Classification of Revenue in NFPs
advertisement

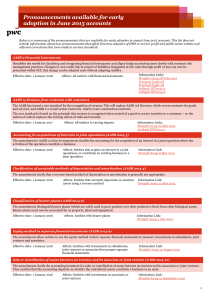
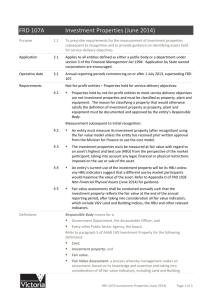
Classification of Revenue in NFPs Prestented by: Dr Ted Fack Queensland University of Technologhy Brisbane Background to the issue AASB are sector neutral NFP variations allowed under “Aus” paras “Income” is defined in para 70(a) of the AASB Framework (2009) as: “..increases in economic benefit during the accounting period in the form of inflows or enhansements of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases of equity, other than those relating to contributions from equity participants.” Income • Income comprises both revenue and other income that arises in the ordinary course of the entities operations; • Revenue is reported in the Income Statement on a gross basis; • AASB 118 revenue is classified into: • sale of goods • rendering of services • the use by others of entity assets, eg. interest, royalties and dividends Contributions (aka “transfers”) Appendix to AASB 1004 “a non-reciprocal transfer is defined as a transfer in which the entity receives an assets (being cash, the right to receive cash, or other asset) without giving approximately equal value to the other party or parties to the transfer.” AASB 1004 states that “Reciprocal transfers are transfers in which the transferor and the transferee receive and sacrifice approximately equal value.” What’s the problem? – Comparability! Determining whether a transaction is reciprocal or non-reciprocal is often difficult in practice: For example: Government “grant” to fund certain services Government “grant” to support NFP’s work Donor contribution for special puposes Philanthropic Trust “grant” to fund a new service Revenue Recognition AASB 1004 (para 12) revenue recognition criteria If classified as a “contribution”, then NFP must recognise contribution as revenue when all following conditions are met: a. Entity gains control or right to receive contribution; b. It is probable that the economic benefits comprising the contribution will flow to the entity; and c. The amount of the contribution can be measured reliably. NFP to recognise enire amount of the contribution as income upon receipt – unless….. Multi-year policy agreement exception AASB 1004 (para 14) gives example of a multi-year policy agreement where the entity does not obtain control of the contribution until it has met conditions or provided services that make it eligible to receive the contribution. Where such an agreement – income recognised only in relation to contributions received or receivable under the agreement. Change is in the wind! • IFRS 15 Revenue from contracts with customers replaces IAS 18 Revenue • AASB 15 (the Aus equivolent) has not yet been issued (due 4th Qtr 2014) • AASB 1004 Contributions under review AASB15 is coming IFRS 15 Step process Core principle of IFRS 15 requires 5 step process: 1. Identify the contract(s) 2. Identify the performance obligations 3. Determine the transaction price 4. Allocate the transaction price 5. Regonise revenue when each performance obligation is satisfied Recommendations from recent QUT Research Statement of Profit and Loss and Other Comprehensive Income Note Revenue Sales of goods Provision of services Gifts Transfers Investment income Total Revenue Other Income Total Income 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sale of Goods Lottery sales Art unions Raffles Tax-deductible contributions Other sales Total Sales of Goods 2 Provision of services Government grants (reciprocal) Membership fees Sponsorships (commercial) Event ticket sales Total Income from provision of services 3 Sale of Goods and Provision of Services Gifts Transfers Investment Other Gifts Gifts Bequests/Legacies Total Gifts 4 Transfers Government Grants (non-reciprocal) Grants from Trusts and Foundations Total Transfers 5 Investment Income Interest Dividends Rents Royalties Total Investment Income 6 Other Income Gains on sale of non-current assets Foreign exchange gain Total Other Income 7 Examples A. State Government provides $25,000 grant “to support your wonderful work with disadvantaged youth” B. Local government provides a “grant” of $5,000 to assist disabled children holiday program C. XYZ Trust makes a grant of $125,000 over 3 years for a pilot program to teach older people computer skills. D. Commonwealth Government grant of $350,000 pa for three years to deliver range of HACC–type services Questions? 1. 2. 3. 4. Are government grants “reciprocal” or “non reciprocal”? Are government grants “purchases of service” or “contributions”? What are “relative stand-alone selling prices?” What are the issues re recognition of liability for “special purpose” funds received in advance? Where to from here? AASB 15 Revenue from Contracts expected in Q4 2014 New standard expected to apply for annual periods after 1 January 2017 Step 1 & 2 IDENTIFY CONTRACTS Applies to Oral, Written or Implied contracts Identify performance obligations under each contract Step 3 DETERMINE Identify the transaction price Step 4 ALLOCATE Step 5 RECOGNISE Allocate transaction price to performance obligation Recognise revenue when each performance obligation is satisfied AASB project on NFP Income • Currently AASB 118, 111 and 1004 are relevant to NFP income recognition • AASB Project under way to replace all except parts of 1004 re restructure of admin arrangements • Expected in Q4 2014 Questions?