Dihybrid Crosses Using the Fork
advertisement

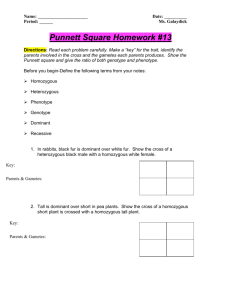
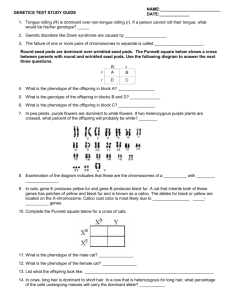
Name: ________________________________________________ Hour: _____ Number: _____ Dihybrid Crosses Using the Fork-line Method 1. Gregor Mendel researched pea plants and discovered the following. Round peas (allele is R) and Tall plants (allele is T) traits are both dominant to wrinkled peas and short plants. If a pea plant is both heterozygous for round peas and heterozygous for tall plant is crossed with a pea plant has wrinkled peas and is a short plant, what would be the probabilities for each possible offspring phenotype? Cross: __________ X __________ Gametes: ___ ___ ___ ___ Fork-line: ___ ___ ___ ___ Probability: 2. If a two pea plants where crossed that are both heterozygous for both genes (a true dihydrid). What is the probability of getting a pea plant with wrinkled peas and being a tall plant? Cross: __________ X __________ Gametes: ___ ___ ___ ___ Fork-line: Probability: ___ ___ ___ ___ Name: ________________________________________________ Hour: _____ Number: _____ 3. In tomatoes, red color is dominant over yellow color, and juiceless tomatoes are dominant over juicy tomatoes. Cross a tomato plant that is hybrid (heterozygous) for both traits with a plant that does not show either dominant phenotype. What is the chance of getting a tomato that is yellow and juiceless? _________________ Cross: __________ X __________ Gametes: ___ ___ ___ ___ Fork-line: ___ ___ ___ ___ Probability: 4. Using the information from problem #3, cross a tomato plant that is homozygous red and is juicy with a plant that is yellow and is heterozygous for juicelessness. What is the chance of getting a plant that shows both dominant traits? ___________________ Cross: __________ X __________ Gametes: ___ ___ ___ ___ Fork-line: ___ ___ ___ ___ Probability: 5. Explain why Heinz Tomato Company would be interested in the genetics of tomatoes.