Biology – Scope & Importance of Biology
advertisement
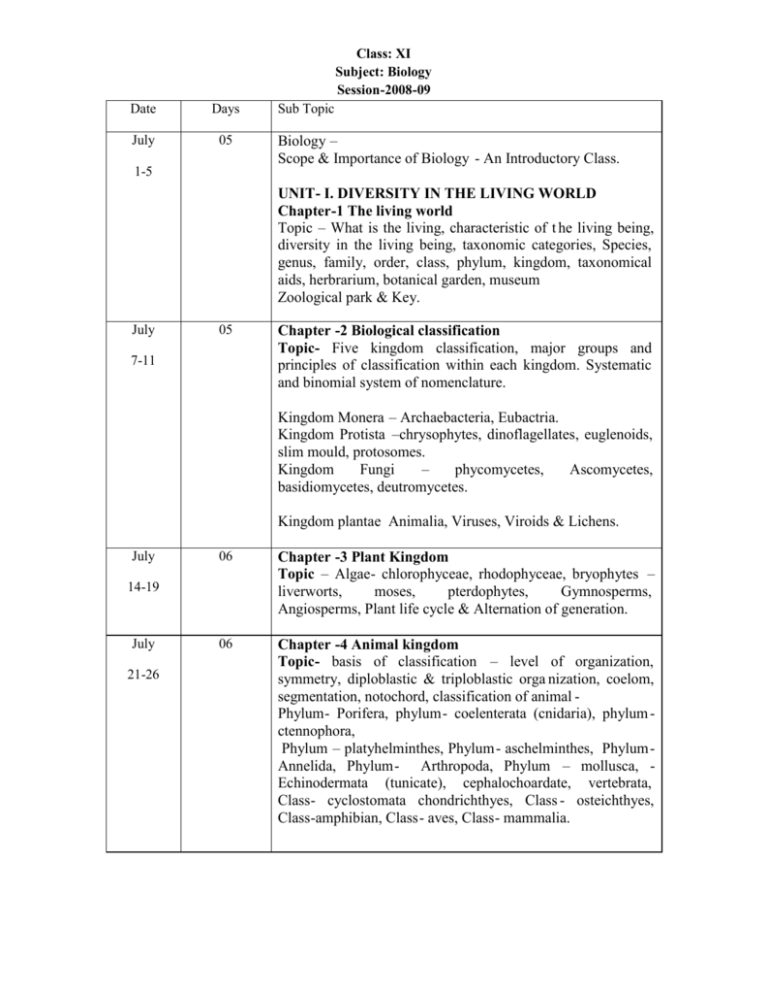
Class: XI Subject: Biology Session-2008-09 Date Days July 05 1-5 Sub Topic Biology – Scope & Importance of Biology - An Introductory Class. UNIT- I. DIVERSITY IN THE LIVING WORLD Chapter-1 The living world Topic – What is the living, characteristic of t he living being, diversity in the living being, taxonomic categories, Species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, taxonomical aids, herbrarium, botanical garden, museum Zoological park & Key. July 05 7-11 Chapter -2 Biological classification Topic- Five kingdom classification, major groups and principles of classification within each kingdom. Systematic and binomial system of nomenclature. Kingdom Monera – Archaebacteria, Eubactria. Kingdom Protista –chrysophytes, dinoflagellates, euglenoids, slim mould, protosomes. Kingdom Fungi – phycomycetes, Ascomycetes, basidiomycetes, deutromycetes. Kingdom plantae Animalia, Viruses, Viroids & Lichens. July 06 Chapter -3 Plant Kingdom Topic – Algae- chlorophyceae, rhodophyceae, bryophytes – liverworts, moses, pterdophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms, Plant life cycle & Alternation of generation. 06 Chapter -4 Animal kingdom Topic- basis of classification – level of organization, symmetry, diploblastic & triploblastic orga nization, coelom, segmentation, notochord, classification of animal Phylum- Porifera, phylum- coelenterata (cnidaria), phylum ctennophora, Phylum – platyhelminthes, Phylum- aschelminthes, PhylumAnnelida, Phylum- Arthropoda, Phylum – mollusca, Echinodermata (tunicate), cephalochoardate, vertebrata, Class- cyclostomata chondrichthyes, Class - osteichthyes, Class-amphibian, Class- aves, Class- mammalia. 14-19 July 21-26 July 05 Unit- II Structure organization in animals and plant Chapter-5 Morphology of Flowering plant Topic: The root – regions of root, modification of root, the stem-modification of stem, The leaf- venation, type of leaves, phylllotaxy, modification of leave, the inflorescence, The Flower- parts of flower, the fruit, The Seed- structure of dicotyledonous seed, structure of monocotyledonpous seed. 05 Chapter-5 contd……. Semi-technical Description of typical Flowering plant floral formula, floral diagram. Description of some important families- fabaceae, solonaceae, lileaceae. 04 Chapter -6 Anatomy of flowering plants Topic – The tissues- meristemetic tissue, permanent Tissues – simple tissues, complex tissues, the tissue system epidermal tissue system, the ground tissue system, the vascular tissue system, anatomy of dicotyledonous & monocotyledonous plants – dicotyledonous & monocotyledonous root, dicotyledonous & monocotyledonous stem. 28-30 Aug 1-2 Aug 4-8 Aug 11-16 Class - XI Week wise Syllabus – Biology 2008-09 Week Days Aug 18-21 04 Sub – Topic Dorsiventral (Dicotyledonous) Leaf, isobilateral (Monocotyledonous) leaf, Secondry growth, vascular cambium, cork cambium, Secondary Growth in Roots. Aug-22 I CCEP EXAM Aug 25-29 Chapter 7. structural organization in animals 06 Topic- Animal tissue- epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, neural tissue, Organ & organ system, Earthworm - Morphology, Anatomy. Sept 1-6 