Environmental Biology Homework
advertisement
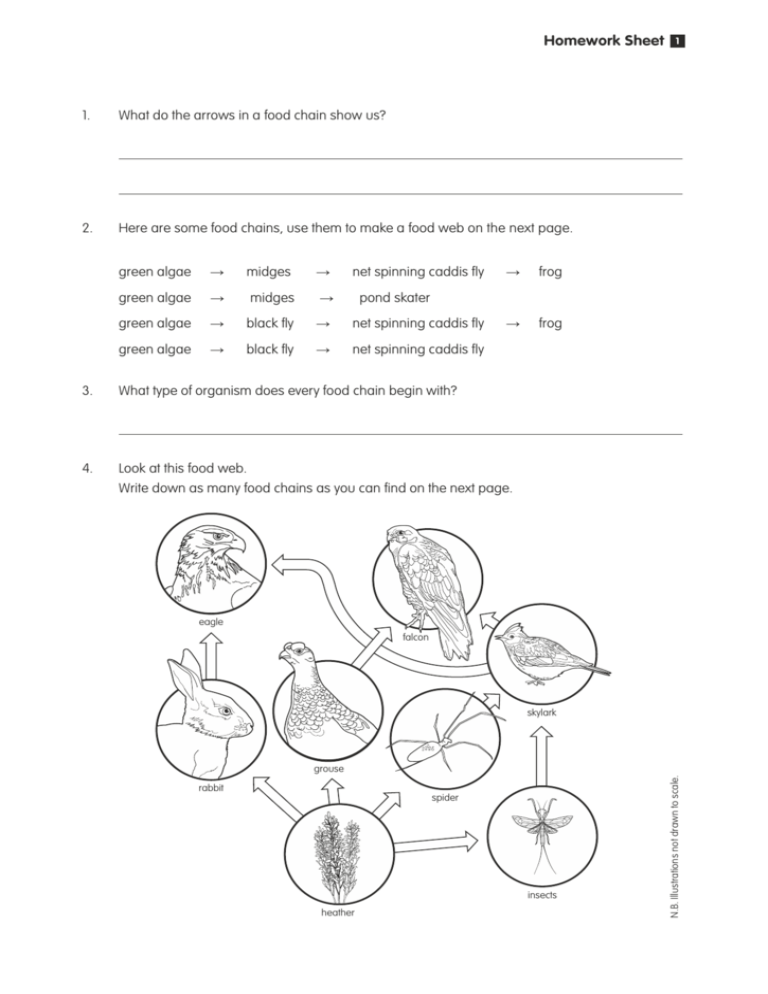
Homework Sheet 1. What do the arrows in a food chain show us? 2. Here are some food chains, use them to make a food web on the next page. green algae → midges → net spinning caddis fly green algae → midges → green algae → black fly → net spinning caddis fly green algae → black fly → net spinning caddis fly → frog → frog 1 pond skater 3. What type of organism does every food chain begin with? 4. Look at this food web. Write down as many food chains as you can find on the next page. eagle falcon skylark rabbit spider insects heather N.B. Illustrations not drawn to scale. grouse 2. 4. Homework Sheet 1 The dodo is one famous example of an extinct animal. This flightless bird was first discovered around 1600, when sailors first landed on the island of Mauritius. For many years the dodo had lived an easy life, roaming the forests on the island where there was plenty of food and shelter for nesting. Because the dodo was one of the largest animals on the island, there were no natural predators hunting it. When the sailors landed on Mauritius they began to hunt the dodo for food. However as well as the sailors hunting the dodo, the cats and rats which lived on the ships came on to the island and also began to hunt the dodo. The dodo was an easy bird to catch and very quickly the population became very small. As well as looking for food, the sailors also landed on the island looking for wood. To repair their ships, the sailors took trees that they had chopped down in the forests on the island. The forest gradually grew smaller, and as the forest shrank the population of dodos became smaller and smaller until the last dodo was seen in 1680. a. Give two reasons why life on Mauritius was easy for the dodo. 1. 2. c. Suggest a reason why the passage says ‘The dodo was an easy bird to catch… ’. d. Apart from hunting, what else did the sailors do that affected the dodos? e. How long did it take for the dodo to become extinct? Homework 2 Food webs Look at the food web below and write down five different food chains. hawk snake frog grasshopper marsh grass 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. cricket cat tail N.B. Illustrations not drawn to scale. shrew Homework 2 Making food webs Use the food chains below to construct a food web only appears in the food web ). (remember the organism’s name green plant herring seal green plant herring killer whale green plant mosquito salmon N.B. Illustrations not to scale. Construct another food web using the table below. ANIMAL FOOD slug dandelion rabbit dandelion; grass cow dandelion; grass fox rabbit; frog frog slug killer whale Homework Sheet The diagram opposite shows part of a pond food web. pike water beetle perch tadpole minnow N.B. Illustrations not drawn to scale. 1. 3 water weed Use the words increase, decrease or stay the same to suggest what might happen to the minnows and water beetles if all the tadpoles were removed. Minnows would Reason Water beetles would Reason Homework 2. The food chains below are examples of food chains found in a. heather → vole → owl heather → grouse → fox heather → grouse → golden eagle heather → vole → fox Use the food chains above to construct a food web. The grouse population dies out and this affects the other populations in the web. b. Describe what will happen to the populations below (i.e. increase or decrease) and give a reason to explain your choice. The vole population will because The fox population will because c. Suggest a reason why heather will only grow on an open hillside and not under the cover of a forest. 