Accurately detecting and establishing effective strategies to alleviate
advertisement

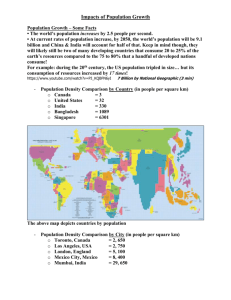
MUNiSC'2016'General'Conference' Accurately detecting and establishing effective strategies to alleviate environmental issues that are to be caused by human overpopulation over the next century Forum: General Conference Student Officer: Daniel Choi, President Contributed by: Emma Martin, QSI Chengdu Introduction Graph showing exponential growth in human population in the modern era. Martin Luther King Jr. once said, “Unlike plagues of the dark ages or contemporary diseases we do not understand, the modern plague of overpopulation is soluble by means we have discovered and with resources we possess. What is lacking is not sufficient knowledge of the solution, but universal consciousness of the gravity of the problem and education of the billions who are its victim.” Whether humans want to acknowledge it or not, overpopulation is a grieve issue that is not receiving the attention that it deserves. The UN’s Panel on global sustainability released a report on stating that as the world's population looks set to grow to nearly 9 billion by ©MUNiSC'2016' ! MUNiSC'2016'General'Conference' 2040 and the number of middle-class consumer increases by 3 billion over the next 20 years, the demand for resources will rise exponentially. Background Resources Throughout the last couple of decades, the human population has been dramatically increased due to sharp rise of productivity in agriculture and medical advancements. While all these are commendable, and by no means a subject to be condemned, every additional person means additional resources. Each people require food, water and other vital, yet limited resources for adequate survival in our crowded planet. The environment continues to suffer as the mankind try to fulfill the needs of a growing Series of charts showing exploitation of population. For example, trees are continually natural resources cut down, coal, oil and natural gas reserves are depleting, and ecosystems continue to suffer. With 220,000 new people being born every day, there is a greater demand for these resources. Land for instance, is a necessary component in providing the general population with food, shelter and many more natural resources that are used as various products. According to the UNEP Global Environment Outlook, “each person on Earth now requires a third more land to supply his or her needs than the planet can supply.” However, such statement only touches the surface of the issue, which indeed has many more aspects in need of our immediate attention. Amid of such depletion of energy sources, alternative energy sources are needed to supply the tremendous energy needs of the growing population. Seeing such need, the international community can turn towards renewable energy sources, which are intended to produce energy without harming the environment. The known sources of renewable energy are sunlight, rain, tidal wave and wind. However, these sources are often criticized for its inefficiency and high costs. Nuclear energy is both environmentally friendly and productive in energy production, but its frequent malfunction and disasters cause fear among environmentalists and regular citizens alike. Geothermal energy is known to be sustainable, reliable, efficient and environmentally friendly, but its geographic restrictions to only few regions in Earth and high costs often arise as obstacles. Though it is estimated that Earth’s geothermal resources are more than sufficient to fulfill the needs of the human population, current technological capability isn’t enough the overcome the above mentioned difficulties. Biomass and biofuel are also alternative energy sources, however their efficiency is challenged by high costs and low energy output. Currently China and United States are leaders of researching and developing renewable energy sources. Yet, more investments and efforts from other countries are needed to secure safe and quick transition into renewable energy sources. Global Patterns Increase in human population not only used up Earth’s scant resources, but also contributed to the recent patterns of climate change. The rise in population increased industrial output, with new vehicles and industries emitting even more greenhouse gases than before. The Center for Biological Diversity stated that while humans are beginning to realize that our climate ©MUNiSC'2016' MUNiSC'2016'General'Conference' is changing and have begun decreasing consumption, it is equally important to realize that “we not only need smaller footprints, but fewer feet.” However, population and carbon emissions also deal with consumption patterns. A child in the US is 168 times more responsible for carbon emissions than a child in Bangladesh, and seven times more than a child in China. Also, in certain developed countries, one-third of all carbon emissions can be credited to the transportation sector as compared to industrial or telecommunication sectors. The irreversible damages to our environment is evident all throughout the world. In the past, rainforests covered up to 14% of the Earth’s surface. Today, it only covers 6%. Approximately 30% of the ocean’s reefs have disappeared, and permanent ice covers on the two poles are disappearing at a rate of 11.5% per year. Moreover, it is predicted that from global change, habitat loss and pollution at least half of all animals and plants will be extinct. In such ways, the effects of overpopulation occur worldwide, however, measures concerning strategies to alleviate environmental issues have been rarely discussed. Therefore, it is now time for the UN to take more proactive and vibrant actions to deal with overpopulation. International Actions The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) was established in 1969 to tackle the issue of overpopulation by promoting different population programs. Since then, the UNFPA has worked with the International Institute for Environment and Development as well as Wolfram research to develop a system called, Demographic Exploration for Climate Adaptation (DECA). Because climate change is a major effect of overpopulation, DECA analyzes demographic impacts on climate change by combining data on of the current population with climate hazards. The United Nations World Population Plan, provided by the United Nations Population Information Network (POPIN), presents a plan of action to address the issue of human population, specifically overpopulation. Some of the recommendations for actions dealing with human population include adopting certain policies in LEDC’s that deal with consumption and investment, carrying out intensive programs for economic and social improvement, and adopting more rational utilization of natural resources. The ultimate goal of this organization is to harmonize population trends. Places of High Concern India India, with its population surpassing 1 billion mark, is known for