06 September 8-12 05 Cockroach- morphology, anatomy Frog - morphology, anatomy Unit III Cell: structure and function Chapter –8 : Cell : the unit of life Topic – What is cell? Cell theory. An overview of cell, prokaryotic cell- cell envelope & its modification, ribosomes & inclusion bodies. IST TERM EXAM Sep 15-22 Sep 2327,29 06 Chapter 8 contd…. Eukaryotic cells- membrane, cell wall. Endo membrane system – endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, centrosomes & centrioles, nucleus, microbodies. Oct 1-8 AUTUMN BREAK CHAPTER-9 Biomolecules Oct 9-18 06 Oct 27, Nov 1 02 Topic- How to analyes chemical composition? Primary& secondary metabolites, biomacromolecules, Portions, polysaccharides, nucleic acid, structure of Proteins, nature of bond linking monomers in a po lymers, dynamic state of body constituents – concept of metabolism, metabolic bas ic for living. The living state,enzymes-Type, property and function. Chapter 10 cell cycle & division Topic – cell cycle – phases of cell cycle – interphone. Metaphase, anaphase, telephone, cytokines is Chapter 10 contd….. Significance of mitoses & meiosis meiosis I , meiosis II Week Days Nov 3-7 05 Nov 10-15 05 Week wise Syllabus – Biology 2008-2009 Sub –Topic Unit IV Plant physiology Chapter – 11. Transport in plants Means of transport – diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, comparison of different transport processes, plant – water relation- water potential. Osmosis, plasmolusis, imbibition. Chapter 11 contd Long distance transport of water, how do pants absorb water? Water movement in plant, transporation & photosynthesis, uptake & transport of minneral nutrients uptake of mineral ions, translocation of mineral ions, pholem transport: flow from source t o sink – the pressure flow or mass flow hypothesis. Nov 17-22 Nov21 05 Chapter-12 Mineral Natrition Topic- Method to study the Mineral requirement of plants, Essential minneral element, criteria for essentiality of mineral element, macro nutrients, micronut rient role of macro & micro nutrient, deficiency symptoms of Essential element, toxicity of macro nutrients mechanism of absorption of element, translocation of solutes, soil as a reservoir of Essential nutrients, metabolism of nitrogen, nitrogen cycle, biological nitrogen fixation. Nodule formation CCEP II Nov 24-28 05 Chepter-13 Photosynthesis in higher plants Topic – What do we know about photosynthesis? Early experiment, where does photosynthesis take place? How many pigments are involved in ph otosynthesis? What is light reacation? The electron transport, splitting (photolysis) of water. Cyclic & non c yclic photo – phosphorylation, chemiosmotic hypothesis, where are ATP & NADPH used? Primary acceptor of CO2 , the Clavin cycle the C4 pathway, photo respiratio, factors affecting photosynthesis – light, CO2 concentration, Temperature & water. Dec 1-6 06 Chapter 14. Respiration in plant Topic- Do plant breath? Glycolysis, Fermenation, Aerobic Respiration, tricarboxylic Acid cycle. Electron Transport system (ETS) & oxdative phosphoprylation, the respiratory blanced sheet, Amphibolic pathway, respiratory quotient. Week Days Dec 8-12 04 Dec 15-22 DEC 23 Dec 26-31 Jan 1-3 Week wise Syllabus – Biology 2008-09 