Chapter 1 & 3 Review Worksheeet
advertisement

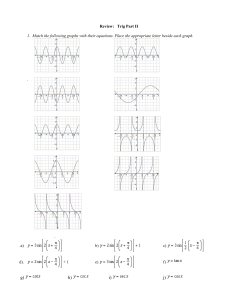
Chapter 1 & 3 Review Worksheeet Matching Match each item with the correct statement below. a. absolute zero b. Kelvin temperature scale c. Celsius temperature scale d. weight ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. e. f. g. h. mass significant figure precision accuracy closeness to true value narrowness of range of measurements known or estimated in a measurement the quantity of matter an object contains the lowest point on the Kelvin scale the SI scale for temperature the force of gravity on an object the non-SI scale for temperature Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 9. Which of the following would a chemist be most likely to study? a. a leaf floating on water c. a leaf being blown by the wind b. a leaf changing color in autumn d. a leaf being eaten by insects 10. Which of the following was a major contribution to chemistry by Antoine Lavoisier? a. He showed that oxygen is required for material to burn. b. He demonstrated the presence of phlogiston in air. c. He encouraged scientists to form explanations based on philosophical arguments. d. He developed the science of alchemy. 11. One characteristic of a scientific theory is that ____. a. it can never be proved c. it cannot be modified b. it can be proved d. it summarizes a set of observations 12. A theory is a ____. a. proposed explanation for an observation b. well-tested explanation for a broad set of observations c. summary of the results of many observations d. procedure used to test a proposed explanation 13. Which step in the scientific method requires you to use your senses to obtain information? a. revising a hypothesis c. making an observation b. designing an experiment d. stating a theory 14. The variable that is observed during an experiment is called what type of variable? a. independent c. controlling b. manipulated d. responding 15. Collaboration and communication are important in science because ____. a. most research problems are not very complex b. most scientists have the knowledge to solve any scientific problem c. they increase the likelihood of a successful outcome d. they keep scientists from having to repeat experiments 16. Which of these steps should always be followed for effective problem solving? a. buying a larger quantity of material than estimated b. performing metric conversions c. developing a plan and then implementing the plan d. using a trial-and-error approach and then evaluating 17. The step that usually comes last in solving numeric problems is ____. a. calculate c. evaluate b. measure d. analyze ____ 18. The diameter of a carbon atom is 0.000 000 000 154 m. What is this number expressed in scientific notation? a. 1.54 10 m c. 1.54 10 m b. 1.54 10 d. 1.54 10 m m ____ 19. The expression of 5008 km in scientific notation is ____. a. 5.008 10 km c. 5.008 b. 50.08 10 km d. 5.008 ____ 20. ____ 21. ____ 22. ____ 23. ____ 24. ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. ____ 34. 10 km 10 km The closeness of a measurement to its true value is a measure of its ____. a. precision c. reproducibility b. accuracy d. usefulness Which of the following measurements contains two significant figures? a. 0.004 00 L c. 0.000 44 L b. 0.004 04 L d. 0.004 40 L Which of the following measurements (of different masses) is the most accurate? a. 3.1000 g c. 3.122 22 g b. 3.100 00 g d. 3.000 000 g Which group of measurements is the most precise? (Each group of measurements is for a different object.) a. 2 g, 3 g, 4 g c. 2 g, 2.5 g, 3 g b. 2.0 g, 3.0 g, 4.0 g d. 1 g, 3 g, 5 g Three different people weigh a standard mass of 2.00 g on the same balance. Each person obtains a reading of 7.32 g for the mass of the standard. These results imply that the balance that was used is ____. a. accurate c. accurate and precise b. precise d. neither accurate nor precise Which of the following measurements is expressed to three significant figures? a. 0.007 m c. 7.30 10 km b. 7077 mg d. 0.070 mm In the measurement 