writing with Negative Exponents
Writing a Fraction as a Sum
Inserting Factors and Terms
P.8
Graphical Representation of Data
The Cartesian (x-y) Plane
Plotting Points
Sketching a Scatter Plot
The Distance Formula
Finding a Distance
Verifying a Right Triangle
The Midpoint Formula
1.1
1.2
Graphs of Equations
Graph Sketching
Plug in points
x- and y- intercepts
symmetry (and symmetry testing)
x- axis
f(x,-y) = f(x,y)
y- axis
f(-x,y) = f(x,y)
origin
f(-x,-y) = f(x,y)
Equation of a circle
(x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2 where center = (h,k)
Linear Equationss in Two Variables
Using Slope
Slope-Intercept Form of linear equation
Point-Slope Form of linear equation
Standard Form
y = mx + b
y = m(x – x1) +y1
Slope:
Slope of Parallel Lines
mparallel = m
Slope of Perpendicular Lines mperpendicular = -1/m
1.3
Functions
Function vs Relation
Functional Relation of x into y:
Graphical Form: Vertical Line Test
Numeric, Algebraic, Verbal Forms: For every x there is only one y
Functional Relation of y into x: For every y there is only one x
Graphical Form: Horizontal Line Test
Numeric, Algebraic, Verbal Forms: For every y there is only one x
Function Notation
Dependent variable vs independent variable
Given f(x) = 3x + 3, then f(x+x) = 3(x+x) + 3 = 3x + 3x + 3
Piecewise-Defined Functions
Step Functions
Evaluating Difference Quotients (Pg. 130: Ex. 9)
Domains of Functions
Domain of a function is all possible x- values
Range of a function is all possible y- values
Implied Domain is a restricted domain resulting from a practical
interpretation of a model (ex. volume would not be negative.)
Applications
See Pg. 130: Ex.6, 7, 8
1.4
Analyzing Graphs of Functions
Graphs
Finding Domain and Range
Vertical Line Test
Zeros of a Function
Increasing, Decreasing, and Constant Regions
Definition of Relative Minimum and Relative Maximum
Step Functions
Greatest Integer Function:
Evaluate
Graph using calculator
Piecewise-Defined Functions
Evaluate
Graph using calculator
Even and Odd Functions
Even: f(-x) = f(x)
Odd: f(-x) = -f(x)
1.5
Shifting, Reflecting, and Stretching Graphs
Shifting Left and Right
Shifts Left “c” units: f(x) = x2
Shifts Right “c” units: f(x) = x2
g(x) = (x+c)2
g(x) = (x-c)2
Shifting Up and Down
Shifts Up “c” units:
Shifts Down “c” units:
Reflecting
Reflection about the x- axis:
Reflection about the y- axis
Vertical Stretch/Shrink
1.6
f(x) = x2
f(x) = x2
g(x) = x2 + c
g(x) = x2 - c
g(x) = -f(x)
g(x) = f(-x)
Combinations of Functions
Arithmetic Combinations of Functions
(f + g)(x) = f(x) + g(x)
(f – g)(x) = f(x) – g(x)
(f·g)(x) = f(x) · g(x)
Composition of Functions
(f g) = f(g(x))
Domain of a Composite Function
Domain of (f g) = f(g(x)) is all values of x that can be plugged
into g(x) such that g(x) can be plugged into f(x)
Identifying Composite Functions
See Example 6 on Page 166
2.1
Quadratic Functions
2.2
Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
2.3
Long and Synthetic Division of Polynomials
2.4
Complex Numbers
2.5
Zeros of Polynomial Functions
2.6
Rational Functions
2.7
Partial Fraction Decomposition
3.1
3.2
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs
3.3
Properties of Logarithms
3.4
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
3.5
Partial Fraction Decomposition
4.1
Radian and Degree Measure
4.2
Trigonometric Functions: The Unit Circle