ERCOT Design and Implementation of Internal

ERCOT Design and Implementation of
Internal Controls and benefits for
NERC CMEP/RAI
Matt Mereness, ERCOT Compliance Director
August 2015
Anfield Summit
Outline of discussion
– ERCOT Background
– Business Case for Internal Controls
– Building a Controls Program
– Assessing Controls
– Preparing for Recent Audit
– 2015 Audit Experience
– Broader GRC Implementation and Benefits
2
2
ERCOT BACKGROUND
3
ERCOT Background- Reliability Regions
ERCOT connections to other grids are limited to direct current (DC) ties (~1100 MW with
SPP and Mexico)
• Electric Reliability Council of
Texas – the ERCOT grid:
– Covers 75% of Texas land
– Serves 85% of Texas load
– More than 40,500 miles of transmission lines
– 550+ generation units (more than 84,000 MW of capacity)
– Physical assets are owned by transmission providers and generators, including
Municipal Utilities and
Cooperatives
– Peak Load was set on August
3, 2011 at 68,305 MW (today)
4
ERCOT Background
Key Features of ERCOT
– Electrical island with several DC Ties
– Deregulated Market in 2000, Nodal 2010
– Non-Profit System Operator funded by state
– Dispatches real-time energy market every 5 minutes
– Executes energy markets and settlement
– Facilitates retail switching
5
5
ERCOT Background - NERC Audit experiences
Registered as BA, PC, RC, RP, TOP, TSP
• 2008 Compliance Violation Investigation 693
• 2008 Annual 693 Audit
• 2009 Annual 693 Audit
• 2009 CIP Spot Check
• 2010 Annual 693 Audit
• 2010 Annual CIP Audit
• 2011 FERC, NERC and Texas RE Investigation (Cold Weather)
• 2011 Three 693 Spot Checks (Laredo 2008, Valley 2011, 693 Clean-up)
• 2012 693 Spot Check (Cold Weather)
• 2012 Annual 693 Audit
• 2013 Annual CIP Audit
• 2015 Audit underway (note not 693 or CIP)
6
BUSINESS CASE FOR
INTERNAL CONTROLS
7
Internal Reasons for Change –
Scope and Lessons Learned
– Historically ERCOT managed a relatively large number of controls using manual processes to maintain alignment with changing NERC requirements.
– For audits, managing people and evidence was challenging across departments
• Multiple department silos of responsibility/processes in meeting a requirement
• Organizing and reviewing evidence/RSAW responses is tedious and manually intensive
(emails, sharepoint, meetings)
– Lack of centralization can create gaps and overlaps in data collection
– Often the quality of the audit is only as organized as the person responsible for assessing the requirements.
– Audits historically are an all-hands-on-deck exercise
– ERCOT committed to improving this manual and repeatable process
8
External Reasons for Change
-Transitioning NERC Audit Approach
• Reliability Assurance Initiative (RAI)
– A national effort between the NERC, the Regional Entities, and registered entities to implement changes that enhance the effectiveness of the Compliance Monitoring and Enforcement Program (CMEP). o It is an effort to retool and refocus compliance and enforcement o RAI processes will focus on risk to grid reliability in developing scope of audit o RAI is a customized compliance approach with individualized scoping for each registered entity o To NERC not all requirements are created equally when it comes to audit scope & monitoring. o Risk factor for NERC Requirement (Risk factor in standard) o National risk focus (published CMEP plan) o Regional risk focus (appendix of CMEP plan) o Historical findings (consider ERCOT RFIs, audit scope, self-reports)
9
NERC Audit Changes
Uncertainty of
Internal Controls Evaluation
(ICE) process
10
NERC Audit Changes
11
BUILDING CONTROLS
PROGRAM
12
Internal Controls
Controls building blocks
1.
Define categories of internal controls
• Preventative, Detective, Corrective
2.
Define & document internal controls with SMEs
• Procedures, Logs, Alarms
3.
Define & document process flows and responsible parties
• Tabletop walk-throughs for complicated processes (across silos)
4.
Map the controls to requirements
• Many requirements - relate - to - many controls
5.
Develop test sequences
• Agree to process to observe control and see evidence of compliance
6.
Optional- Automation and tracking for collection of evidence
• Implement system with built in business process flows and collection
13
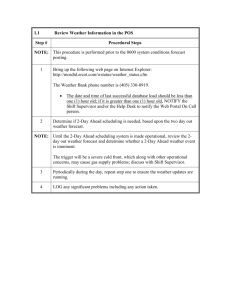
Example of Internal Control (manual paperwork process)
14
Internal Controls
• Internal Controls in AlertEnterprise system q Centralized record of NERC requirements in effect at a point in time q Inventory of controls for requirements q Mapping of requirements to controls q Programmable business process flows for running assessments and evidence
15
Implementation Alert Roadmap
2Q2014 3Q2014 4Q2014
Initial NERC 693 & Protocols for System Operations and Planning Effort
1Q2015
6 week mapping effort for each business unit
NERC CIP
Requirements
Maintain update standards/protocols
Quality check
Close gaps
Complete NERC self-certification
Maintain with changes to requirements
Develop CIP v5
16
Compliance system- Requirement screenshot
17
Compliance Requirement mapped to multiple Internal Controls
18
ASSESSING CONTROLS
19
Internal Controls Assessments
• ERCOT performs periodic “assessments” to verify controls are effective.
