Overview - ASTD
Competency Model
Patty Davis (DDI)
Bill Rothwell (R&A)
Jennifer Naughton (ASTD)
revised and restated by
Janis Houston (PDRI)
Rothwell & Associates
Presentation Objectives
Understand How and Why the New
Competency Model was Developed
Understand the New Model and its
Components
Understand How Model Can Be Used to
Foster Professional Development
2
Mapping the Future:
Three Research Goals
Identify Trends Driving Change in
Workplace Learning and Performance
(WLP)
Update Past Competency Model
Provide a Foundation for CompetencyBased Applications, including
Credentialing
3
1
Research Highlights:
Maximum Involvement
Comprehensive Literature Review, Including
Existing Models and Programs (CSTD,
IBSTPI, ICF, etc.)
Interviews/Focus Groups with Over 250
Thought Leaders, Experts and Practitioners
Broad-based Survey of Over 2000 WLP
Professionals to Validate New Model
North American Focus, Global Input
ASTD Board/Chapter Participation
4
Research Highlights:
Sample of Who We Involved
Elaine Biech • Peter Block • Warner Burke • Bill
Byham • Pat Crull • Gloria Gery • Judith Hale • Phil
Harkins • Ann Herrmann-Nehdi • Diane Hessan •
Katherine Holt • John Humphrey • Tom LaBonte •
Pat McLagan • Jeanne Meister • Kevin Oakes • Peter
Senge • Martyn Sloman • Bonita Stoufer • Brenda
Sugrue • Meg Wheatley • Jean Barbazette • Dianna
Booher • Richard Chang • Janet Cherry • Judith
Hale • Janis Houston • Jane Massy • Donna
McNamara • William Nijhof • Daryl Sink • Martyn
Sloman • Nancy Thomas • Mark Van Buren • Linda
Waters • Laura Whitworth • John Coné . . .
5
Findings: Trends Impacting
Our Profession
Drastic times, drastic measures
Blurred lines—life or work?
Small world and shrinking
New faces, new expectations
Work be nimble, work be quick
Security alert!
Life and work in the e-lane
A higher ethical bar
Source: Jan 04 T+D “8 Trends You Need to Know Now”
© 2004 American Society for Training and Development. All Rights Reserved.
6
2
Implications of These Findings
for the WLP Profession
Rank
Implication
% Agreeing
Very
Important
or Essential
Mean
5-point
scale
1
Aligning learning and performance strategies with the
organization’s strategy
93%
4.62
2
Demonstrating a payback from your efforts in the form of
improved organizational performance and measurable results
85%
4.32
3
Operating ethically and with social responsibility
83%
4.38
4
Developing or offering learning tools to meet the need for just-intime learning and knowledge
82%
4.25
5
Developing and implementing strategies for retaining and
developing talent
81%
4.26
6
Increasing competence in understanding technology alternatives
and their use and application in delivering learning and training
77%
4.15
7
Understanding and responding to globalization and diversity issues
61%
3.76
© 2004 American Society for Training and Development. All Rights Reserved.
7
Desired Features of the
New Model
Comprehensive - Apply to WLP Professionals
at Different Levels, in Different Roles
Define Current and Emerging Competencies
(Mapping the “Future”)
Create a Foundation for HR Functions
Provide Sufficient Specific Detail
Definitions, Behaviors, Key Actions
Key Knowledge Areas, Lists of Common Outputs
8
ASTD Competency
Model™
Roles
are groupings of targeted competencies. They
are not job titles. An individual’s job may
encompass one or more roles, similar to different
“hats” that one wears.
Areas of Expertise
are the specialized knowledge/skills an
individual needs over and above the
foundational competencies. An individual
may need expertise in one or more areas.
Foundational Competencies
define the relevant behaviors for all
learning and performance professionals
to varying degrees.
