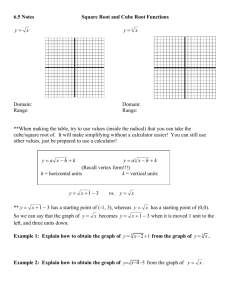
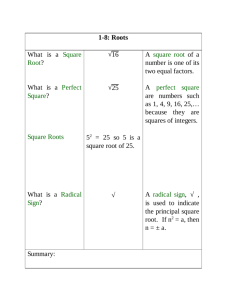
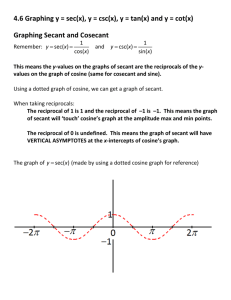
Glossary Term Definition cosine In a right triangle with acute angle A
advertisement

Glossary Term cosine cotangent coterminal angles counterexample Cramer’s Rule critical points cross products Definition In a right triangle with acute angle A, the cosine of A = the measure of the leg adjacent to A . the measure of the hypotenuse In a right triangle with acute angle A, the cotangent of A = the measure of the leg adjacent to A . the measure of the leg opposite A Two angles in standard position that have the same terminal side. A specific case which proves a statement false. A method that uses determinants to solve a system of linear equations. Points at which the nature of a graph changes. The product of the terms on the diagonals when two ratios are compared. Example: In the proportion cube of a number cube (geometric figure) cubic function cubic units cumulative frequency histogram cumulative frequency table cup cylinder data decagon 2 8 = , the cross 3 12 products are 2 × 12 and 3 × 8. The product in which a number is a factor three times. Example: The cube of 2, or 2 cubed, is 8 because 2 × 2 × 2 = 8. A solid figure with six square faces. A function that can be described by an equation of the form y =ax3 + bx2 + cx + d, where a ≠ 0. Used to measure volume and tells the number of cubes of a given size needed to fill a three-dimensional figure. A histogram organized using a cumulative frequency table. A table in which the frequencies are accumulated for each item. A customary unit of capacity equal to 8 fluid ounces. A solid figure whose bases are formed by congruent circles in parallel planes and whose lateral surface is curved. The segment whose endpoints are the centers of the circular bases is called the axis of the cylinder. The altitude is a segment perpendicular to the bases with an endpoint in each base. Numerical information gathered for statistical purposes. A polygon having ten sides.