Research Article Analysis Worksheet
advertisement

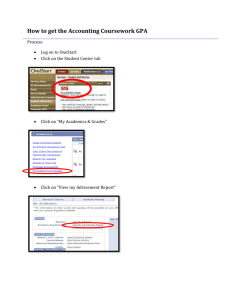
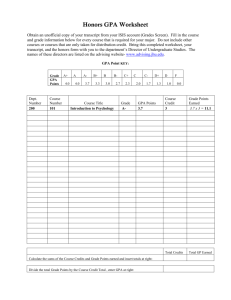
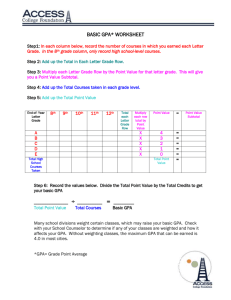
Research Article Analysis Worksheet Name: Christina Schaefer Article: (Properly cite the article here) Morisano, D., Hirsh, J.B., Pihl, R.O., and Shore, B.M. (2010). Setting, elaborating, and reflecting on personal goals improves academic performance. Journal of Applied Psychology,95(2), 76-86. ______________________________________________________________________________ Introduction – The Research Question: (What is the research question? What topic is the researcher seeking to address?) The research question at hand is whether a goal-setting intervention would help retention rates for students in college, as well as whether or not the same intervention would have positive effects on academic achievement for students who are struggling. The topic being addressed in the research is the increased discrepancy between the number of students who enroll in colleges and the number who actually graduate. Leading to the search for ways to increase academic success/graduation rates and in turn lowering retention rates. ___________________________________________________________________________ Method – The Study: (Who participated in the study? What were the participants asked to do? What procedures were taken for the study?) The idea behind the method used is a student who experiences attains a goal successfully tends to increase their self-efficacy, enhancing goal commitment. The researcher attempts to address the given problem with a formalized, intensive, online personal goal setting program to break the cycle between mediocre school performance and lack of motivation. Participants in the study consisted of self-nominated students who were struggling academically, with GPAs below 3.0. Students who were interested took part in a brief ten minute phone interview in order to assess feelings of academic difficulty. Students had to meet three criteria components: a.) have planned to take a full-time course load each semester while in study b.) have been on academic probation or had a cumulative GPA under 3.0 c.) have stated the were experiencing academic difficulty Once the criteria were met students were randomly assigned to one of two intervention groups, (Group 1) goal setting group and (Group 2) the control group, neither were guaranteed to improve grades but they were not expected to have a negative effect either, financial remuneration was also offered for time spent in study. A total of eighty-five students were included in the study, ranging from 18 to 23, 60 were women. Students were informed the study would occur in two stages 1.) Consisted of informed consent and demographics, as well as the intervention itself 2.) Concluding questionnaire and permission forms for releasing official transcripts Stage 1 Group 1 (goal group) participated in a web-based, intensive, goal-setting program, which led them through a series of eight steps facilitating the setting of specific personal goals and detailed ways to achieve them. They were then asked to allow for 2.5 uninterrupted hours for a free writing intervention, where they would write down their private thoughts and feelings, without regard to grammar or spelling errors, they were informed they may be asked to carefully revise what they had written. They were also informed that everything they wrote would be confidential, the writing program was meant to benefit them and they would receive a copy of what they had written shortly after the program was completed. Group 2 (control group) participated in three different web-based tasks in lieu of the goal setting intervention. 1.) A series of questionnaires measuring positive psychology traits, the questionnaires were not scored and no feedback was provided. They were used to get the control group thinking about different personal characteristics (without a specific focus) and to increase the face validity of the intervention. 2.) For the second task students wrote about some positive past experiences. They were told to write nonstop without regard to grammar or spelling. They were asked to answer three out of six questions based on neutral topics, to spend 10-15 min. on each response and answer each in an objective way, with minimum emotional expression, as well as thoughtfully and seriously. This task was included to match the free-writing done by the Group 1. 3.) Lastly they completed a widely used career-interest measure: the Strong Interest Inventory Assessment, of which each student was sent a computer generated report of his or her results. Stage 2 Roughly sixteen weeks after stage one was completed all participants (Group 1&2) were asked to complete the concluding questionnaire and sign the transcript-release form. The Concluding Questionnaire was designed to elicit information about emotional status, concentration, motivation, and the seriousness participants took in their involvement in the study. It was also at this time they were remunerated for their time spent in the study (four months). ______________________________________________________________________________ Results – The Findings: (What was the answer to the research question? What quantitative or qualitative data were produced?) Overall the intervention proved to be a success in regards to both questions being asked, Group 1 (goal group) showed a much higher retention rate than that of Group 2 (control group), it is also important to note no participants in Group 1 dropped below a full course load in the semester post intervention, compared to eight students in the control group dropped below the full course load, with two withdrawing from school completely. When comparing the GPA 1 for both groups no baseline differences were found. However, in the post intervention comparison the goal groups GPA2 was significantly higher than their baseline GPA1, compared to the lack of significant difference found between pre and post intervention GPA’s for the control group. When comparing post intervention GPA’s for both the control and goal group, the goal group GPA 2 was significantly higher than that of the control group GPA2. After further calculations the reduced negative affect scores were significantly higher for the goal group than for the control group. No significant differences were seen for the enthusiasm scores. Thus showing there lies a correlation between reduced negative affect scores and grade improvement, further relating the grade improvements to the positive effects of the intervention. The only other significant predictor of academic improvement was the number of words used in describing the ideal future, with those who wrote more demonstrating greater improvements in their grades. Thus proving the goal setting exercise was able to successfully improve GPA among undergraduate students. Data shows it would be necessary to develop a variety of interventions to accommodate different native languages for students. The findings showed the intervention was to be most effective for native English speakers, where the academic performance of nonnative English speakers was affected by the linguistic challenges rather than the motivational problems, which limited the outcome of success for this study. Most importantly the data shows improvements in goal clarity and the increased motivation students attributed to the intervention were both related to academic achievement outcomes. Leaving the question as to whether effective goal setting in one domain can assist generalized self-efficacy and performance improvements in other domains. ______________________________________________________________________________ Discussion: (The “So What” Factor. What meaning can you draw from this study? How can YOU use this information as a student?) As a student this research article has reinforced the importance of having and maintaining my academic goal, if I lose sight of it I am likely to give up on school and all the time, effort and money I have put in thus far would all be for nothing. Not to mention that would be a decision I would have to live with for the rest of my life. However, after reading the article I know what to seek if I were to ever get in a situation where I was really struggling in school. As a mother it has sparked my interest to create my own study with my children. As a parent I obviously want them to have goals and pursue them, however this article has given me some insight on how important it is to reinforce those goals to my children. I already use positive reinforcement when they do something good like picking up their toys, or going to the bathroom on the toilet, but this article shows the importance of continuing the reward system. I found this article to be a little repetitive of itself but very interesting and useful.