Roles
Expertise
Foundation
9
3
Find Out More…
Go to the ASTD website for status updates,
answers to Q&A’s, feature articles, narrated
presentations www.astd.org/competency
2004 competency study report can be
ordered via the ASTD Store
http://store.astd.org/product.asp?prodid=2660
Send an email to ASTD
competencystudy@astd.org
11
Leveraging Diversity
Miriam Vaughn-Lee
Director, Employment, Diversity and
Workforce Strategies
City of Minneapolis
Human Resources Department
4
Role
Design and implement a 5-Year Strategic
Plan for Diversity which is connected to the
City’s vision and business planning process.
Seek endorsement and approval from the
City Council and Executive Committee.
Establish community outreach and
engagement activities to insure full
participation.
13
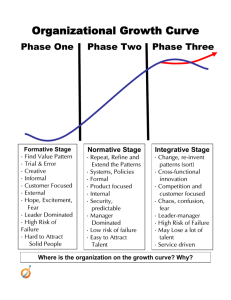
Four Stages of Diversity
Inclusiveness
Managing Diversity
Valuing Diversity
Affirmative Action
14
Gaps and Needs
Uniform and consistent definition of diversity
Inconsistent leadership commitment
Implementation of performance metrics
Department Head Leadership
Department Results to Plan
Employee Selection, Retention, Development,
Turnover, Complaints and Grievances
Employee Involvement and Satisfaction
15
5
Workforce Needs
Resistance from bargaining units who see
diversity as AA
Rule of “3”
Lack of clarity regarding EEO reporting
requirements and diversity “values”
16
External Trends and Indicators
Population Shifts
Unfamiliar Languages
Different Cultures
Tradition, Customs, Lifestyles
Values, Norms and Beliefs
Aging of Population
17
Internal Trends and Indicators
Intergenerational Workforce
Demographic Shifts
Cultural Shifts
Unfamiliar Languages
Different Cultures
Retirement Projections and Knowledge Lost
Rule of Three
18
6
Leveraging Diversity
Competencies Needed
Interpersonal
Building Trust
Communicating Effectively
Influencing Stakeholders
Developing Cultural Competency
Business Management
Analyzing Needs and Proposing Solutions
Developing Cultural Competency
Driving Results and Measuring Outcomes
Planning and Implementing Assignments
Thinking Strategically
Personal
Demonstrating Adaptability
Modeling Personal Behavior
19
Meeting Future Goals
Conduct City Leadership Study Sessions
Formation of a Leadership Advisory Council on
Diversity
Outside Expert to work with Department Heads
Hiring diversity competent staff
Formation of Diversity Action Councils at the
department level
Designing and implementing SMDP in partnership
with Training and Development to build diversity
competence at the supervisor/manager ranks.
Assessing present recruiting and selection practices
to determine effectiveness
Developing diversity leadership competence through
HRGs who serve as internal consultants to business
partners
20
Role, Area of Expertise &
Competencies Needed to Meet
Future Goals
21
7
Building Managerial Leadership for the Future
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Linda Zehnbauer –
Sr. Manager of Talent
Development Solutions
Leslie Vatne – Principal
Talent Development
Specialist
.
0
How is Medtronic Talent Development Solutions
contributing to workplace learning and
performance?
ASTD Competency Model
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Our Challenge
“I would like to see our management at all levels
spend more time attracting, developing, and
ensuring that we keep the diverse talent needed to
make Medtronic successful in the future.”
Art Collins, Chairman & CEO
From Art Collins’ State of the Company Address
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
8
Why Talent Management?
• Talent Management is the most critical
organizational challenge that Medtronic will
face in the next decade.
• Talent Management requires a fundamental
change in the way we think about attracting,
deploying and developing people at
Medtronic.
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Why is Talent Development
Important at Medtronic?
• Helps build skills and competencies to
achieve business results
• Results in having the right people in the right
jobs at the right time
• Aligns with the following strategic imperatives:
– Talent Management
– Diversity
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
What is Talent?
