IFE
advertisement
Lecture 5
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
Logical operations on bits
Bitwise operations
NOT
– bitwise NOT (complement),
AND
– bitwise AND ,
OR
– bitwise OR,
XOR
– bitwise XOR,
TEST – logical comparison.
Shifting operations
SHL
– logical shift left,
SHR
– logical shift right,
ROL
– cyclic shift left,
ROR
– cyclic shift right,
RCL
– cyclic shift left with carry,
RCR
– cyclic shift right with carry.
String operations
REP/REPE/REPNE – iterative execution of a string operation,
MOVS – move block of data,
CMPS – compare blocks of data,
SCAS – search in block of data,
STOS – fill block of data
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
Bitwise operations
NOT (from not byte, word or double word)
Instruction performs logical negation on each bit (0->1, 1->0).
The only argument can be represented by registers or memory locations.
Affects no flags.
Available variants:
NOT r/m8
NOT r/m16
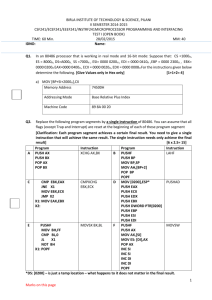
EXAMPLE:
NOT(00101001)=11010110
(…)
a db 10h
(…)
NOT AX
NOT a
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
NOT r/m32
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
AND (from AND byte, word or double word)
Performs logical bitwise AND operation on its two arguments. Result is hold in the first
argument. AND operation gives 1 only for a pair of 1s (00->0, 01->0, 10->0, 11->1).
Arguments can be given in the form of memory location, register or immediate value.
Affects: OF=0, CF=0, SF, ZF, PF.
Available variants:
AND r,r/m8
AND r/m8,r
AND r/m8,imm8
AND r,r/m16
AND r/m16,r
AND r/m16,imm16
EXAMPLES
(…)
a dw 120Ah
(...)
MOV AX,0010h
AND a,AX
(…)
MOV AL,13h
AND AL,01h
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
AND r,r/m32
AND r/m32,r
AND r/m32,imm32
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
How to check the state of bit with number n?
1. Prepare mask: mask=1<<n,
2. Use AND operation,
3. IF ZF==0 THEN Bit equals 0 ELSE Bit equals 1.
00100101 (n=5)
00100000 (mask)
00100000 (result of AND operation)
How to unset bit with number n?
1. Prepare mask: mask=1<<n,
2. Negate mask NOT mask,
3. Use AND operation.
00100101 (n=5)
00100000 (mask)
110111111 (NOT mask)
00000101 (result after AND)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
How to keep bits with numbers n1 to n2 (n1<=n2)?
1. Prepare mask: mask=(1<<(n2-n1+1))-1)<<n1,
2. Use AND operation.
00100101 (n1=1, n2=3)
00001110 (mask)
00000100 (result of AND operation)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
OR (from OR byte, word or double word)
Performs logical bitwise OR operation on its two arguments. Result is hold in the first
argument. OR operation gives 0 only for a pair of 0s (00->0, 01->1, 10->1, 11->1).
Arguments can be given in the form of memory location, register or immediate value.
Affects: OF=0, CF=0, SF, ZF, PF.
Available variants:
OR r,r/m8
OR r/m8,r
OR r/m8,imm8
OR r,r/m16
OR r/m16,r
OR r/m16,imm16
EXAMPLES
(…)
a db 1Fh
(...)
MOV BL,01h
OR a,BL
(…)
MOV CL,13h
OR CL,0Fh
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
OR r,r/m32
OR r/m32,r
OR r/m32,imm32
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
How to set bit with number n?
1. Prepare mask: mask=1<<n,
3. Use OR operation.
00100101 (n=3)
00001000 (mask)
00101101 (result after OR)
How to set bits with numbers n1 to n2 (n1<=n2)?
1. Prepare mask: mask=(1<<(n2-n1+1))-1)<<n1,
2. Use OR operation.
00100101 (n1=1, n2=3)
00001110 (mask)
00101111 (result of OR operation)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
XOR (from exclusive OR byte, word or double word)
Performs logical bitwise XOR operation on its two arguments. Result is hold in the first
argument. Exclusive OR operation produces 1 only for a pair of opposite bits (00->0, 01->1,
10->1, 11->0).
Arguments can be given in the form of memory location, register or immediate value.
Affects: OF=0, CF=0, SF, ZF, PF.
Available variants:
XOR r,r/m8
XOR r/m8,r
XOR r/m8,imm8
XOR r,r/m16
XOR r/m16,r
XOR r/m16,imm16
EXAMPLES
(…)
a db 1Fh
(...)
MOV AH,01h
XOR a,AH
(…)
XOR AX,AX
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
XOR r,r/m32
XOR r/m32,r
XOR r/m32,imm32
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
It should be noted that XOR is reversible.
00100101
10101010 (mask)
10001111 (result after XOR)
00100101 (result after one more XOR with the same mask)
How to clear contents of byte?
1. Use XOR using one value as arguments.
00100101
00100101
00000000 (result after XOR operation)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
TEST (from test or logical compare byte, word or double word)
Instruction performs logical AND operation but in the contrary to AND instruction the result is
volatile and only flags are affected.
Arguments can be given in the form of memory location, register or immediate value.
Affects: OF=0, CF=0, SF, ZF, PF.
Available variants:
TEST r,r/m8
TEST r/m8,r
TEST r/m8,imm8
TEST r,r/m16
TEST r/m16,r
TEST r/m16,imm16
EXAMPLES
(…)
MOV AX,0131h
TEST AX,0001h
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
TEST r,r/m32
TEST r/m32,r
TEST r/m32,imm32
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
Shifting operations
SHL (from shift logical left byte, word or double word)
Instruction shifts left the contents of the first argument by the number of bits indicated by the
second argument. With the number of bits greater than 1 this instruction takes CL as the
second argument. First argument can be given in the form of register or memory location.
