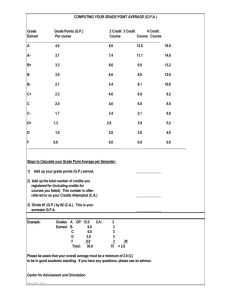
Mechanical Engineering Degree plan
advertisement

MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (M E) Mechanical Engineering (M E) is one of the broadest engineering disciplines. In fact, almost all other engineering disciplines have their roots in mechanical engineering. This breadth of mechanical engineering can be seen in the wide spectrum of problems that mechanical engineers solve. From creating surgical instruments to designing theme park rides to developing airport security devices, mechanical engineers help provide for our health, happiness, and safety. Mechanical engineers are making a difference in the world. For instance, one core idea of mechanical engineering is the conversion of energy from one form to another. For that reason, mechanical engineers are leaders in conventional forms of energy, such as combustion of fossil fuels, as well as alternative energy forms such as fuel cells. Is Mechanical Engineering for You? If you are interested in creating things that help improve our health, happiness, and safety, then mechanical engineering may be for you. As a mechanical engineering major, you will take part in a dynamic course of study involving teamwork and design projects that apply to current world problems. A degree in Mechanical Engineering will prepare you for a secure career in rapidly developing technological fields. Mechanical Engineering is divided into two broad areas: mechanical systems and thermal systems. Mechanical systems include the design of mechanisms and the analysis of strength and wear of materials. These topics are studied in courses such as Dynamics, Material Science, Engineering Mechanics, Vibrations, and Machine Design. Thermal systems include methods of energy conversions, heat transfer, and fluid flow. Thermal systems are covered in Thermodynamics, Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer. Today’s mechanical engineering majors use computers in nearly every aspect of their study. From sophisticated computer simulations of motion and deformation, to three-dimensional “virtual” prototyping, to computer aided design, mechanical engineers become proficient users of the latest technology. Typical class assignments might include the use of design software to create virtual prototypes, stress analysis software to quickly evaluate alternative designs or lab experiments to observe the behavior of a system under varying external influences. Due to the breadth of the mechanical engineering discipline, the following technical tracks have been developed. Through proper selection of courses, students can gain a technical degree with an emphasis in any of the following areas: Biomedical Device Engineering Combustion Based Energy Conversions Control of Mechanical Systems Machinery Dynamics & Design Mechanical Engineering in Aerospace Applications Global Engineering via Study Abroad Mechatronics and Robotics Engineering New Product Design and Manufacturing Power Engineering Turbomachinery Based Energy Conversions Vehicle Engineering for the 21st Century To learn more about the technical electives offered for these different tracks, visit: http://www.mne.psu.edu/Current/UGrad/Curriculum/Section3.html Each senior is required to complete a capstone senior design project. These projects are semester long, industry sponsored team projects and involve the design of a product or process. The project involves the development, design, prototyping, technical analysis, cost analysis, and presentation of the group’s final design. Some example projects including anesthesia needle holder, the Shell Eco-Marathon car, which is an ongoing project, and a Morphing Aircraft Wing. 84 Career Opportunities Mechanical engineers can work almost anywhere: in large companies, such as automotive and aerospace industries; in smaller “high tech” companies; in specialized areas such as robotics, nanotechnology, and in research centers such as government labs and universities. Within any company, mechanical