“The skills, behaviors, experiences, intelligence,
judgment, attitude and energy of every
employee…that when combined, allow us to
deliver superior business results.”
A Focus on Talent at Medtronic
Medtronic View
2/11/05
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
9
Helping YOU Build Skills & Competencies to
Achieve Business Results
www.TalentDevelopmentSolutions.medtronic.com
RS Talent Development Solutions
Management
Employees
Human Resources
Talent Development
Solutions (TDS)
Resources to Borrow
Individual Consulting
Courses
TDS Web Site
•Books/CDs
•Call 763-514-4787
•Video/Audio Tapes
•IDPs / Resumes
•Developing Careers with a
Passion for Life - Suite
•Tip Sheets
•MBTI/Strong
•Development
Planning Tools/
Tips & IDP
•Competency Models
•Career Opportunities
•College / Tech Catalogs
•Back to School
•Career Architect
•eDevelopmentCoach,
•Mentoring at Medtronic: Six
Steps to a Successful
Partnership
•Creating Dream Job
•1-800-678-2500, 46400
•View Saba for Other Courses
•Management Curriculum
•Career Explorer
•Career Vision
• Self-Assessments
•Course Listing
•Course Schedule
•Mentoring
•Competencies
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Development Job Moves &
Work Experiences
• Orientation: Becoming a
Medtronic Manager
Program
• Foundations of
Management Program
Senior Leader
• New Director Program
(new company wide
program for newly
promoted
Directors/other
Directors)
Executive
• New Executive On
boarding
–
ng – Key Talent Pipeline
Talent Reviews – Org Planni
• Leadership
Development Program
(Targeted Schools)
• Emerging Leaders
Program
Early Pipeline
• Targeted Mentoring
Partnerships
• Menttium 100 Program
& Virtual Menttium
Program for Women
Mid Pipeline
• Medtronic Global Leader
Program (revised &
enhanced Medtronic
Leader Program)
• Medtronic Senior
Leader Program
• Menttium 100 Program &
Virtual Menttium Program
for Women
Senior Pipeline
CORPORATE TALENT
Intentional & Targeted Job
Moves & Experiences
• Connections On
Boarding Program for all
New Grads
Mid Level Leader
Business Unit/Geography Talent
Medtronic Talent Pool
Early Career
Executive Pipeline
High Potential Leadership Pipeline
= Managed “centrally” in partnership with the BU/Geographies
= Managed Locally (in partnership with Executive & Leadership Development)
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Becoming a Medtronic Manager Program
Overview
Becoming a Medtronic Manager consists of two course offerings - Orientation
and Foundations of Management.
Orientation
The Orientation is a 4 - 5 week program designed for any new manager
at Medtronic, including experienced management hires. This program
provides the key information and activities managers need to know in
order to function effectively as a manager at Medtronic.
The Foundations of Management is a 7 - 8 month program designed
for new managers who have two years or less management
experience. This program provides an in-depth learning experience
over three stages that will result in a high performing manager at
Medtronic. Completing the Orientation program is a prerequisite.
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
10
Target Audience – Becoming a
Medtronic Manager
Orientation
Stage 1
Management
Basics
Fundamentals
Newly
promoted
<2 years
Experienced
new hires
Stage 2
Management
Proficiency
Stage 3
Managing for
High
Performance
Required
Required
Optional: Based on IDP & with one over mgr support
Optional: Based on IDP & with one over mgr support
In role
>2 years
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Both programs incorporate the best
practices of a blended learning design:
Phased approach:
Managers learn “just what they
need” at “just the right time.”
Learner support:
Learning linked to job
performance
Blended learning:
maximize learning
effectiveness
Medtronic
Foundations of
Management
Program
Content has multiple uses:
learning & performance support
Integrate learning into the job:
Just in time learning provides
knowledge and skills when
needed
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
What does the future hold for
Talent Development Solutions?