Affects: OF, SF, ZF, PF, CF and AF is unpredictable.
Available variants:
SHL r/m8,1
SHL r/m8,CL
SHL r/m16,1
SHL r/m16,CL
EXAMPLE:
(…)
a db 16
(…)
SHL a,1
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
SHL r/m32,1
SHL r/m32,CL
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
SHR (from shift logical right byte, word or double word)
Instruction in opposition to SHL shifts right the contents of its first argument.
CF
n-1
0
0
SHL instruction
n-1
0
0
SHR instruction
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
CF
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
How to conveniently multiply integer number by the power of 2?
1. Write into CL the power indicator.
2. Use SHL number, CL instruction
00000101 (integer number 5)
CL<-2
(multiplication by 4)
00010100 (result after SHL number,CL, in decimal system: 20)
How to conveniently divide integer number by the power of 2?
1. Write into CL the power indicator.
2. Use SHR number, CL instruction
00110000 (integer number 48)
CL<-2
(division by 4)
00001100 (result after SHR number,CL, in decimal system: 12)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
ROL (from rotate left byte, word or double word)
Instruction performs cyclic shift left of the contents of the first argument by the number of bits
hold in the second argument. When the number of bits is greater than 1 it should be provided
with CL register taken as the second argument. First argument can be given in the form of
register or memory location.
Affects: OF, CF.
Available variants:
ROL r/m8,1
ROL r/m8,CL
ROL r/m16,1
ROL r/m16,CL
EXAMPLE:
(…)
MOV AX,1234h
ROL AX,1
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
ROL r/m32,1
ROL r/m32,CL
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
ROR (from rotate right byte, word or double word)
ROR instruction cyclically shift right the first argument. For other information see ROL
instruction.
n-2
CF
n-1
1
0
n-1
n-2
ROL instruction
ROR instruction
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
1
0
CF
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
How to count the number of 1s in byte?
1. Clear the counter value.
2. Use ROL byte,1.
3. ADC counter,1.
4. Execute steps 2 and 3 eight times.
MOV AL, 1234h
XOR CL,CL
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
ROL AL,1
ADC CL,0
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
RCL (from rotate through carry left byte, word or double word)
Instruction cyclically shifts left the contents of the first argument through CF flag by the number
of bits provided by the second argument. If the number of bits is greater than 1 it should be
given as the argument in CL register. First argument can be given in the form of register or
memory location.
Affects: OF, CF.
Available variants:
RCL r/m8,1
RCL r/m8,CL
RCL r/m16,1
RCL r/m16,CL
EXAMPLE:
(…)
a db 0A10h
(…)
MOV CL,3
RCL a,CL
(…)
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
RCL r/m32,1
RCL r/m32,CL
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
RCR (from rotate through carry right byte, word or double word)
Instruction cyclically shifts right the contents of the first argument through CF flag by the
number of bits provided by the second argument. For further information see RCL instruction.
CF
n-1
1
0
n-2
n-1
n-2
RCL instruction
RCR instruction
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
1
0
CF
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
EXAMPLES (cont.)
How to obtain bits in reversed order in byte?
1. Clear the result value.
2. Use ROL byte,1.
3. Use RCR result,1.
4. Execute steps 2 and 3 eight times.
MOV AL, 1234h
XOR CL,CL
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
ROL AL,1
RCR CL,1
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
REP/REPE/REPNE (from repeat, repeat while equal, repeat while not equal string operation)
1. checks CX and if CX equals 0 it goes to step 5,
2. executes string operation
3. decrements CX by 1,
4. REPE and REPNE additionally check ZF flag. If ZF=1 for REPE or ZF=0 for REPNE then
go to step 1. REP always goes to step 1,
5. finish.
Affects no flags.
Available variants:
REP/REPE/REPNE
string_instruction
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
MOVSB/MOVSW/MOVSD (from move string of bytes, words or double words)
1. sends byte, word or double word from address DS:SI to ES:DI,
2. If DF=0 then SI=SI+1{2,4}, DI=DI+1{2,4}, otherwise SI=SI-1{2,4}, DI=DI-1{2,4},
Affects no flags.
EXAMPLE:
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
CMPSB/CMPSW/CMPSD (from compare string of bytes, words or double words)
1. compares two bytes, words or double words at locations DS:SI to ES:DI and sets flags (see
CMP instruction),
2. If DF=0 then SI=SI+1{2,4}, DI=DI+1{2,4},
otherwise SI=SI-1{2,4}, DI=DI-1{2,4},
Affects like CMP instruction.
EXAMPLE:
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
SCASB/SCASW/SCASD (from scan string of bytes, words or double words)
1. it subtracts from AL{AX,EAX}register byte, word or double word. The result is not kept but
flags are affected,
2. if DF=0 then SI=SI+1{2,4}, DI=DI+1{2,4},
otherwise SI=SI-1{2,4}, DI=DI-1{2,4},
Affects flags like SUB instruction.
EXAMPLE:
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing
Instruction Set of Intel x86 Microprocessors
STOSB/STOSW/STOSD (from store byte, word or double word in a string of data)
1. it stores AL{AX,EAX} register at location ES:DI,
2. if DF=0 then SI=SI+1{2,4}, DI=DI+1{2,4},
otherwise SI=SI-1{2,4}, DI=DI-1{2,4},
Affects no flags.
EXAMPLE:
IFE: Course in Low Level Programing