9th Grade Social Studies Economics
advertisement

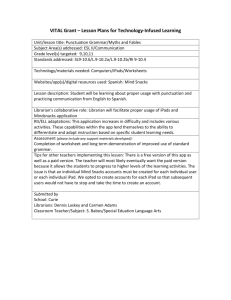
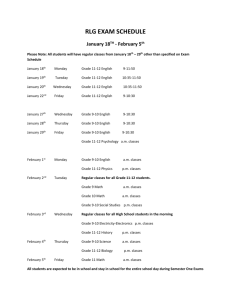
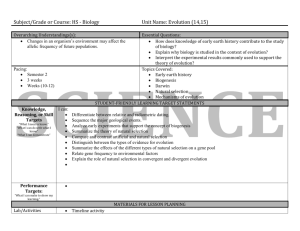
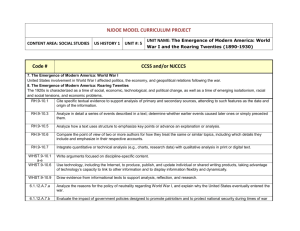
9th Grade Social Studies: Economics Pacing Guide Common Core State Standards 1st Nine Weeks Strand: ECONOMIC FUNDAMENTALS Content Standard 1: Student shall examine scarcity and choice. EF1 E.1 - Explain the role scarcity and opportunity cost plays in making choices using the PACED decision making model: individuals, businesses, and governments. EF1 E.2 - Describe the use of cost/benefit analysis in making choices: individuals, businesses, and governments. EF1 E.3 - Explain the concepts of tradeoffs (e.g., budget, career choices, earnings potential, education and/or training). EF1 E.4 - Discuss individual or societal economic choices, which are guided by incentives and based on rational self-interest (e.g., employee benefits, tax incentives). Strand: ECONOMIC FUNDAMENTALS Content Standard 2: Students shall examine the roles of economic systems in the use and distribution of resources. EF2 E.1 - Analyze the four factors of production: natural resources, human resources, capital resources, and Entrepreneurship. EF2 E.2 - Examine the three basic economic questions that must be answered by every economic system: • What goods and services are to be produced and in what quantities? • How will the goods and services be produced? • For whom will the goods and services be produced? EF2 E.3 - Compare and contrast the four major economic systems: command economy, market economy, mixed economy, and traditional economy. EF3 E.4 - Summarize global patterns of economic activity: world trading partners, trading blocs, regional trade agreements, regional trade organizations, and free trade. Content Standard 3: Students shall analyze the reasons individuals, businesses, and governments’ trade. EF3 E.1 - Explain the role of specialization and voluntary exchange in the marketplace (e.g., absolute advantage, comparative advantage). EF3 E.2 - Examine trade barriers: tariffs, quotas, embargos, preservation of standards (protectionism), and Subsidies. EF3 E.3 - Explain the effect of exchange rates on global purchasing power. EF3 E.4 - Summarize global patterns of economic activity: world trading partners, trading blocs, regional trade agreements, regional trade organizations, and free trade. Strand: PERSONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Content Standard 11: Students shall analyze career choices, education, skills, and economic conditions affecting earnings potential. PFM11 E.1 - Compare and contrast career options including entrepreneurial activities using available resources (e.g., Occupational Outlook Handbook, Internet, guest speaker, job shadowing). PFM11 E.2 - Interpret factors affecting income: career choices and potential income and education and training. PFM11 E.3 - Analyze the costs and benefits of personal choices in education and training that affect earnings potential: intrinsic and extrinsic. PFM11 E.4 - Evaluate the importance of interpersonal skills in the workplace (e.g., workforce readiness skills, ethics). 1 Content Standard 12: Students shall evaluate the impact of credit on personal financial decisions. PFM12 E.1 - Compare and contrast forms of credit: loans (e.g., home, car, education, personal) and credit cards. PFM12 E.2 - Evaluate the costs and benefits of using credit: interest rates, fees and penalties, and rewards. PFM12 E.3 - Explain factors that affect credit worthiness: credit score and credit report, debt management (e.g., credit counseling, debt consolidation, bankruptcy), credit protection laws, and identity protection (e.g., identity theft, phishing, scams). PFM12 E.4 - Explain ways to avoid and correct credit problems (e.g., credit counseling, identity protection, debt consolidation, bankruptcy). Content Standard 13: Students shall evaluate wealth management choices available to individuals. PFM13 E.1 - Research sources of conflict and confrontation during the Cold War (e.g., atomic/hydrogen bomb, Korea, Vietnam, China, United Nations, Berlin, Afghanistan, Cuba, Truman Doctrine, U2 spy plane, division of Germany, espionage). PFM13 E.2 - Analyze the role of alliances and treaties in shaping the world during the Cold War (e.g., North Atlantic Treaty Organization, Warsaw Pact, Marshall Plan, Molotov Plan, Strategic Arms Limitation Treaties, Intermediate Nuclear Forces Treaty). PFM13 E.3 - Investigate the consequences of the space race on the Cold War (e.g., education, technology, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, satellites, Strategic Defense Initiative). PFM13 E.4 - Investigate the consequences of the space race on the Cold War (e.g., education, technology, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, satellites, Strategic Defense Initiative). PFM13 E.5 - Analyze the effects of the Red Scare on United States society (e.g., McCarthyism, Hollywood black list, pumpkin papers, Rosenburgs, Federal Bureau of Investigation, Central Intelligence Agency, bomb shelters). Strand: Reading – Historical Text Instructional Focus: Key Ideas and Text RH 9-10.1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, attending to such features as the date and origin of the information. RH 9-10.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. Instructional Focus: Craft and Structure RH 9-10.4. Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary describing political, social, or economic aspects of history/social science. RH 9-10.5. Analyze how a text uses structure to emphasize key points or advance an explanation or analysis. RH 9-10.6. Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. Instructional Focus: Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RH 9-10.7. Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g., charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. RH 9-10.8. Assess the extent to which the reasoning and evidence in a text support the author’s claims. RH 9-10.9. Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources. Strand: Writing in Social Studies/History, Science & Technical Subjects – CCSS - Grades 9-10 Instructional Focus: Text Types and Purposes WHST 9-10.1. Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. 2 o Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. o Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. o Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. o Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. o Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented. WHST 9-10.2. Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/experiments, or technical processes. o Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. o Develop the topic with well-chosen, relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic. o Use varied transitions and sentence structures to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. o Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to manage the complexity of the topic and convey a style appropriate to the discipline and context as well as to the expertise of likely readers. o Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. o Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic). Strand: WRITING in History/Social Studies, Science & Technical Subjects Grades 9-10 Instructional Focus: Production and Distribution of Writing WHST 9-10.4. Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. WHST 9-10.5. Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. WHST 9-10.6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Instructional Focus: Research to Build and Present Knowledge WHST 9-10.7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. 3 WHST 9-10.8. Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. WHST 9-10.9. Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Instructional Focus: Range of Writing WHST 9-10.10. Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 2nd Nine Weeks Strand: MICROECONOMICS Content Standard 4: Students shall assess the role of supply and demand. MI4 E.1 - Illustrate the effects of supply and demand in determining equilibrium price and quantity using a supply curve and a demand curve. MI4 E.2 - Demonstrate changes in supply and demand that influence equilibrium price and quantity using a supply curve and demand curve: shifts in supply and demand, changes in quantity supplied and quantity demanded, and shortages and surpluses. MI4 E.3 - Describe the signals sent to buyers and sellers by price (e.g., cost, availability). MI4 E.4 - Describe the signals sent to buyers and sellers by price (e.g., cost, availability). Content Standard 5: Students shall analyze the organization of business firms in a market economy. MI5 E.1 - Compare and contrast major forms of business organizations: sole proprietorship, partnership (e.g., limited, general), corporation (e.g., public, private, hybrid business), and non-profit. Content Standard 6: Students shall analyze the organization of business firms in a market economy. MI6 E.1 - Compare and contrast different models of market structures: perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly, and cartel. MI6 E.2 - Describe the role that the stock market plays in the economy of the United States. Content Standard 7: Students shall examine the importance of increasing productivity in a market economy. MI7 E.1 - Distinguish between fixed costs and variable costs. MI7 E.2 - Analyze the influence improved factors of production have on the productivity of individual industries (e.g., technology, education, training, specialization, division of labor). Strand: MACROECONOMICS Content Standard 8: Students shall examine measurements of economic performance. MA8 E.1 - Analyze the following economic indicators used to measure economic performance: Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross Domestic Product per capita, Real Gross Domestic Product, unemployment rates, Consumer Price Index (CPI) (e.g., inflation), and stock market. MA8 E.2 - Compare and contrast the causes and types of unemployment (e.g., underemployment, outsourcing, off-shoring, cyclical unemployment, structural unemployment, frictional unemployment, seasonal unemployment). MA8 E.3 - Explain stages of the business cycle: peak, trough, expansion, and contraction (e.g., recession, depression). Content Standard 9: Students shall analyze roles that governments play in the economy. MA9 E.1 - Discuss the roles of governments in the economy: establish and enforce private property rights and the Law; deal with external costs and benefits; ensure market competition; stabilize the economy; 4 consumer protection; promote economic security; provide public goods and services; regulatory agencies; and redistribution of income. Content Standard 10: Students shall evaluate monetary policy and fiscal policy and their relationship to economic stability and growth. MA10 E.1 - Compare and contrast the functions of money in a market economy: medium of exchange, measure of value, and store of value. MA10 E.2 - Assess the characteristics of money in a market economy: portability, durability, divisibility, and limited supply. MA10 E.3 - Examine the different types of financial institutions in the United States (e.g., banks, credit unions, investment firms, cooperatives). MA10 E.4 - Describe the roles and functions of banks and financial institutions in the United States (e.g., saving, checking, investment, loans, trust). MA10 E.5 - Describe the organization and roles of the Federal Reserve system: Federal Reserve organizational structure and monetary policy (e.g., open market operations, discount rate, reserve requirement). MA10 E.6 - Discuss the role of fiscal policy in setting and maintaining economic stability and growth (e.g., expansionary, contractionary). MA10 E.7 - Illustrate the major sources of government revenue (e.g., taxes, fees, interest, government securities). MA10 E.8 - Illustrate the major expenditures of tax revenues: national level (e.g., national security, social programs, education, civil services); state level (e.g., social programs, education, civil services); and local level (e.g., civil services, education). MA10 E.9 - Explain different types of taxes: progressive tax, regressive tax, and proportional tax. MA10 E.10 - Distinguish between budget deficit and national debt. Strand: Reading – Historical Text Instructional Focus: Key Ideas and Text RH 9-10.1. Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of primary and secondary sources, attending to such features as the date and origin of the information. RH 9-10.2. Determine the central ideas or information of a primary or secondary source; provide an accurate summary of how key events or ideas develop over the course of the text. RH 9-10.3. Analyze in detail a series of events described in a text; determine whether earlier events caused later ones or simply preceded them. Instructional Focus: Craft and Structure RH 9-10.4. Determine the meaning of words and phrases as they are used in a text, including vocabulary describing political, social, or economic aspects of history/social science. RH 9-10.5. Analyze how a text uses structure to emphasize key points or advance an explanation or analysis. RH 9-10.6. Compare the point of view of two or more authors for how they treat the same or similar topics, including which details they include and emphasize in their respective accounts. Instructional Focus: Integration of Knowledge and Ideas RH 9-10.7. Integrate quantitative or technical analysis (e.g., charts, research data) with qualitative analysis in print or digital text. RH 9-10.8. Assess the extent to which the reasoning and evidence in a text support the author’s claims. RH 9-10.9. Compare and contrast treatments of the same topic in several primary and secondary sources. Instructional Focus: Range of Reading and Complexity of Text 5 RH 9-10.10. By the end of grade 10, read and comprehend history/social studies texts in the grades 9–10 text complexity band independently and proficiently. Strand: Writing in Social Studies/History, Science & Technical Subjects – CCSS - Grades 9-10 Instructional Focus: Text Types and Purposes WHST 9-10.1. Write arguments focused on discipline-specific content. o Introduce precise claim(s), distinguish the claim(s) from alternate or opposing claims, and create an organization that establishes clear relationships among the claim(s), counterclaims, reasons, and evidence. o Develop claim(s) and counterclaims fairly, supplying data and evidence for each while pointing out the strengths and limitations of both claim(s) and counterclaims in a discipline-appropriate form and in a manner that anticipates the audience’s knowledge level and concerns. o Use words, phrases, and clauses to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships between claim(s) and reasons, between reasons and evidence, and between claim(s) and counterclaims. o Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. o Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from or supports the argument presented. WHST 9-10.2. Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/experiments, or technical processes. o Introduce a topic and organize ideas, concepts, and information to make important connections and distinctions; include formatting (e.g., headings), graphics (e.g., figures, tables), and multimedia when useful to aiding comprehension. o Develop the topic with well-chosen, relevant, and sufficient facts, extended definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other information and examples appropriate to the audience’s knowledge of the topic. o Use varied transitions and sentence structures to link the major sections of the text, create cohesion, and clarify the relationships among ideas and concepts. o Use precise language and domain-specific vocabulary to manage the complexity of the topic and convey a style appropriate to the discipline and context as well as to the expertise of likely readers. o Establish and maintain a formal style and objective tone while attending to the norms and conventions of the discipline in which they are writing. o Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the information or explanation presented (e.g., articulating implications or the significance of the topic). Strand: WRITING in History/Social Studies, Science & Technical Subjects Grades 9-10 Instructional Focus: Production and Distribution of Writing WHST 9-10.4. Produce clear and coherent writing in which the development, organization, and style are appropriate to task, purpose, and audience. WHST 9-10.5. Develop and strengthen writing as needed by planning, revising, editing, rewriting, or trying a new approach, focusing on addressing what is most significant for a specific purpose and audience. 6 WHST 9-10.6. Use technology, including the Internet, to produce, publish, and update individual or shared writing products, taking advantage of technology’s capacity to link to other information and to display information flexibly and dynamically. Instructional Focus: Research to Build and Present Knowledge WHST 9-10.7. Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation. WHST 9-10.8. Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the usefulness of each source in answering the research question; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and following a standard format for citation. WHST 9-10.9. Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Instructional Focus: Range of Writing WHST 9-10.10. Write routinely over extended time frames (time for reflection and revision) and shorter time frames (a single sitting or a day or two) for a range of discipline-specific tasks, purposes, and audiences. 7