3 Homework 3 Upsetting a food web hawk shrew wagtail wasp chafer beetle caterpillar roots flower 3. Use the food web to predict what would happen to the number of died of a disease. leaf if the wasps Prediction Reason Look at the food web again and explain why the numbers of the wasps all died. Explanation might go up if N.B. Illustrations not drawn to scale. moth Homework Abiotic factors Complete the diagram below. ABIOTIC FACTORS Explain what is meant by abiotic factor. 4 Homework 4 2. Different plants like to grow in different places. Each environment has its own set of conditions, with different levels of abiotic factors. Choose two different abiotic factors and describe how you would measure them. Factor 1 How it would be measured: Factor 2 How it would be measured: 3. Which of the following statements are true and which are false? An organism’s is where it lives All the living things in an ecosystem is the population. Consumers are organisms that can make their own food. Producers are plants that can make their own food. Homework 1. Which of the following is an abiotic factor, affecting where organisms are found? a) food b) disease c) light d) predators 2. What piece of apparatus would you use to measure this abiotic factor? 3. Name another two abiotic factors. 4. The table below shows the changes in numbers of pond skaters in a year. MONTH NUMBERS PER ML January February March April May June July August September October November December 5 7 14 25 30 35 45 45 40 20 10 6 a) Use the information to draw a b) What happens to the numbers of pond skaters from January to July? c) During which two months is the number of pond skaters at their lowest? d) Suggest a reason for the low numbers in these two months. e) Suggest what the pond skaters have to compete for during the months of July and August? on the next page. 5 Homework 5. 5 The table below show the results of a plant survey and light intensity A = dark 6. light intensity A A G H I C B B A % daisies 10 9 60 70 65 12 11 10 10 a) Do you think daisies grow best in light or dark conditions? b) Explain how you reached your answer. I = bright The table below shows a survey of worms and moisture values taken from a garden. 1 = dry 7. moisture content 10 10 9 8 7 5 2 1 1 number of worms 120 110 90 90 60 40 5 3 3 a) In what sort of soil would you find most worms? b) How would you test the soil to find out how much moisture was present? 10 = damp Some animals and plants are endangered species, and some animals and plants are extinct. Explain the difference between endangered and extinct. Name two animal species which are endangered. 8. Using an example, explain why it is important for plants and animals to be adapted to their environment. Homework 5 Places where plants like to grow… 6. The table below shows the results from a plant survey and light intensity. AREA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 light intensity A B C D E F G H H H DARK BRIGHT PLANT TYPE NUMBERS daisies 0 0 0 0 5 11 16 19 22 22 wood sorrel 20 15 15 10 10 5 0 0 0 0 Which plant grows best in light conditions? Which plant is found only growing in darker conditions? The table below shows another survey of plants and moisture values. AREA 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 moisture content 8 7 7 7 7 5 5 3 2 1 WET DRY PLANT TYPE NUMBERS Plant A 2 2 3 2 3 4 5 7 10 12 Plant B 24 22 20 20 19 10 3 3 1 0 Which area has the most moisture? Which area has the least moisture? Does Plant B grow best in wet or dry conditions? Name the piece of apparatus you would use to measure moisture and describe how it is used. Homework The plant competition Look at the diagrams below; what might the plants in Dish 3 be competing for? Dish 1 Dish 2 1. 