as a densely-populated country, and is considered one of the highest contributor of greenhouse gas emission within G20 countries. Overpopulation in India is mainly due to its higher birth rate in comparison to the death rate as well as the its high fertility rate. As a result, resources in India are overexploited. Among some of the biggest environmental issues in India include water scarcity, deforestation, and air pollution. Industries are growing, and the amount of water is simply not enough to support its large population. Almost 5.3 million hectares of forest have been demolished due to industrialization and housing. Due to such ruthless deforestation and surplus of toxic gas emitting factories and transportation devices India has one of the worst air qualities in the world. Sub-Saharan Africa Overpopulation is becoming a serious issue on many countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Within the next fifty years, populations of countries like Ethiopia and Nigeria could possibly triple ©MUNiSC'2016' MUNiSC'2016'General'Conference' the current number. The main reasons for overpopulation is the declining infant and children mortality rates as well as very high fertility rates. On average, a woman in Africa has 5.5 children. The dramatic increase of population in these areas is affecting the environment as the availability of their resources constantly decreasing. It also led to more disposal of wastes, which has polluted water and land supplies. Africa’s largest lake, Lake Victoria is an example of such tragedy, with an immense amount of sewage being dumped into the lake every day. Stance of the P5 Nations United States of America The United States’ population growth is in fact comparable to many first world countries, and the country has the reputation as the world’s highest-consuming nation. However, the U.S. has been very aware of the detrimental effects of overpopulation, and the President's Commission on Population Growth and the American Future, headed by John D. Rockefeller III, conducted researches that concluded that the nation should welcome and plan for a stabilized population.” United Kingdom, France and Russia The UK’s population is expected to reach 77 million in 2050. Most of the current population growth in the UK can be attributed to immigration. The same is true for UK’s European neighbors, France and Russia, both of which have historically been more concerned by low population. With the Syrian crisis only fueling the current migration crisis, European leaders will be encountered with a dilemma that surely includes environmental aspect of Europe. China China has dealt with overpopulation by implementing the one child policy in the 1970’s and 1980’s However, such efforts have only caused more problems, such as demographic irregularities, rather than solving its desired issue. Because of such results, China repealed its one-child policy in 2016. In such regard, population control might not always turn out to be the best solution to this issue. Today, China consumes almost half of the world’s supply of coal, causing tons of carbon dioxide emissions, therefore, contributing to global warming. Some of the current environmental damage created from overpopulation include denuded landscapes, massive fish killings, and an increase in the amount of smog on urban areas Possible Solutions As there are many facets to this problem, many strategies are required to yield beneficial results. One possible solution is integrating a curricula in schools that includes lessons on population, environment, and development to spike interest towards the issue. Another solution may propose different government incentives and programs designed to adjust current population. An example of government provided incentive can be tax exemptions to those who limit the amount of children they have. However, such incentives must be done with consideration of country’s demographic and economic status, as more developed countries, such as Japan, who are concerned of its old, aged population, need to encourage its younger citizens to bear more children. Implementing effective resource allocation to decide what resources are currently available and how to distribute these resources fairly based on merit, social worth, or need can lead to more efficient use of resources. Moreover, promotion of renewable energy sources is advised to accelerate the coming of renewable energy era. Lastly, working with NGO’s such as the Natural ©MUNiSC'2016' MUNiSC'2016'General'Conference' Resources Defense Council (NRDC) and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) to promote environmental conservation, is advised to curb extravagant consumption. Glossary Resource: a country’s way of supporting itself by means of minerals, land, etc. Overpopulation: it is the amount of individuals compared with the amount of available resources to survive UNFPA: United Nations Population Fund LEDC - Less economically developed country Timeline 1951- The Nature Conservancy is established to protect significant lands and waters worldwide. 1972- “The Limits of Growth,” is published investigating the interaction between population and many other things aspects such as ecosystem limits. 1988- The World Meteorological Organization and the United Nations Environmental Program establish the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 2005- World population exceeds 6 billion. ©MUNiSC'2016' MUNiSC'2016'General'Conference' Bibliography "Climate Change." United Nations Population Fund. UNFPA, n.d. Web. 2 Nov. 2015. Elbel, Fred. "U.S. Population and the Environment." U.S. Population Growth. SUSPS, n.d. Web. 2 Nov. 2015. "HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH AND CLIMATE CHANGE." Center for Biological Diversity. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2015. "Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment of the Russian Federation." The Russian Government. Government of the Russian Federation, n.d. Web. 3 Nov. 2015. Nrdc.org,. "What Is Renewable Energy, Types Of Renewable Energy Sources | NRDC". N.p., 2016. Web. 17 Jan. 2016. "Overpopulation Effects." Everything Connects. Everything Connects, n.d. Web. 11 Nov. 2015. Pathfinder.org,. "Population, Health, And Environment (PHE)". N.p., 2015. Web. 17 Jan. 2016. the Guardian,. "Alberta To Introduce Carbon Tax". N.p., 2015. Web. 11 Jan. 2016. "TYPES OF RESOURCE ALLOCATION." Basics of Ethics. N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2015. "UNITED NATIONS POPULATION INFORMATION NETWORK (POPIN)." World Population Plan of Action. N.p., n.d. Web. 3 Nov. 2015."World Population Plan of Action." UNITED NATIONS POPULATION INFORMATION NETWORK (POPIN) UN Population Division, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, with Support from the UN Population Fund (UNFPA). N.p., n.d. Web. 20 Nov. 2015. ! ! ©MUNiSC'2016'

![[标签:标题]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007514640_1-d06ca384d6a6efac05ae8c0c925f8675-300x300.png)