UNIT #5 EXAM -- SURFACE PROCESSES AND LANDSCAPES
advertisement
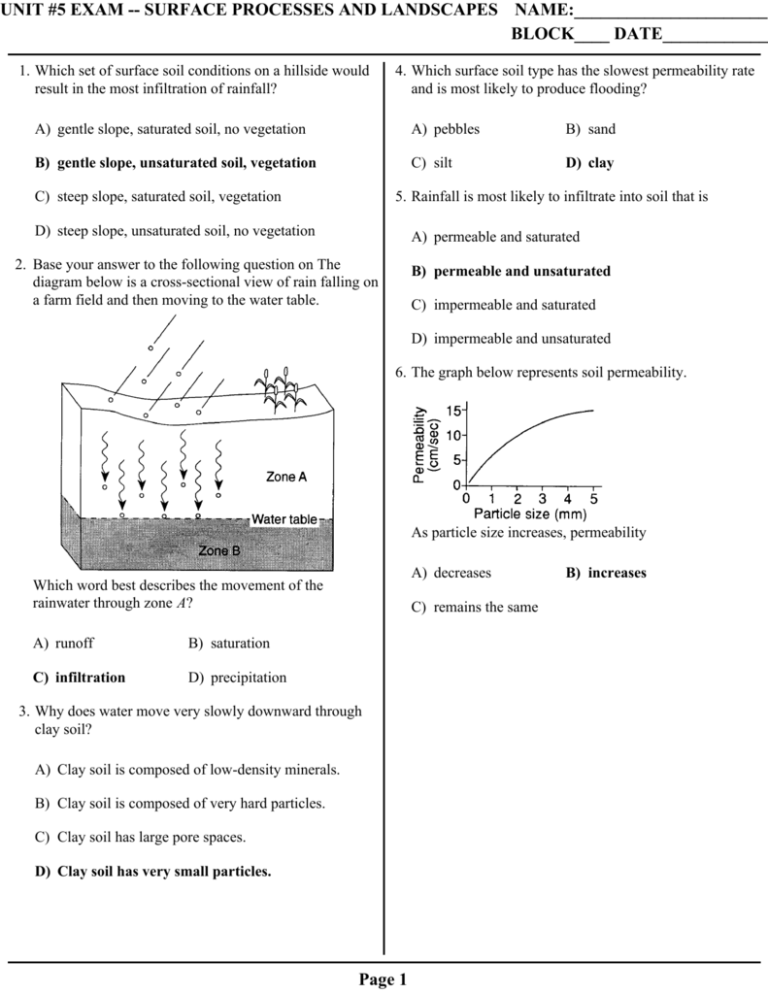
UNIT #5 EXAM -- SURFACE PROCESSES AND LANDSCAPES NAME:______________________ BLOCK____ DATE____________ 1. Which set of surface soil conditions on a hillside would result in the most infiltration of rainfall? 4. Which surface soil type has the slowest permeability rate and is most likely to produce flooding? A) gentle slope, saturated soil, no vegetation A) pebbles B) sand B) gentle slope, unsaturated soil, vegetation C) silt D) clay C) steep slope, saturated soil, vegetation 5. Rainfall is most likely to infiltrate into soil that is D) steep slope, unsaturated soil, no vegetation A) permeable and saturated 2. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. B) permeable and unsaturated C) impermeable and saturated D) impermeable and unsaturated 6. The graph below represents soil permeability. As particle size increases, permeability A) decreases Which word best describes the movement of the rainwater through zone A? A) runoff B) saturation C) infiltration D) precipitation C) remains the same 3. Why does water move very slowly downward through clay soil? A) Clay soil is composed of low-density minerals. B) Clay soil is composed of very hard particles. C) Clay soil has large pore spaces. D) Clay soil has very small particles. Page 1 B) increases 7. The diagram below represents three identical beakers filled to the same level with spherical beads. A) B) If the packing of the beads within each beaker is the same, which graph best represents the porosity within each beaker? C) D) 8. Which soil characteristic allows greater amounts of water retention? A) large-size particles B) small-size particles C) high-density particles D) low-density particles Page 2 9. Soil with the greatest porosity has particles that are A) poorly sorted and densely packed B) poorly sorted and loosely packed C) well sorted and densely packed D) well sorted and loosely packed 10. Soil composed of which particle size usually has the greatest capillarity? A) silt B) fine sand C) coarse sand D) pebbles 11. Which conditions produce the most surface water runoff? A) steep slope, heavy rain, and frozen ground B) steep slope, gentle rain, and unfrozen ground C) gentle slope, heavy rain, and frozen ground D) gentle slope, gentle rain, and unfrozen ground Page 3 12. Base your answer to the following question on The cross section below shows the movement of wind-driven sand particles that strike a partly exposed basalt cobble located at the surface of a windy desert. Which cross section best represents the appearance of this cobble after many years of exposure to the wind-driven sand? A) B) C) D) Page 4 13. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below shows granite bedrock with cracks. Water has seeped into the cracks and frozen. The arrows represent the directions in which the cracks have widened due to weathering. 15. At high elevations, which is the most common form of physical weathering? A) abrasion of rocks by the wind B) alternate freezing and melting of water C) dissolving of minerals into solution D) oxidation by oxygen in the atmosphere 16. Which event is an example of chemical weathering? A) rocks falling off the face of a steep cliff B) feldspar in granite being crushed into clay-sized particles C) water freezing in cracks in a roadside outcrop Which statement best describes the physical weathering shown by the diagram? A) Enlargement of the cracks occurs because water expands when it freezes. D) acid rain reacting with limestone bedrock 17. Landscapes will undergo the most chemical weathering if the climate is B) This type of weathering occurs only in bedrock composed of granite. A) cool and dry B) cool and wet C) warm and dry D) warm and wet 18. Which geologic feature is caused primarily by chemical weathering? C) The cracks become wider because of chemical reactions between water and the rock. D) This type of weathering is common in regions of primarily warm and humid climates. A) large caves in limestone bedrock 14. Which type of climate has the greatest amount of rock weathering caused by frost action? A) a wet climate in which temperatures remain below freezing B) a wet climate in which temperatures alternate from below freezing to above freezing C) a dry climate in which temperatures remain below freezing D) a dry climate in which temperatures alternate from below freezing to above freezing Page 5 B) a pattern of parallel cracks in a granite mountain C) blocks