– Assessments are performed based on risk
• ERCOT evaluates changes to requirements to ensure processes and controls are consistent with the changes.
• ERCOT’s goal is to assess all NERC–related controls at least once per year.
20
Control Assessment Life Cycle
Business Analyst(s)
Reviews assessment questions and gathers evidence.
Compliance
Initiates changes and execution of assessments.
Business
Owner/Manager
Reviews and approves assessment and evidence.
Effective with
Date
Compliance
Final review, update in system as completed and effective.
21
Example- Control Assessment
The screenshots below provide assessment details including the start date and the overall status and example of test questions to help determine if control is effective.
Control/procedure is verified, evidence attached, and “passed ” 22
Example of Assessment of Control to Multiple Requirements
By testing this RUC procedure, you can assess/pass 3 requirements
23
PREPARING FOR RECENT
AUDIT
24
Compliance Risk Methodology and Results
Reqt
Risk
Factor
NERC
CMEP
Audit
History
4 Risk
Levels
Critical -
163
High - 117
Med - 257
Low - 389
Self-
Report
25
Risk Methodology and Results
ERCOT
Compliance Risks
Subset of NERC
Requirements
Subset of
ERCOT Controls
Controls inventory to prioritize and assess
26
Critical Requirement (Focus on Risks)
27
Reports of Critical Requirements and Controls
28
2015 AUDIT EXPERIENCE
29
NERC changes in auditing
ERCOT 2015 Audit Scope
1200 Requirements à IRA 26 requirements à ICE 20 requirements
Auditors will be onsite Sep 21-25
30
Audit timeline and details
January 2015- RE advised ERCOT of being scheduled for Sept audit engagement.
May 2015 RE advised ERCOT that IRA was complete and invited to engage in ICE.
• No interaction between ERCOT and RE during IRA evaluation
• Audit scope was unknown at this point, but told it would be “focused”
• ERCOT accepts voluntary ICE invitation
May 2015 ERCOT received ICE notice.
• ICE scope for 26 requirements supporting 2 risk themes (represented the current scope of the forthcoming audit)
• 2 week deadline to respond with controls (provided powerpoint overview of controls program, applicable procedures/controls for each requirement, and listing of dates controls last assessed)
June 2015 ERCOT received formal audit notice for 20 requirements
• Output (benefit) of ICE was that 6 of 26 requirements were removed from scope of audit.
• 40 days deadline to complete and file RSAWs and evidence for 20 requirements
• RSAWs filed and waiting for questions leading into the Sept tabletop and onsite audit activities.
31
Specific to TexasRE ICE
Controls for ICE
• ERCOT submitted the inventory of key controls mapped to requirements.
Assessments for ICE
• In its submission package ERCOT included a summary of the assessment history for the related controls.
Overview of Internal Controls at ERCOT
• GRC System, terminology, goals
32
In summary Alert captured;
Narrative for how Reqt is met
Point-in-Time History of Requirement & Assessments
Links Requirement to Controls (Procedures, Software screens, etc)
Links to Owner(s)
Links to Evidence
33
BROADER GRC
IMPLEMENTATION AND BENEFITS
34
Benefits of Alert
Leveraging the tool to work for company
• Electronic/Query-able System of record
– Traceability for requirements, ownership in a database that can be queried
• Change control
– Provides quick summary of related/impacted changes- ripple effect
– 3 areas of change: Requirements, Staff, Controls/Procedures
• Auto-scheduling
– Calendar tripwires - Systemic reminders of Annual filings, certification, or authority sign-off
• Business owner configures frequency
– How often to be assessed for certain controls (accountability)
35
Benefits of Alert
• Management reports
– Aging reports (when was this requirement last changed or assessed)
– Status of annual assessment progress
• Risk levels
– Flag a requirement as high risk can map to and identify critical controls
– Helped ERCOT prepare for 2015 audit (assess 20% instead of 100% controls)
• NERC CIP v5 readiness path
– Assessment completion creates CIPv5 RSAW and evidence finish line
36
High Level Compliance Implementation (larger GRC)
ICMP Support/SSAE16
Management of corp controls and changes to policies
NERC 693 Support
Processes/Dependencies/
INCREASING
ERCOT Compliance
CFR/ Changes
NERC CIP Support
Processes/software/
Alert Scope of Requirements
800 SSAE/ICMP education (Cyber, Sec, IT)
1,200 NERC
3,000 Protocols
Protocol Must/Shall/Will
Support
Numerous new departments to interface with
Audit Preparation
SSAE, NERC, Protocol
Range of methods
Note- One effective access procedure/control may satisfy multiple reqts/frameworks 37
Extending it into different business areas
Different Compliance Monitoring methods-
• SSAE60/ CorpControls Attestation “ survey-only approach ”
• Alert-routed surveys with questions to execs where they confirm they are compliant
• Solicits changes and confirmation of compliance
• Quick execution/attestation
• Protocols Mapping/Traceability “ controls mapping approach ”
• Traceability/ownership/change management
• Connect words on rules to owner, narrative how they satisfy part of all, provide link to control
• NERC mapping and verification “ controls mapping with evidence approach ”
• Full traceability with testing, collecting evidence, and reviewing quality of results.
38
THANK YOU!
Matt.Mereness@ercot.com
39