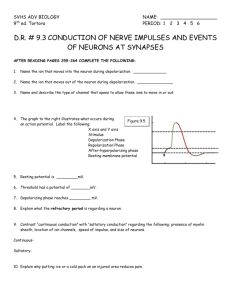
The neuron Label the following terms: Soma Axon terminal Axon
advertisement

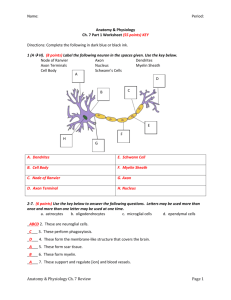
The neuron Label the following terms: Soma Axon terminal Axon Dendrite Nucleus Node of Ranvier Schwaan cell Myelin sheath Neuron Vocabulary You must know the definitions of these terms 1. Synaptic Cleft 2. Neuron 3. Impulse 4. Sensory Neuron 5. Motor Neuron 6. Interneuron 7. Body (Soma) 8. Dendrite 9. Axon 10. Action Potential 11. Myelin Sheath (Myelin) 12. Afferent Neuron 13. Threshold 14. Neurotransmitter 15. Efferent Neurons 16. Axon Terminal 17. Stimulus 18. Refractory Period 19. Schwann 20. Nodes of Ranvier 21. Acetylcholine STEPS IN THE ACTION POTENTIAL 1. The presynaptic neuron sends neurotransmitters to postsynaptic neuron. 2. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell. - This action will either excite or inhibit the postsynaptic cell. - The soma becomes more positive. 3. The positive charge reaches the axon hillock. - Once the threshold of excitation is reached the neuron will fire an action potential. 4. Na+ channels open and Na+ is forced into the cell by the concentration gradient and the electrical gradient. - The neuron begins to depolarize. 5. The K+ channels open and K+ is forced out of the cell by the concentration gradient and the electrical gradient. - The neuron is depolarized. 6. The Na+ channels close at the peak of the action potential. - The neuron starts to repolarize. 7. The K+ channels close, but they close slowly and K+ leaks out. 8. The terminal buttons release neurotransmitter to the postsynaptic neuron. 9. The resting potential is overshot and the neuron falls to a -90mV (hyperpolarizes). - The neuron continues to repolarize. 10. The neuron returns to resting potential. The Synapse Label the following terms: Pre-­‐synaptic membrane Post-­‐synaptic membrane Vesicle Neurotransmitters Synaptic cleft Post-­‐synaptic receptors