of basalt at the base of a steep slope D) the smooth, polished surface of a rock in a dry, sandy area 19. Water is a major agent of chemical weathering because water 21. The diagram below represents a geologic cross section. A) cools the surroundings when it evaporates B) dissolves many of the minerals that make up rocks C) has a density of about one gram per cubic centimeter D) has the highest specific heat of all common earth materials 20. Base your answer to the following question on The generalized cross section below shows the sedimentary rock layers at Niagara Falls in western New York State. Which rock layer appears to be most resistant to weathering and erosion? A) Lockport dolostone B) Rochester shale C) Grimsby sandstone D) Queenston shale Page 6 Which rock type appears to have weathered and eroded the most? A) B) C) D) Base your answers to questions 22 and 23 on the graph below, which shows the effect that average yearly precipitation and temperature have on the type of weathering that will occur in a particular region. 22. Which type of weathering is most common where the average yearly temperature is 5°C and the average yearly precipitation is 45 cm? A) moderate chemical weathering B) very slight weathering C) moderate chemical weathering with frost action D) slight frost action 23. The amount of chemical weathering will increase if A) air temperature decreases and precipitation decreases B) air temperature decreases and precipitation increases C) air temperature increases and precipitation decreases D) air temperature increases and precipitation increases Page 7 24. As a particle of sediment in a stream breaks into several smaller pieces, the rate of weathering of the sediment will 28. What change will a pebble usually undergo when it is transported a great distance by streams? A) It will become jagged and its mass will decrease. A) decrease due to a decrease in surface area B) It will become jagged and its volume will increase. B) decrease due to an increase in surface area C) It will become rounded and its mass will increase. C) increase due to a decrease in surface area D) It will become rounded and its volume will decrease. D) increase due to an increase in surface area 25. A rock will weather faster after it has been crushed because its A) volume has been increased B) surface area has been increased C) density has been decreased D) molecular structure has been altered 26. The formation of soil is primarily the result of A) stream erosion and mass movement B) stream deposition and runoff C) precipitation and wind erosion D) weathering and biological activity 27. Sediments found in glacial moraines are best described as A) sorted and layered B) sorted and not layered C) unsorted and layered D) unsorted and not layered Page 8 29. The diagram below shows the sequence of events leading to the deposition of landslide debris. What was the primary force that caused this landslide? A) gravity B) moving ice C) prevailing winds D) stream discharge 30. The diagram below shows a glacial landscape feature forming over time from a melting block of ice. This glacial landscape feature is best identified as A) a kettle lake B) an outwash plain C) a finger lake D) a moraine Page 9 31. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below shows a section of a meander in a stream. The arrows show the direction of stream flow. 32. The map below represents a meandering stream flowing into a lake. A student measured water depths in the stream at three locations: A–A', B–B', and C–C'. Which set of cross sections best represents the streambed at the three locations? The streambank on the outside of this meander is steeper than the streambank on the inside of this meander because the water on the outside of this meander is moving A) B) A) slower, causing deposition B) faster, causing deposition C) C) slower, causing erosion D) D) faster, causing erosion Page 10 33. The diagram below represents a cross section of a stream. Points A, B, C, D, and E are locations within the stream channel. Which graph best represents stream velocity at locations A through E? A) B) C) Page 11 D) 34. Base your answer to the following question on the map and cross section below. The map shows the shapes and locations of New York State's 11 Finger Lakes and the locations of some major glacial deposits (moraines) left behind by the last ice age. The cross section shows surface elevations, valley depths, and water depths of the Finger Lakes. In which New York State landscape region are the Finger Lakes located? A) Hudson-Mohawk Lowlands B) Erie-Ontario Lowlands C) Allegheny Plateau D) the Catskills Page 12 35. Base your answer to the following question on the map below. Arrows on the map show the location and orientation of glacial striations on the surface bedrock. Dark shading shows the location of large moraines (glacial deposits). How were the striations made? A) Frost action cracked the bedrock during the ice age. B) Rocks at the bottom of the glaciers were dragged over the bedrock. C) Particles carried by winds scratched the bedrock during the ice age. D) Particles carried by glacial meltwater eroded the bedrock. 