lab 5: metamorphic rocks
advertisement
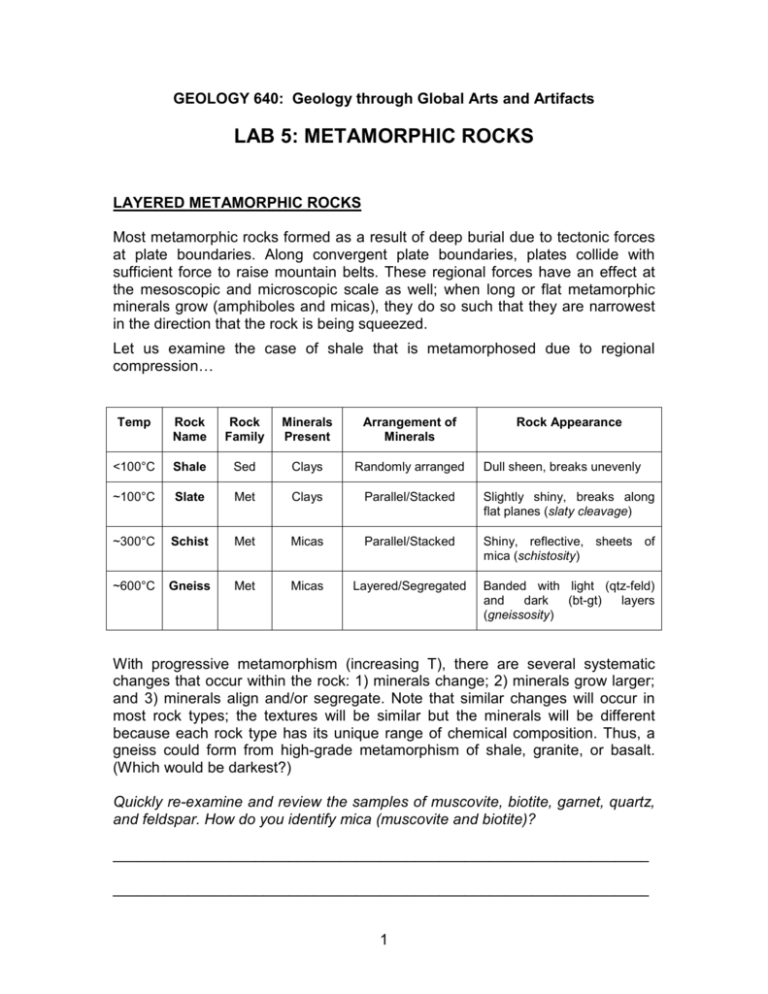
GEOLOGY 640: Geology through Global Arts and Artifacts LAB 5: METAMORPHIC ROCKS LAYERED METAMORPHIC ROCKS Most metamorphic rocks formed as a result of deep burial due to tectonic forces at plate boundaries. Along convergent plate boundaries, plates collide with sufficient force to raise mountain belts. These regional forces have an effect at the mesoscopic and microscopic scale as well; when long or flat metamorphic minerals grow (amphiboles and micas), they do so such that they are narrowest in the direction that the rock is being squeezed. Let us examine the case of shale that is metamorphosed due to regional compression… Temp Rock Name Rock Family Minerals Present Arrangement of Minerals Rock Appearance <100°C Shale Sed Clays Randomly arranged ~100°C Slate Met Clays Parallel/Stacked Slightly shiny, breaks along flat planes (slaty cleavage) ~300°C Schist Met Micas Parallel/Stacked Shiny, reflective, sheets of mica (schistosity) ~600°C Gneiss Met Micas Layered/Segregated Banded with light (qtz-feld) and dark (bt-gt) layers (gneissosity) Dull sheen, breaks unevenly With progressive metamorphism (increasing T), there are several systematic changes that occur within the rock: 1) minerals change; 2) minerals grow larger; and 3) minerals align and/or segregate. Note that similar changes will occur in most rock types; the textures will be similar but the minerals will be different because each rock type has its unique range of chemical composition. Thus, a gneiss could form from high-grade metamorphism of shale, granite, or basalt. (Which would be darkest?) Quickly re-examine and review the samples of muscovite, biotite, garnet, quartz, and feldspar. How do you identify mica (muscovite and biotite)? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 1 Examine the following hand samples (140, 150, 159, 200). They represent various stages in the metamorphism of shale. Sample # Size of Crystals Identifiable Minerals Arrangement of Minerals Rock Appearance Rock Name Arrange these 4 samples (140, 150, 159, 200) in sequence from lowest grade to highest grade (low T to high T). ____________ Lowest T ____________ ____________ ____________ Highest T Explain why slate was commonly used for making blackboards. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Based on the physical properties of 140, 150, 159, and 200, which rock would be most appropriate for building a monument? Which would be least appropriate? Explain your answer with reference to the physical properties. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 2 MASSIVE METAMORPHIC ROCKS Two of the most common sedimentary rocks, limestone and quartz arenite, are each composed predominantly of only one mineral, calcite and quartz respectively. Without other minerals with which to react an all-calcite sedimentary rock will remain an all-calcite rock when it is metamorphosed. A metamorphosed limestone is called marble. Similarly, an all-quartz sedimentary rock will remain an all-quartz rock when it is metamorphosed. A metamorphosed quartz arenite is called a quartzite. Compare limestone (120) with marble (161). What characteristics change during the metamorphic process? What characteristics remain unchanged? Describe how you can distinguish between a limestone and marble. ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 3 Compare sandstone (124) with quartzite (165). What characteristics change during the metamorphic process? What characteristics remain unchanged? Describe how you can distinguish between a sandstone and quartzite? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ Describe the physical properties that allow you to distinguish between a marble and a quartzite. Why might an artist choose to sculpt out of marble? Why might an artist choose to sculpt out of quartzite? ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ 4






