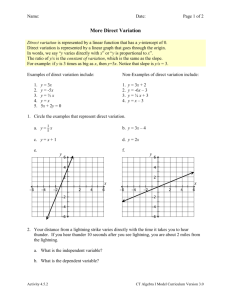
Lecture 25.Thunderstorms. Thunderstorm Life cycle of an ordinary
advertisement

Lecture 25.Thunderstorms. Stages of an ordinary thunderstorm. Severe thunderstorms. Electrification of clouds and lightning. Lightning safety. Reading: Ch. 10, 257–262, 271–275. Thunderstorm • a storm that produces lightning and thunder • Air-mass (ordinary) thunderstorm: develops in warm, moist air masses usually not associated with weather front • Severe thunderstorm: associated with weather fronts produces severe weather Life cycle of an ordinary thunderstorm Mature stage Dissipating stage Cumulus (growth) stage 1 Comments • Cumulus stage: cumulus cloud no precipitation no lightning or thunder • Mature stage: the entrainment of dry air into the updraft results in evaporation of some of the raindrops and cooling of the air, which sets up a downdraft updraft and downdraft constitute a cell, the region between updraft and downdraft is most turbulent heavy rain, gusts, anvil shape, lightning and thunder • Dissipating stage: updrafts cut off, precipitation dies out, cloud evaporates Severe thunderstorm • A severe thunderstorm is different from an ordinary thunderstorm in that it has a tilted updraft in a mature stage (due to a strong wind shear) • the downdraft cannot cut off the updraft and storm continues to intensify Formation of hail in a severe thunderstorm 2 Lightning and thunder • Lightning — a massive discharge of electricity, a giant spark • Lightning can heat the air through which it travels to as high as 30,000oC • Air is being heated very quickly and expands explosively; the resulting booming shock wave is called thunder How far is the thunderstorm? • Speed of light is 300,000,000 m/s • Speed of sound in the air ~ 300 m/s • So if you see a lightning and 5 seconds passes before you hear a thunder, the thunderstorm is 5 " 300=1500m≈1 mi away • Close thunder bangs, and distant thunder rumbles, as it comes from different areas ! of the stroke Different forms of lightning • within the cloud (majority of strikes) [from one part of cloud to another] • cloud-to-cloud [from one cloud to another] • cloud-to-ground (20% of strikes) [from a cloud to the ground] • ground-to-cloud [from the ground to a cloud] 3 Electrification of clouds Positive charges on the tip of the rod Negative charges at the base of the cloud Lightning safety DO • go inside a building, if possible • crouch down and minimize your contact with the ground ! people in a car are usually unharmed, as the lightning goes to the ground through the outside metal casing of the vehicle DON’T • stand under an isolated tree • go near a body of water • go near elevated places • lie down Lightning safety (cont’d) • Signs that lightning is about to strike nearby: Your hair begins to stand on end Your skin begins to tingle You hear clicking sounds 4