Chapter 2: Economic Systems
advertisement

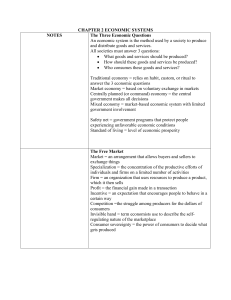
Chapter 2: Economic Systems 1. 2. 3. 4. Answering three Economic Questions? The Free Market Centrally Planned Economics Mixed Economics Command, or Central Authority Economy Free Market Economy Market Allocation Mixed Economy Government Allocation 1. Answering three Economic Questions WHAT? HOW? WHO? Goods and Services • What goods and services should be produced? • How should these goods and services be produced? • Who consumes these goods and services? . . . Because resources are scarce Economic System • The structure of methods and principles a society uses to produce and distribute goods and services • A way a society answers these questions defines its economic system Economic Goals and Societal Values • Different societies answer the questions based on importance they attach to various economic goals Economic Goals • Efficiency-Societies try to maximize their resources • Freedom-the opportunity to make your own choices • Security-”Safety net”-programs that protect people who face unfavorable economic conditions • Equity-How should we divide the pie? • Growth-innovation plays a huge role in economic growth Traditional Economies • An Economic system that relied on habit, custom, or ritual to decide the three economic questions. • There is little room for innovation or change in traditional economies • Led to more modern economic systems Three Economic Systems • Dominates the modern world • The free market economy (capitalism) • The centrally planned economy (communism) (socialism) • The mixed economy –a little of both Differing Systems • The United States • Freedom • Security • Efficiency • Equity • Growth • The Soviet Union • Equity • Growth • Security • Efficiency • Freedom 2. The Free Market • Economic Freedom -highly valued by American Society • Markets -any arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things • We are not producers of all our wants • Examples – fishing market, farmers market, Sporting goods store, New York Stock Exchange Market Why Markets Exist • Specialization -concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and businesses on a limited number of activities • Buying and Selling -sell what we produce and buy what we want Free Market Economy • An economic system in which decisions on the three key economic questions are based on voluntary exchange in markets • Individuals make their own decisions • Capitalism -the capital that entrepreneurs invest in businesses are vital • Individuals and businesses own the factors of production The United States Economy • Free enterprise economy -private or corporate ownership of capital goods • Government of the U.S. plays a major role in the economy • “promote the general welfare” • Some people think that the government intervenes too much in the economy • What do you think? Households and Firms • Household -person or group of people living in a single residence • Firm - business or an organization that uses resources to produce a product, which it then sells Factor and Product Markets • Factor Market -the arena of exchange in which firms purchase the factors of productions from households • Product Market -the arena of exchange in which households purchase goods and services from firms Circular Flow Model Product Flow Product Market Monetary Flow Factor Market Land Labor Product Flow Capital Factor Market Monetary Flow Product Market et rk Ma Pro d u c tM a r ket r cto Fa The Self-Regulating Nature of the Marketplace • Self Interest -an individual’s own personal gain • Incentive -the hope of reward or fear of penalty that encourages a person to behave in a certain way • Competition -the struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers • The Invisible hand-Adam Smith-the self regulating nature of the market place • “Give me that which I want, and you shall have this which you want . . . . It is in this manner that we obtain from one another the far greater part of those good [services] which we stand in need of. It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or that baker that we expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest.” – Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations Adam Smith Advantages of the Free Market • Efficiency -produce what consumers want • Freedom -work where you want, produce what you want, consume what you want • Growth -innovations • Consumer Sovereignty - having the power to decide And here are some disadvantages of the free market economy, or capitalism 3. Centrally Planned Economics • How Central Planning Works • Government makes all the decisions on three questions (command economy) • Government owns all factors of production • Direct contrast to free market structure Socialism and Communism • Socialism – range of economic and social systems based on belief that wealth should be distributed evenly throughout a society • Communism- political system in which government owns all resources and means of production and makes all economic decisions • “Capitalist production . . . Develops technology and the combining together of various processes . . . Only by sapping the original sources of all wealth- the soil and the laborer.” – Karl Marx, The Communist Manifesto • All my hard work and all the money ends up in the hands of capitalists Authoritarian • Form of government that limits individual freedoms and requires strict obedience from its citizens • Communist governments are always authoritarian Three Communist Economies • The Soviet Union -1917-Bolshevik RevolutionJoseph Stalin-broke up in 1991 • China - 1949 to late 1970’s-government planners controlled all aspects of Chinese society; adopted some free market • Cuba – Fidel Castro – 1959 – Cuban Revolution Disadvantages of Centrally Planned Economies • • • • Efficiency -no incentive to work hard Freedom -discourages competition Growth -no innovation no growth Equity -human intuition prohibits equity The need to satisfy all wants and needs 4 Mixed Economies • Reasons for Government Involvement • Laissez-faire -government generally should not intervene in the marketplace • Private Property -property owned by individuals not the government • Mixed economy -market-based economics in which government is involved to some extent Government in Market • Factor Market -government instead of individual owns factors of production Product Market -government purchases all goods and services and provides them the public Greatest Expenditure in U.S. Government – Social Security Factor Market Monetary Flow Product Market et rk Ma Pro d u c tM a r ket r cto Fa Continuum of Mixed Economies Central Planned North Korea Cuba Iran, Russia Mixed Mexico, France, South Africa China Germany Japan, Poland Free Market United States United Kingdom Canada Hong Kong