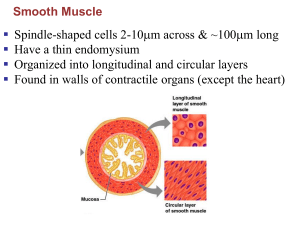
Classification of smooth muscles
advertisement

Classification of smooth muscles • multi unit smooth muscle (A) – Cells work independently of one another – Each cell receives it own innervation • unitary smooth muscle (B) – gap-junctions between cells – innervation in forms of varicosities – In the wall of hollow organs Classification of smooth muscles • multi unit smooth muscle (A) – Cells work independently of one another – Each cell receives it own innervation • unitary smooth muscle (B) – gap-junctions between cells – innervation in forms of varicosities – In the wall of hollow organs The smooth muscle AP I. • Major characteristics – resting membrane potential (if exists) -50 and -60 mV – amplitude 60 and 70 mV – The time between AP and the start of contraction (latency) > 100 ms The smooth muscle AP II. The contractile proteins • no sarcomere – Instead of the Z line “dense bodies” • thin filament – actin – tropomyosin • thick filament – myosin The acto-myosin cycle • • • • [Ca2+]i increases Ca2+ - calmodulin (CaM) CaM kinase (CaMK) gets activated myosin light chain (MLC) gets phosphorylated • actin-myosin interaction → contraction • MLC gets dephosphorylated (phosphatases) → relaxation Regulation of contraction I. the role of the thin filament and calponin • In the dephosphorylated state calponin binds to the thin filament – the number of possible cross-bridges decreases → tension ↓ • In the phosphorylated state calponin detaches from the thin filament – the number of possible cross-bridges increases → tension ↑ Regulation of contraction II. the role of the phosphatases change in the phosphorylation state of the regulatory proteins tension – [Ca2+]i function shifts Regulation of contraction III. the „latch-bridge” • “latch-bridge” = sustained contraction with decreased energy consumption – Dephosphorylation of MLC takes places in the AM state → myosin ATPase activity ↓ → AM is maintained → maintained tension • Plasticity → smooth muscles have no resting length Regulation of smooth muscle function humoral and hormonal effects Tissue factors • hypoxia • hipercapnia • tissue metabolites (e.g. lactic acid, adenosine) • NO Other humoral effects • acetylcholine (mAchR) • histamine (H1 and H2 receptors) • serotonin • kinins and other vasoactive polypeptides • • • • noradrenalin (α-adrenerg) adrenalin (β-adrenerg) ADH (vasopressin) oxytocin (uterus, ducts of the mammary gland) • estrogens • progesterone • permissive effect of glukocorticoids, thyroid hormones Comparison of different muscle types Striated m. Smooth m. Heart m. thin and thick filaments yes yes yes sarcomeres yes no yes speed of contractions fast & slow very slow slow SR ER & extracellular SR & extracellular place of activating Ca2+ troponin myosin & ? troponin stretch increases muscle activity no yes yes excitation excitation or inhibition excitation or inhibition some large large activating Ca2+ effect of nerve stimulation effects of hormones