0.503 L, which digit is the estimated digit? a. 5 b. the 0 immediately to the left of the 3 c. 3 d. the 0 to the left of the decimal point How many significant figures are in the measurement 0.003 4 kg? a. two c. five b. four d. This cannot be determined. How many significant figures are in the measurement 40,500 mg? a. two c. four b. three d. five How many significant figures are in the measurement 811.40 grams? a. two c. four b. three d. five Express the sum of 1111 km and 222 km using the correct number of significant digits. a. 1300 km c. 1333 km b. 1330 km d. 1333.0 km Express the sum of 7.68 m and 5.0 m using the correct number of significant digits. a. 12.68 m c. 13 m b. 12.7 m d. 10 m Express the product of 2.2 mm and 5.00 mm using the correct number of significant digits. a. 10 mm c. 11.0 mm b. 11 mm d. 11.00 mm What is the measurement 111.009 mm rounded off to four significant digits? a. 111 mm c. 111.01 mm b. 111.0 mm d. 110 mm What is the measurement 1042 L rounded off to two significant digits? a. 1.0 10 L c. 1050 L b. 1040 L d. 1.1 10 L ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 35. When multiplying and dividing measured quantities, the number of significant figures in the result should be equal to the number of significant figures in ____. a. all of the measurements b. the least and most precise measurements c. the most precise measurement d. the least precise measurement 36. What quantity is represented by the metric system prefix deci-? a. 1000 c. 0.1 b. 100 d. 0.01 37. What is the metric system prefix for the quantity 0.000 001? a. centic. kilob. decid. micro38. Which of the following units is NOT an official SI unit? a. kilogram c. mole b. ampere d. liter 39. Which of the following volumes is the smallest? a. one microliter c. one milliliter b. one liter d. one deciliter 40. What is the SI unit of mass? a. liter c. candela b. joule d. kilogram 41. What is the temperature of absolute zero measured in C? a. –373 C c. –173 C b. –273 C d. –73 C 42. Which temperature scale has no negative temperatures? a. Celsius c. Joule b. Fahrenheit d. Kelvin 43. What is the boiling point of water in kelvins? a. 0 K c. 273 K b. 100 K d. 373 K 44. Which of the following mass units is the largest? a. 1 cg c. 1 mg b. 1 dg d. 1 ng 45. The weight of an object ____. a. is the same as its mass c. is not affected by gravity b. depends on its location d. is always the same 46. What is the temperature –34 C expressed in kelvins? a. 139 K c. 239 K b. 207 K d. 339 K 47. If the temperature changes by 100 K, by how much does it change in C? a. 0 C c. 100 C b. 37 C d. 273 C 48. Chlorine boils at 239 K. What is the boiling point of chlorine expressed in degrees Celsius? a. 93 C c. –61 C b. 34 C d. –34 C 49. Which of the following equalities is NOT correct? Use the table on page 74 in your textbook to help you. a. 100 cg = 1 g c. 1 cm = 1 mL b. 1000 mm = 1 m d. 10 kg = 1 g 50. Density is found by dividing ____. a. mass by volume c. mass by area b. volume by mass d. area by mass 51. What is the density of an object having a mass of 8.0 g and a volume of 25 cm ? a. 0.32 g/cm c. 3.1 g/cm b. 2.0 g/cm d. 200 g/cm 52. If a liter of water is heated from 20 C to 50 C, what happens to its volume? a. The volume decreases. ____ b. The volume increases. c. The volume first increases, then decreases. d. The volume first decreases, then increases. 53. If the temperature of a piece of steel decreases, what happens to its density? a. The density decreases. b. The density increases. c. The density does not change. d. The density first increases, then decreases. Short Answer 54. The following length measurements were taken by students using several different measuring devices. Find the average of the measurements. Make sure that your answer has the correct number of significant figures. 10.05 cm, 10.1 cm, 9.741 cm, 10.6 cm, 10.5 cm 55. Round off the measurement 0.003 095 5 m to three significant figures. 56. What is the sum of 2.7 g and 2.47 g expressed in the correct number of significant digits? 