36. Which erosional agent typically deposits hills of unsorted sediments? A) glaciers B) streams C) winds D) ocean waves 37. Which natural agent of erosion is mainly responsible for the formation of the barrier islands along the southern coast of Long Island, New York? A) mass movement B) running water C) prevailing winds D) ocean waves Page 13 38. The map below shows some features along an ocean shoreline. In which general direction is the sand being moved along this shoreline by ocean (long–shore) currents? A) northeast B) southeast C) northwest D) southwest 39. The diagrams below represent landscape features found 40. Clay, silt, and sand are added to a jar of water. The jar is along the seacoast. The arrows show ocean-wave shaken and then allowed to stand quietly for a number direction. Which shoreline has been shaped more by of hours. The result of this demonstration could be best deposition than by erosion? used as a model to show that A) B) C) D) A) particles with the lowest density settle the fastest B) particles with the largest diameter settle the fastest C) water has a higher specific gravity than clay, silt, and sand D) the bottom layer of a series of sediments is the youngest Page 14 41. Four quartz samples of equal size and shape were placed in a stream. Which of the four quartz samples below has most likely been transported farthest in the stream? A) 44. The diagram below represents a landscape region and its underlying bedrock structure. B) Which stream pattern is most likely present in this area? C) D) 42. A stream with a velocity of 100 centimeters per second flows into a lake. Which sediment-size particles would the stream most likely deposit first as it enters the lake? A) boulders B) cobbles C) pebbles D) sand A) B) C) D) 45. New York State's generalized landscape regions are identified primarily on the basis of elevation and A) bedrock structure B) climate zones 43. A stream is entering the calm waters of a large lake. Which diagram best illustrates the pattern of sediments being deposited in the lake from the stream flow? C) geologic age D) latitude 46. In which New York State landscape region is Niagara Falls located? A) A) Tug Hill Plateau B) St. Lawrence Lowlands C) Allegheny Plateau D) Erie-Ontario Lowlands B) 47. The particles in a sand dune deposit are small and very well-sorted and have surface pits that give them a frosted appearance. This deposit most likely was transported by C) D) A) ocean currents B) glacial ice C) gravity D) wind 48. A paved blacktop parking lot was built on what was once a soil-covered field. This area will now experience increased runoff when rain occurs because the paved parking lot has Page 15 A) less capillarity B) less permeability C) greater infiltration D) greater porosity Base your answers to questions 49 and 50 on the diagram below, which shows several different landscape features. Points X and Y indicate locations on the streambank. 49. Explain why the stream meanders on the floodplain, but not in the mountains. 50. Explain why the upper valley in the mountains is U-shaped and the lower valley is V-shaped. Page 16 Answer Key UNIT #5: SURFACE PROCESSES AND LANDSCAPES 1. B 37. D 2. C 38. B 3. D 39. B 4. D 40. B 5. B 41. D 6. B 42. C 7. D 43. C 8. B 44. B 9. D 45. A 10. A 46. D 11. A 47. D 12. B 48. B 13. A 49. 14. B 15. B 16. D 17. D 18. A 19. B 20. A 21. C 22. D 23. D — The stream began to flow over a nearly flat landscape. — Stream velocity decreased. — Gradient decreases from the mountains to the floodplain. — The stream flows more slowly on the floodplain.— The floodplain is composed of loose sediment. 24. D 50. 25. B 26. D 27. D 28. D 29. A 30. A U-shaped: — It was eroded by glaciers. — A glacier formed the valley. — formed by glacial ice V-shaped: — Running water cut the V-shaped valley. — A stream formed the valley. 31. D 32. A 33. A 34. C 35. B 36. A Page 17