2. 3. Identify factors kept the same to give a fair comparison between the dishes. 1. 2. 3. Dish 3 6 Homework 6 2. Mrs. Smith notices that rabbits eat the lettuces in her garden. There is also a fox, which hunts and eats the rabbits. Greenfly also eat the lettuce, but thankfully ladybirds eat these annoying insects. The fox also eats blackbirds eggs if it finds the nest. Blackbirds eat worms and ladybirds. Worms are actually good for the soil because their burrowing lets oxygen into the soil and they eat dead lettuce leaves that drop to the ground. Use the information to construct a food web 3. Grey squirrels are not native to Britain. The introduction of the grey squirrel has affected red squirrels. Select the correct options to complete the statement below. Since the arrival of the grey squirrel, the population of red squirrels has Because they are similar species, the competition between them is increased decreased greater less Homework 1. What word is used to describe the process plants use to make starch? 2. Which of the samples recorded in the table below contains starch. 3. 4. Sample Colour with iodine A orange B black Put the following stages into the correct A Rinse the leaf in warm water. B Boil leaf in water. C Cover in iodine. D Boil leaf in ethanol. What precaution must be taken when we are using ethanol? 7 Homework 5. Brad and Jennifer, two pupils were carrying out a leaf test on a leaf with green and white stripes. They found that not all of the leaf was making starch. Which parts of the leaf were able to make starch? Use the chemicals listed below to answer the following iodine starch carbon dioxide ethanol oxygen chlorophyll water light 6. Choose the two raw materials for 7. Where does the energy for photosynthesis come from? 8. What useful gas is made by photosynthesis? 7 Homework Sheet 1. Write a word equation to summarise photosynthesis. 2. Complete the table Type of use Name of plant Details medicine food raw materials raw materials 3. Describe another important role that plants play. TRUE/FALSE 4. Chlorophyll is a raw material for photosynthesis. 5. Starch is a product of photosynthesis. 6. A variable leaf has green and white parts. 7. Alcohol dissolves chlorophyll. 8 Homework 8 8. Three containers A, B and C were set up to investigate seed = no germination = germination A 30 ml water a. C 5 ml water What is the ratio of seeds germinated in A to B? A b. B 20 ml water :B Calculate the percentage of seeds which germinated in each dish. dish volume of water (ml) A 30 B 20 C 5 % germination c. Draw a line graph with volume of water against percentage germination. d. What would the percentage germination be if 10 ml of water were added? e. Suggest one way to improve this investigation. % Homework 9. What are the two products of photosynthesis? directional light 10. Fred and Holly used the table below to record their results using the experiment above. Put the correct number of oxygen bubbles in the correct place in the table. 17 48 Situation plant left in the dark lamp 1 metre away lamp 10 cm away 0 Number of oxygen bubbles per minute 8