57. What is the sum of 6.210 L and 3 L expressed in the correct number of significant digits? 58. What is the product of the number 1000 and the measurement 0.003 57 m expressed in the correct number of significant digits? 59. The mass of the electron is 9.109 39 10 kg. Express the mass of the electron to 1, 2, 3, and 4 significant figures. 60. Perform the following operation: 3.43 cm figures. 5.2 cm. Make sure that your answer has the correct number of significant 61. What is the temperature 128 K expressed in degrees Celsius? 62. What is the density of an object having a mass of 4.0 g and a volume of 39.0 cubic centimeters? 63. A cube of a gold-colored metal with a volume of 59 cm has a mass of 980 g. The density of pure gold is 19.3 g/cm . Is the metal pure gold? Show calculations to justify your answer. Numeric Response 64. How many steps are involved in solving numeric problems? Essay 65. Describe the rules that are used to determine the number of significant figures in the results of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. 66. Explain the difference between mass and weight. Provide an example to illustrate the distinction. 67. You are given a jar containing a mixture of three different solid substances. The particles of each substance are larger than 0.5 cm in diameter. All you know about the substances is that each is a pure metal. Describe a method for determining the identities of the metals that make up the mixture. Assume that each metal is a different color, so you can tell one from the others. Chapter 1 & 3 Review Worksheeet Answer Section MATCHING 1. ANS: OBJ: 2. ANS: OBJ: 3. ANS: OBJ: 4. ANS: OBJ: 5. ANS: OBJ: 6. ANS: OBJ: 7. ANS: OBJ: 8. ANS: OBJ: H 3.1.2 G 3.1.2 F 3.1.3 E 3.2.1 A 3.2.1 B 3.2.1 D 3.2.2 C 3.2.2 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 66 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 76 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 76 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 76 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 7 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 20 | p. 21 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 23 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 23 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 22 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 22 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 24 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 28 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 29 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 63 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 63 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 66 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 64 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 66 MULTIPLE CHOICE 9. ANS: OBJ: 10. ANS: OBJ: 11. ANS: OBJ: 12. ANS: OBJ: 13. ANS: OBJ: 14. ANS: OBJ: 15. ANS: OBJ: 16. ANS: OBJ: 17. ANS: OBJ: 18. ANS: OBJ: 19. ANS: OBJ: 20. ANS: OBJ: 21. ANS: OBJ: 22. ANS: OBJ: 23. ANS: OBJ: 24. ANS: OBJ: 25. ANS: B 1.1.1 A 1.3.1 A 1.3.2 B 1.3.2 C 1.3.2 D 1.3.2 C 1.3.3 C 1.4.1 C 1.4.2 D 3.1.1 A 3.1.1 B 3.1.2 C 3.1.2 D 3.1.2 C 3.1.2 B 3.1.2 C OBJ: 26. ANS: OBJ: 27. ANS: OBJ: 28. ANS: OBJ: 29. ANS: OBJ: 30. ANS: OBJ: 31. ANS: OBJ: 32. ANS: OBJ: 33. ANS: OBJ: 34. ANS: OBJ: 35. ANS: OBJ: 36. ANS: OBJ: 37. ANS: OBJ: 38. ANS: OBJ: 39. ANS: OBJ: 40. ANS: OBJ: 41. ANS: OBJ: 42. ANS: OBJ: 43. ANS: OBJ: 44. ANS: OBJ: 45. ANS: OBJ: 46. ANS: OBJ: 47. ANS: OBJ: 48. ANS: OBJ: 49. ANS: OBJ: 50. ANS: OBJ: 51. ANS: OBJ: 52. ANS: OBJ: 53. ANS: OBJ: 3.1.2 C 3.1.3 A 3.1.3 B 3.1.3 D 3.1.3 C 3.1.3 B 3.1.3 B 3.1.3 B 3.1.3 A 3.1.3 D 3.1.3 C 3.2.1 D 3.2.1 D 3.2.1 A 3.2.1 D 3.2.1 B 3.2.1 D 3.2.1 D 3.2.1 B 3.2.1 B 3.2.2 C 3.2.3 C 3.2.3 D 3.2.3 D 3.3.2 A 3.4.1 A 3.4.1 B 3.4.2 B 3.4.2 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 66 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 66 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 66 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 66 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 