Final review
advertisement

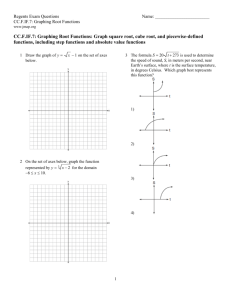
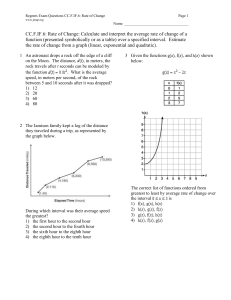
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Final review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Image-forming x-rays include those which have been _____. a. transmitted without interaction b. scattered through Compton interaction c. absorbed through photoelectric interaction d. all the above ____ 2. Which kVp selection would result in the most scattered x-rays in the image-forming beam? a. 90 kVp c. 60 kVp b. 75 kVp d. 50 kVp ____ 3. The x-ray interaction that contributes to the white parts of the image is _____. a. coherent scatter c. photoelectric interaction b. Compton interaction d. pair production ____ 4. The three primary factors influencing the intensity of scatter in the image-forming beam are _____. a. mAs, kVp, and collimation c. kVp, field size, and patient thickness b. mAs, filtration, and grids d. filtration, patient thickness, and mAs ____ 5. Photoelectric interactions increase when _____ is decreased. a. mAs c. filtration b. patient thickness d. kVp ____ 6. Scatter radiation increases as _____ increases. a. photoelectric absorption c. b. field size d. filtration contrast ____ 7. The most commonly used beam restricting device is the _____. a. extension cone c. aperture diaphragm b. variable collimator d. compression device ____ 8. The positive beam limiting device (PBL) assures that the x-ray beam is collimated to _____. a. the exact target size c. 14 X 17 inches b. 25 cm X 25 cm d. inserted cassette size ____ 9. ALARA stand for a. As Little Active Radiation Allowed b. As Low As Reasonable Achievable c. d. Active Limits Around Radiation Always Limits Active Radiation ____ 10. Three main ways to limit radiation exposure is to control a. time, distractions, sound emission c. time, distance, shielding b. through-put, distance, shielding d. time, duration, shielding 1 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 11. Computed radiography screens respond to radiation with _____. a. fluorescence c. photostimulable luminescence b. electron emission d. biological phosphorescence ____ 12. The computed radiography cassette is called a(n) _____ plate. a. optical c. laser b. imaging d. thermoluminescent ____ 13. In a CR cassette reader, optical filters are used to filter out the _____ light and allow the _____ light to reach the photodetector. a. stimulating, emitted b. emitted, stimulated c. d. emitted, monochromatic stimulating, monochromatic ____ 14. The principal source of noise in computed radiography is _____. a. scatter radiation c. computer noise b. background radiation d. phosphor scatter ____ 15. The laser beam must be less than 100 nm in order to maintain _____. a. consistent beam shape c. high spatial resolution b. smooth image edges d. high speed ____ 16. In digital radiography, the brightness of the image is determined by _____. a. pixel values c. automatic brightness control b. Hounsfield units d. grid ratio ____ 17. The component used to convert radiation to visible light in DR is the a. charge coupled device c. RIS b. scintillator d. PACS ____ 18. PACS stands for a. Picture Assesment Computer System b. Picture Archival and Communication System ____ 19. DICOM stands for a. Diagnostic Imaging and Communication in Medicine b. Diagnostic Information and Communication in Medicine c. d. Procedure Assesment Control System Physician Appointment Control System c. Direct Information Control in Medicine d. Digital Imaging Control in Medicine ____ 20. All of these are common safety items on a Fluoroscopy system except a. exposure timer c. lead shielding / aprons b. dead-man style switch d. cassette detection ____ 21. A fluoroscopy-specific item used to aid in ALARA is the a. lead shielding c. door interlock b. exposure timer d. tube chiller 2 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 22. Automatic Brightness Stabilization in fluoroscopy adjusts _______ to maintain image brightness a. rotor prep time c. mAs b. mA d. time ____ 23. The time-interval delay mode is principally used in _____ imaging. a. renal angiography c. cardiac b. barium enema d. run-off ____ 24. Remasking may be required due to _____. a. noise artifacts c. b. motion artifacts d. technical factors any of the above ____ 25. Energy subtraction technique takes advantage of the difference in _____ during contrast injection. a. tissue density c. Compton scatter b. Z effective values d. patient thickness ____ 26. What is the principal disadvantage of third generation CT scanners? a. slow speed c. patient dose b. ring artifacts d. poor reconstruction ____ 27. Many CT x-ray tubes have the capacity for millions of _____ with each exam. a. heat units c. volts b. rotations d. Hertz ____ 28. The patient dose in CT is determined by the _____ collimator. a. predetector c. postpatient b. prepatient d. both A and B ____ 29. Each pixel of information in the CT image contains numerical information in _____ units. a. voxel c. Hounsfield b. reconstruction d. pixel ____ 30. The CT scanner must be calibrated so that _____ represents a CT number of zero. a. water c. nylon b. Plexiglas d. polyethylene ____ 31. On a CT system, the high voltage generator is located a. in the electronics cabinet in the room c. under the patient table b. on the gantry d. on the gantry support structure ____ 32. The radiology specific Federal standard all x-ray systems must meet is a. NFPA 99 c. 22 AEC b. 21 CFR d. 62 TRNS ____ 33. Which of the following readings must be taken invasively? a. kV c. time b. mA d. AEC response 3 ID: A Final review Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D A C C D B B D B C C B A A C A B B A D B B C D B B A B C A B B B REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: page 224 page 224 page 224 page 224 page 224 page 225 page 243 page 232 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: page 413 page 414 page 418 page 422 page 415 page 430 REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: page 445 page 445 page 446 page 370 page 373 page 374 page 376 page 383 1