engineers have many job opportunities including the development, testing, manufacturing, reliability, packaging, and distribution of a product. Some mechanical engineers pursue professional degrees in medicine or law. The need for mechanical engineers spans a large segment of both the public and private sectors, making the job market for mechanical engineering graduates very stable and diverse, as shown in the three examples below. Janine Kowalczyk, Structural Analyst, Boeing Janine graduated in December 2006. She works for the Boeing Satellite Development Center in El Segundo, CA. As a structural analyst, she creates and analyzes finite element models. She also supervises mechanical tests subjecting units to random vibration and pyroshock environments. She has recently taken on a temporary assignment in Seattle, WA as a structural analyst and is working on the Boeing 747-8I fuselage. Brandon Rosati, Patent Examiner, United States Patent & Trademark Office Brandon graduated in 2007 and now works for the Department of Commerce as a Patent Examiner.“Being a Patent Examiner allows me to apply my knowledge of engineering with my passion of law and help to preserve Intellectual Property rights for the United States.” Kristin Culkar McInerney, Consultant, Accenture After graduating in 2004 Kristin has gone on to work as an IT and Strategy Consultant in Philadelphia and Washington, DC for a variety of clients. In addition to her consulting work focusing in the area of business intelligence, she is currently organizing a worldwide women’s event for her company, featuring female political figures from DC. Visit the Department website for more information: http://www.mne.psu.edu/ Or contact the Undergraduate Programs Office in Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering at undergrad@mne.psu.edu or by phone at 814-863-1503. Visit the Societies & Organizations website to learn more about student organizations! http://www.mne.psu.edu/Directories/students.html 1. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) 2. Society of Women Engineers (SWE) 3. Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) Visit the Learning Factory website to learn more about senior design projects: http://www.lf.psu.edu Mechanical Engineering is accredited by the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET), 111 Market Place, Suite 1050, Baltimore, MD 21202-4012; 410-347-7700; www.abet.org. Program Educational Objectives The objective of the Mechanical Engineering program is to prepare students for a wide range of career paths that use mechanical engineering principles and methodology. We will maintain and provide a curriculum that prepares our recent graduates for: 1. working in industry and government including computer-aided design, simulation and analysis of products or systems, experimentation and testing, manufacturing, and technical sales. 2. assuming increasing levels of responsibility in project, personnel, and budget management. 3. working and leading effectively in multi-disciplinary and multi-cultural teams. 4. communicating effectively and recognizing the global, societal, and ethical contexts of their work. 5. entering into graduate and professional studies. ME Program Outcomes can be found at http://www.mne.psu.edu/Current/UGrad/Assessment/. 85 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 1ST SEMESTER 17 Credits 2ND SEMESTER 17 Credits 3RD SEMESTER 17 Credits 4TH SEMESTER 16.5 Credits 5TH SEMESTER 16.5 Credits 6TH SEMESTER 15 Credits 7TH SEMESTER 16 Credits 8TH SEMESTER 16 Credits (Option: 18 Credits) (Option: 14 Credits) CHEM 110 CHEM 112* E MCH 211 E MCH 212 E MCH 315 M E 360 M E 450 M E 440W (CAPSTONE OPTION 1) EDSGN 100 ECON 2, 4 or 14 MATH 220 E MCH 213 MATSE 259 M E 340 M E 410 M E 441W (CAPSTONE OPTION 2) MATH 140 MATH 141 MATH 231 MATH 251 M E 320 M E 370 M E 442W (CAPSTONE OPTION 3) M E 443W (CAPSTONE OPTION 3) M E LAB SEMINAR ENGL 15 PHYS 211 AHS PHYS 212 PHYS 214 M E 345 I E 312 M E LAB CMPSC 200 M E 300 E E 212 ENGL 