68 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 68 | p. 70 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 68 | p. 71 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 66 | p. 68 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 66 | p. 68 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 68 | p. 71 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 74 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 74 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 73 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 74 | p. 75 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 76 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 74 | p. 76 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 76 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 | p. 78 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 77 | p. 78 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 77 | p. 78 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 84 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 90 | p. 91 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 90 | p. 91 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 91 PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 91 SHORT ANSWER 54. ANS: Average = (10.05 + 10.1 + 9.741 + 10.6 + 10.5) / 5 = 10.2 cm PTS: 1 55. ANS: 0.003 10 m DIF: L2 REF: p. 68 | p. 71 OBJ: 3.1.3 PTS: 1 56. ANS: 5.2 g DIF: L2 REF: p. 68 OBJ: 3.1.3 PTS: 1 57. ANS: 9L DIF: L2 REF: p. 63 | p. 70 OBJ: 3.1.3 PTS: 1 58. ANS: 3.57 m DIF: L2 REF: p. 63 | p. 70 OBJ: 3.1.3 PTS: 1 59. ANS: one: 9 10 DIF: L2 REF: p. 68 | p. 71 OBJ: 3.1.3 kg; two: 9.1 PTS: 1 DIF: 60. ANS: 3.43 cm 5.2 cm = 18 cm 10 kg; three: 9.11 L2 10 kg; four: 9.109 10 REF: p. 63 | p. 71 OBJ: 3.1.3 REF: p. 68 | p. 71 OBJ: 3.1.3 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. 77 | p. 78 62. ANS: Density = mass/volume = 4.0 g/39.0 cm = 0.10 g/cm OBJ: 3.2.3 PTS: 1 DIF: L2 63. ANS: No; mass/volume = 980 g/59 cm = 17 g/cm PTS: 1 DIF: L2 61. ANS: C = K – 273 = 128 – 273 = –145 C PTS: 1 REF: p. 91 OBJ: 3.4.1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 90 | p. 91 OBJ: 3.4.1 DIF: L1 REF: p. 29 OBJ: 1.4.2 kg NUMERIC RESPONSE 64. ANS: 3 PTS: 1 ESSAY 65. ANS: The answer of an addition or subtraction can have no more digits to the right of the decimal point than are contained in the measurement with the least number of digits to the right of the decimal point. The answer of a multiplication or division can have no more significant figures than the measurement having the least number of significant figures. For multiplication and division, the position of the decimal point has nothing to do with the number of significant figures. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 70 OBJ: 3.1.3 66. ANS: Mass is a measure of the quantity of matter in an object. Weight is a measure of the strength of the pull of a gravitational force (usually Earth's) on an object. The weight of an object changes, however, with the object's distance from the center of the gravitational field it is in. The mass of a person is exactly the same whether the person is on Earth or on the moon. The weight of that person will be much less on the moon than on Earth because the gravitational pull of the moon is much less than that of Earth. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 78 OBJ: 3.2.2 67. ANS: Each substance is a pure metal, so they should be identifiable by determining their densities. Separate the solids by color into three separate batches. Determine the mass of each metal using a balance. Determine the volume of each metal as follows. Immerse each metal in a measured volume of a suitable liquid in a graduated cylinder. Measure the volume of the liquid plus the metal. Calculate the difference between the volume of the liquid plus the metal and the liquid by itself. To calculate the density, divide the mass of each metal by its volume. Compare the density and color of each metal to the density and color listed in reference books. PTS: 1 DIF: L3 REF: p. 90 OBJ: 3.4.1