• Leading a Talent Development Mindset
• Creating opportunities for development to be
a process not an event
• Partnering to provide skill development for
critical organizational strategies
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
11
Role, Area of Expertise, and Competencies
Needed to Meet Future Goals
ASTD Competency Model
TALENT DEVELOPMENT SOLUTIONS
Strategic Talent Planning – The Competitive Edge
Darcy Mattinen
AMS Organizational Development
January 27, 2006
Key Differentiators –
AMS Talent Review
Talent Review at AMS = A formal mechanism for assessing
talent, calibrating viewpoints, and building organizational capacity
Strategic Planning Process, Part B (The Who)
Beyond Executive Succession Planning Risk Management
Focus on Building Talent for Tomorrow’s Image
Created in Partnership with Top 3 AMS Leaders
Small Group Talent Review Presentations Focus on Robust Matrix
Leadership Dialogue and Action Planning
Team Effort With Executive Roll-Up Ownership – Managers, Directors,
HR, OD (no silos)
– Seamless Integration with Other Strategic Talent Processes
12
Priority Positions & Profiles
•
Executive Successor Candidate
Emerging Leader
Generally Sr. Manager-VP levels
Generally Candidates for Sup/Mgr roles
Viable candidate for Executive role
within 3 years
•
Currently a high-performing AMS
Leader
•
Demonstrates potential for increased
responsibility and scope of decision
making
•
Aspirations, core values, and
experience align to future AMS Leader
role needs
•
Passes the Competency and Derailer
test
•
Demonstrates leadership and initiative
•
Has taken on new and stretch
assignments
•
Has demonstrated the appetite to learn
and grow and has taken on additional
responsibilities
•
Evidence of ability to make effective
decisions and stand by them
•
Communicates well within and across
departments and teams
•
Demonstrates each leadership
competency, at an earlier stage; may
show less consistency in its
demonstration
Critical Technical/Functional Talent
Could be a non-leader or leader employee
•
Individual possesses unique
knowledge/skills/credentials, which
critically impact AMS ability to succeed
in an aspect of current or future
business
•
AMS could be at risk if the individual
unexpectedly leaves the company –
critical to have a pipeline of back-up
talent
•
Possesses individual leadership skills,
shares knowledge and information with
others, elevates team’s competence
•
Ability to lead or be a positive
contributing member on crossfunctional teams
Process Overview
AMS Strategic Planning
Talent Implications of 5-Year Strategic Plan
Kickoff to Functional Level
Talent Review – Q1, 2006
Organizational Structure
Leadership Needs
Technical/Functional Knowledge Needs
•
Identification of Key Talent
Executive Successor Candidates
Emerging Leaders
Critical Technical/Functional Talent
•
All leaders invited to a 2-day
offsite event; majority of first day =
kick-off to Functional Level Talent
Review
Managers highly involved in this
phase of the Talent Review
process
Functional Talent Review
Assess Current Talent Portfolio and Organizational Structure
Against Strategic Vision
Presentations (2) of
Findings and
Recommendations
Organizational Structure, OT Successor
Candidates, Emerging Leaders, Critical
Technical/Functional Talent
Meeting 1 – Q4, 2005
•
•
•
Future OT Position Profile
List of OT Candidates
Short-List of Emerging Leaders and
Critical Technical/Functional Talent
Strategic Action Plans
•
Meeting 2 – Q1, 2006
Action
Planning
•
•
•
•
Functional Assessment – all Exempt
List of Emerging Leaders and Critical
Technical/Functional Talent
Organizational Structure Analysis &
Recommendations
Functional & Individual Action Plans
Wrap-Up
Talent is a Critical Competitive Advantage & Must Be a Component of
Strategically Planning for the Company’s Future
Leaders Need to Be Held Accountable for Talent Development
All Talent Processes Must Align & Fit with Organizational Culture
Engaged Top Leadership is Key!
American Medical Systems
Organizational Development
(952) 930-6591
10700 Bren Road West
Minnetonka, MN 55343
13
Q&A
40
14