202C M E Tech Elective ENGR Tech Elective AHS CAS 100 GHA Gen. Tech Elective AHS GHA * BIOL 141 may be substituted for CHEM 112 CAPSTONE OPTION 1 - M E 440W can be taken after completing M E 360, M E 340, M E 370, I E 312, and ENGL 202C. M E 440W can be taken 7th or 8th semester. CAPSTONE OPTION 2 - M E 441W can be taken after completing M E 340, M E 410, and ENGL 202C. M E 441W can be taken 7th or 8th semester. CAPSTONE OPTION 3 - Both M E 442W and 443W must be completed if selecting this option to satisfy Senior Design (CAPSTONE) requirement. US Cultures and IL Cultures requirements are satisfied in conjunction with AHS courses = Prerequisite ENGR Tech Elective AHS AHS = Prerequisite or Concurrent Page 1 Mechanical Engineering Starting at University Park Go to www.engr.psu.edu/AdvisingCenter/StudyAbroadME.aspx for a sample scheduling plan that incorporates a semester of study abroad. 1st Semester •CHEM 110 •MATH 140 or 140E EDSGN 100 ENGL 15 or 30 First-Year Seminar GA, GH or GS course Chemical Principles Calculus I Engineering Design & Graphics Rhet. & Comp. (or ECON 2/4/14) MATH 231 MATH 220 PHYS 212 CMPSC 200 +E MCH 211 CAS 100A/B Calc. of Several Var. Matrices Electricity & Magnetism MATLAB Statics Effective Speech 2nd Semester 3 4 3 3 1 3 17 ^CHEM 112 Chemical Principles •MATH 141 or 141E Calculus II •PHYS 211 Mechanics ECON 2, 4 or 14 (GS) (or ENGL 15/30) GA, GH or GS course 2 2 4 3 3 3 17 +M E 300 Engr. Thermodynamics I MATH 251 Ordinary & Partial Diff. Eqns. PHYS 214 Waves & Quantum Physics +E MCH 212 Dynamics Strength of Materials + E MCH 213r Health & Physical Activity (GHA) 3rd Semester 4th Semester 5th Semester +M E 320 +M E 345 Fluid Flow Instrumentation, Measurements, and Statistics E MCH 315 Mech. Response of Engr. Materials E E 212 Intro. to Elec. Measuring Sys. MATSE 259 Prop. & Proc. of Engr. Materials Health & Physical Activity (GHA) 7th Semester Modeling of Dynamic Systems Heat Transfer +M E 450 +M E 410 *M E Lab Course M E Technical Elective (METE)1 ENGR Technical Elective (ETE) 2 GA, GH or GS course 3 4 4 3 3 17 3 4 2 3 3 1.5 16.5 6th Semester 3 4 +M E 360 +M E 340 +M E 370 I E 312 ENGL 202C 2 3 3 1.5 16.5 Mechanical Components Design Mech. Engr. Design Methodology Vibrations of Mechanical Systems Product Des. & Manuf. Processes Technical Writing 8th Semester M E 440W or 441W Design Project *M E Lab Course ENGR Technical Elective (ETE)2 General Technical Elective (GTE)3 GA, GH or GS course GA, GH or GS course 3 3 1 3 3 3 16 Total Credits - 131 • Courses listed in boldface italic type require a grade of C or better for entrance into this major. + Courses listed in boldface type require a grade of C or better for graduation in this major. r E MCH 213D may be used instead, if offered. * To graduate a student must take at least two of the following lab courses: M E 315, M E 325, M E 355, M E 375, E MCH 316. If M E 445(4) is taken as a technical elective, one credit can be used as an M E Lab Course. ^ Students may substitute Biol 141 for Chem 112. 1 M E Technical elective - 3 credits of 400-level M E courses except M E 410, M E 440W, M E 441W, M E 450, M E 494 or M E 496. 2 Engineering Technical Elective is a 3-credit 400-level course in the College of Engineering including a non-required Mechanical Engineering course. 3 General Technical Elective is 3 credits of engineering, science, or math courses beyond the level required for the major. See department list. Three credits of Co-op can be used for the General Technical Elective after completion of three Co-op rotations. Six ROTC credits may be substituted for 3 credits of GHA and 3 credits of General Technical elective upon completion of the basic ROTC program. Only use this curriculum plan for first and second year course scheduling. Your degree requirements are defined when enter the major and may be different than listed on this page. Please refer to the ME Planning Manual for your Entrance to Major year (http://www.mne.psu.edu/undergrad/degree.htm). 87 3 3 3 3 3 15 3 1 3 3 3 3 16