Topic Chapter –15 plant Growth & Development Topic – growth plants growth is generally indeterminate, Growth is measurable, phase of Growth, Growth rate, condition for Growth, differentiation, differentiation, & redifferentiation, development plant Growth regulators characteristics, the discovery of pl ant growth regulators, physiological effects of plant Growth regulators auxin, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, abscisic acid, photoperiodism, vernalisation. II TERMINAL EXAM 01 Discussion of question paper Winter break 03 Unit V. Human physiology,chapter16.digestion &absorption. Topic – Digestive system, alimentary canal & its parts, types of teeth & dental formula, digestive Jan 5-9 05 Jan 12-17 06 glands, Digestion of food absorption of digested products. Chapter 16 contd… Disorder of digestive system- Jaundice, vomiting, Diarrhea, Constipation, Indigestion. Chapter 17. Breathing & exchange of gases Topic – Respiratory organ human respiratory system, mechanism of Breathing, respiratory volumes & capacities. Exchange of gases, transport of gases, transport of oxygen, transport of CO2, regulation of respiration, disorder of respiratory system. Class: XI Subject: BIOLOGY 2008-09 Date Jan 19-24 Days 06 Sub Topics Chapter 18 body fluids & circulation Topic- Blood – composition of blood- plasma, formed Element (erythrocytes, leucocytes & thrombocytes) Blood Group – A, B, C, D, O blood, group, rh groping – rh - ve, coagulation of blood, lymph (tissue fluid), circulatory pathways, human circulat ory system, structure of human heart, cardiac cycle, Electro cardio graph (Ecg), double Circulation, Regulation of cardiac Activity, Disorders of circulatory system – high blood pressure, CAD, angina, Heart Failure. Jan 27-30 04 Chapter 19 Excretory products & their elimination Topic:-Human Excretory system, urine formation, function of the tubules, mechanism of concentration of filtrate, regulation of kidney function, role of other organs in excretion, disorders of excretion. Feb2-6 06 Chapter 20 Locomotion & movement Topic:- Types of movement, muscles, structure of contractile protein, mechanism of muscles contraction, Skeletal system. Bones & girdles. Joints, types of joints, disorders of muscular & Skeletal system. Feb 9-14 06 Chapter 21 Neural control & coordination Topic- Neural system, Human Neural system (CNS&PNS), somatic Neural system, Autonomic Neural System, Neuron as structural & function unit of Neural system. Generation & conduction of Nerve impulse, transmission f impulse Central nervous system – forebrain, midbrain & hindbrain, reflex action & reflex arc, Sensory reception & Processing – The eye – parts of Eye, mechanism of vision, the ear – outer ear, middle ear, inner ear & their structure, mechanism of Hearing. Feb 16-21 06 Chapter 22. Chemical coordination & integration Topics:- Endocrine gland & hormones, human endocrine system- the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, Thymus gland adrenal gland, pancreas, testis, mechanism of hormone action. Feb 23-27 05 Revision & Practical Examination (1) Mrs. Rita Talwar (PGT Biology) R.P.V.V., Lajpat Nagar, Prepared By New Delhi. (2) Mrs. Poonam Anand, PGT. Biology R.P.V.V., Tyagraj Nagar







