New Seats - Verona School District
advertisement

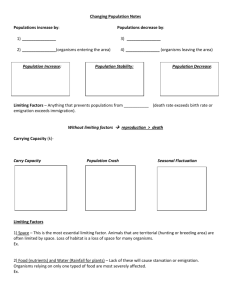
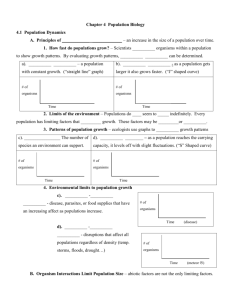
New Seats Before we start with our next topic, we have new seating assignments for everyone. Please take your new seats. Do Now – 3 Minutes Topic – Describing Populations • Recall from your notes what a “population” is. • How is a population different from a community? • What factors affect a population? Studying the Population Why is it important to study populations of creatures? Why are humans be concerned about the decreasing population of bees? Studying the Population Population size describes the number of individual organisms in a given population at a given time. When the population increases, this is a sign of a healthy population. What factors would lead to a population increasing? Studying the Population When the population decreases rapidly, this can be an indicator that the species may become extinct. Golden Toad Dodo Determining Population Size How could you go about determining the population size of a species in an area? If we wanted to determine the number of blades of grass in the football field, how could we do this? Assume that the field is 120 yds long. Determining Population Size The current population of the United States is approximately 320,132,000 people (3rd highest population in the world) The population of China is about 1,367,510,000 (1st in the world) How do you think these populations are determined? Population Density Population density describes the number of individuals within a population per unit area. The population of Verona is 12,411 residents (as of 2010) and the total area is 4.378 sq. mi. What is the population density of Verona in residents/sq. mi.? Population Density Why would a high population density be beneficial for a species? Why would it be detrimental for a species? Population Density Why would a low population density be beneficial for a species? Why would it be detrimental for a species? Population Distribution Depending on the species, populations may organize themselves into different arrangements. Population distribution describes how organisms are arranged within an area. The three distribution types are: Random Uniform Clumped Random Distribution In a random distribution, there is no particular order to the distribution of the species. Uniform Distribution In a uniform distribution, organisms organize themselves evenly in an area. This occurs when individuals hold territories or compete for space. Clumped Distribution In a clumped distribution, organisms organize themselves according to the availability of resources. Age Structure Populations are made up of varying proportions of age, as well as males and females present in the population. Age structure describes the relative number of organisms of each age within a population. It is often very helpful to graphically show this information using an… Age Structure Diagram An Age structure diagram is a tool used to show the age structure of populations. Age Structure Diagram Populations with a large young population are capable of creating many offspring. Age Structure Diagram These diagrams are helpful in predicting future population growth. China’s A.S. Diagram France’s A.S. Diagram Germany’s A.S. Diagram India’s A.S. Diagram Japan’s A.S. Diagram Nigeria’s A.S. Diagram United State’s A.S. Diagram Sex Ratios A population’s sex ratio is the proportion of males to females. A population needs a proper number of males to females in order to ensure their population does not dwindle. To ensure proper survival of a species, a ratio of 50:50 is ideal.