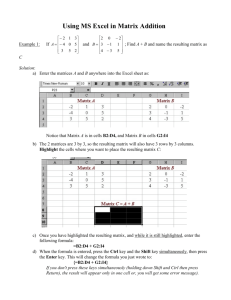
Oracle Navigation
advertisement
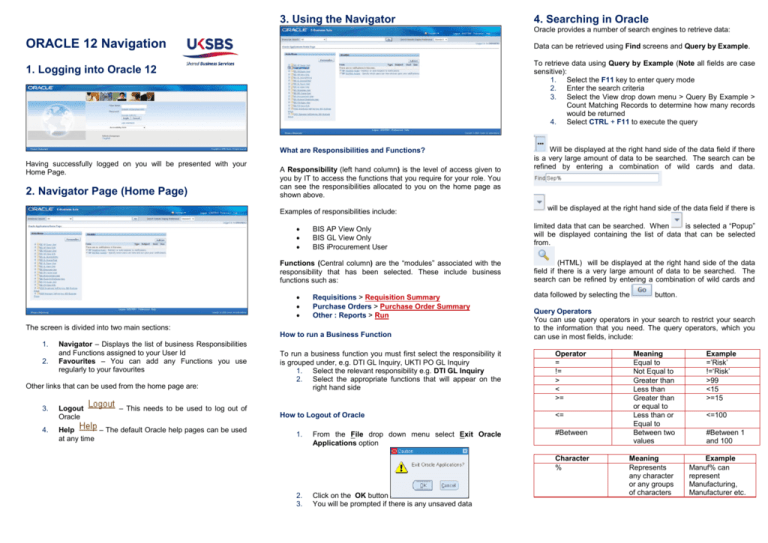
3. Using the Navigator 4. Searching in Oracle Oracle provides a number of search engines to retrieve data: ORACLE 12 Navigation Data can be retrieved using Find screens and Query by Example. To retrieve data using Query by Example (Note all fields are case sensitive): 1. Select the F11 key to enter query mode 2. Enter the search criteria 3. Select the View drop down menu > Query By Example > Count Matching Records to determine how many records would be returned 4. Select CTRL + F11 to execute the query 1. Logging into Oracle 12 What are Responsibilities and Functions? Having successfully logged on you will be presented with your Home Page. 2. Navigator Page (Home Page) A Responsibility (left hand column) is the level of access given to you by IT to access the functions that you require for your role. You can see the responsibilities allocated to you on the home page as shown above. Examples of responsibilities include: BIS AP View Only BIS GL View Only BIS iProcurement User Functions (Central column) are the “modules” associated with the responsibility that has been selected. These include business functions such as: Requisitions > Requisition Summary Purchase Orders > Purchase Order Summary Other : Reports > Run The screen is divided into two main sections: How to run a Business Function 1. 2. Navigator – Displays the list of business Responsibilities and Functions assigned to your User Id Favourites – You can add any Functions you use regularly to your favourites Other links that can be used from the home page are: – This needs to be used to log out of 3. Logout Oracle 4. Help – The default Oracle help pages can be used at any time Will be displayed at the right hand side of the data field if there is a very large amount of data to be searched. The search can be refined by entering a combination of wild cards and data. will be displayed at the right hand side of the data field if there is limited data that can be searched. When is selected a “Popup” will be displayed containing the list of data that can be selected from. (HTML) will be displayed at the right hand side of the data field if there is a very large amount of data to be searched. The search can be refined by entering a combination of wild cards and data followed by selecting the Query Operators You can use query operators in your search to restrict your search to the information that you need. The query operators, which you can use in most fields, include: To run a business function you must first select the responsibility it is grouped under, e.g. DTI GL Inquiry, UKTI PO GL Inquiry 1. Select the relevant responsibility e.g. DTI GL Inquiry 2. Select the appropriate functions that will appear on the right hand side Operator = != > < >= How to Logout of Oracle <= 1. From the File drop down menu select Exit Oracle Applications option #Between Character % 2. 3. Click on the OK button You will be prompted if there is any unsaved data button. Meaning Equal to Not Equal to Greater than Less than Greater than or equal to Less than or Equal to Between two values Meaning Represents any character or any groups of characters Example =’Risk’ !=‘Risk’ >99 <15 >=15 <=100 #Between 1 and 100 Example Manuf% can represent Manufacturing, Manufacturer etc. 5. The Oracle Toolbar New – Open a new blank record Find – Find an existing record Show Navigator – Display the Navigator Window Save – Save the data Next Step – Jumps to the next step in the process Switch Responsibility – Provides you with a list of responsibilities you can choose from Print – Print the current screen Close Form – Close the current form Cut – Cut any selected data to the clipboard Copy – Copy any selected data to the clipboard Paste – Paste the clipboard into the selected field Clear Record – Clear the data displayed on the screen Delete – Delete the record Edit Field – Opens an editor for the current field Zoom – Quick entry of an address by entering the Post Code Translations – Opens the translations window Attachments – Attach documents to a record Folder Tools – Displays the folder tool palette 6. Oracle Keyboard Shortcuts Block Menu Ctrl + B Clear Block F7 Clear Field F5 Clear Form F8 Clear Record F6 Count Query F12 Copy Ctrl + C Cut Ctrl + X Paste Ctrl + V Delete Record Ctrl + Up Display Error Shift + Ctrl + E Duplicate Field Shift + F5 Duplicate Record Shift + F6 Edit Ctrl + E Enter Query (entering search criteria for records) Execute Query (retrieve records) Ctrl + F11 Re-Do Ctrl + Y Undo Ctrl + Z 7. Other Oracle Tips Mandatory Fields Mandatory fields in Oracle are highlighted in yellow. If you see a yellow field like the one shown below it must be filled in before the record can be saved. Flexfields Flexfields are found in forms where additional information has been added to a standard Oracle form. They may include mandatory or important fields so it is worth checking what they contain. Flexfields normally appear at the end of the form in a small box as shown below: To open a flexfield simply click inside the white box and the additional information will appear on your screen. Exit Query Mode F4 Help Ctrl + H Insert Record Ctrl + Down List of Values (Lov) Ctrl + L List Tab Pages F2 Next Block Shift + Page Down Next Field Tab Next Primary Key Shift F7 Next Record Down Arrow Key Previous Block Shift + Page Up Caution Note: Under no circumstances should you use your Previous Field Shift + Tab Previous Record Up Print Ctrl + P Date Track History – Show the history of date changes Return Return (Enter Key) Save Ctrl + S Scroll Down Page Down Scroll Up Page Up Show Keys Ctrl + K Window Help – Help for the particular area of Oracle you are currently in Ctrl + U F11 Alter Effective Date – Change the date the event took place Export Data – Export your record to a Word Document Update Record An example of additional information on a Payables Invoice function can be seen below. browser and buttons as this may cause Oracle to disconnect and you will lose any unsaved data.