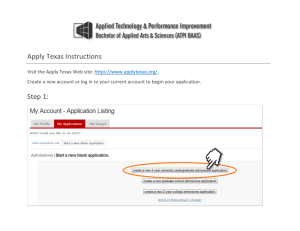
UNIT 5- PART A PUBLIC OPINION AND INTEREST GROUPS
advertisement

UNIT 5- PART A PUBLIC OPINION AND INTEREST GROUPS Issue: Does public opinion have any influence on American government? 1. DEFINE POLITICAL SOCIALIZATION & DISCUSS THE ROLES PLAYED BY THE MAIN AGENTS OF POLITICAL SOCIALIZATION. Political Socialization – The process by which you acquire your political beliefs, opinions and at attitudes. Six agents of Political Socialization: 1. Parents/Family 1. your political party identification and loyalty. If you are split, you are more likely to take on the mother’s party. – (republican) 2. Political Philosophy – liberal or conservative or moderate 3. If you are an activists and participate, then your parents more than likely were also. If they didn’t vote, you are more likely to be an apathe tic non-participant. 4. Image of the United States. "It's the best country in the world and you are lucky to an American – be a good citizen; pay your taxes, obey the law, fight for your country Change : Less parental influence today. Due to divorces mobility, and more apathy, And more leisure time – we spend it with our peers. 2. Church ♦ Protestant, Catholic, and Jews ♦ Jews are the most liberal and Democratic ♦ Protestants are the most conservative and Republican ♦ Catholics more moderate. – 60% Democrats, 40% Republicans ♦ Will have the most impact on moral-political issues. Ex: Gay rights, abortion, pornography, and organized prayer in the schools, sexual education, drinking, creationism and evolution. Change : Less influence today because church attendance is down significantly. Also the secularism of American society. – separation of church & state. In early United States – Church was hub of community social life and the minister was usually the most educated person in the entire community. – we put him on a pedestal -- & people didn’t easily disagree with their minister. 3. School/Education 1. Children taught our history as heroic in grade school 2. Children taught patriotism early on "Pledge of allegiance" 3. “Citizenship training” taught about the political system through high school. 4. Taught a balance of views and actual history in college. – mistakes our nation has made 5. Litt study. Edgar Litt political scientist and his theory. Rationalized that dependant upon the the type of schools they attended politically. Examples: 1. Upper Middle Class Suburban (White Collar) (Permian) ♦ Encouraged to vote ♦ Encouraged to become involved politically ♦ Encouraged to question the system. healthcare 24 2. Lower Middle Class (Blue-Collar) (Odessa High) ♦ Encouraged to vote and not much else 3. Inner City Poor (non-white school) (Ector High) ♦ Not encouraged to become involved in the political system. ♦ Instructed to fight for their country and obey the laws Change : Effects of education on political socialization have increased. The more someone is educated the more those persons become involved in politics and the more influence their education has on them. 4. Peers ♦ Friends, Co-workers, acquaintances. 1. Most have your same views and reinforce your political views. 2. Strong emphasis to conforming to group beliefs. 3. Strongest pull from conforming in teen and high school years. Change : The effect has increased. More leisure time and availability of those friends, autos, city living. 5. Media 1. Newspapers - less convenient and more time consuming. Biased and one-sided. Odessa America is predominantly conservative. Also Newspapers are more vulnerable to public opinion. – most cities have only one news paper today- lack of choice. 2. Newsmagazines- Time, Newsweek, U.S. News and world report. Newsmagazines middle of the road on views and appeal to a national audience. ♦ Greater cost and time involved sitting and reading one. ♦ News is dated by the time magazine reached you ♦ Best in-depth, best coverage of each story. ♦ Smallest Audience. 3. Radio- Was once more effective and popular. Talk radio is much more conservative News is very brief and concise. Not much in-depth reporting. Unless it's a 24 hour talk Show. 4. Television- 2/3rds of us rely on television as their major source and 50% rely on it as our only source. Easy convenient and regularly scheduled. Most up to date. Pictures and film footage make it more entertaining. However time constraints, because of commercials. Twenty-six minutes of actual air time. Television can only cover the important coverage. Television airs stories with good film footage and stories that will bring in more viewers. FCC regulates television and radio broadcast. Used to have a fairness doctrine (equal time on opposing viewpoints) Ended as a result of cable television. Also we now have satellite technology to report live and up to the second reporting from all parts of the world. 5. Internet♦ Get news anytime you want at your fingertips when you want it. ♦ Danger on the Internet is that it is not always accurate. Must take care to receive news from reputable or consistent sources. Change : Increased influence by media, especially TV. healthcare 25 6. Generational Events ♦ 1930's - Great Depression - FDR - Frugal people saving for a rainy day. Created good loyal democrats ♦ 1940's - W.W.II - FDR - Created very patriotic democrats ♦ 1960's - Kennedy assassination, civil rights revolution and the beginning of the Vietnam War. Created liberal generation very democratic and distrustful of government. ♦ 1970’s - Nixon - Vietnam war escalates - crated liberal democrats but distrustful of government. ♦ 1980’s - Reagan - Became conservatives and more republican.( because of popularity of Republican President Reagan; 80's children were of the more liberal 60's parents.) ♦ 1990’s - Clinton - Democratic President and counterbalancing his influence there is a Republican Congress.--which will be more influential ?? The verdict is still out. healthcare 26 UNIT 5 – PART B INTEREST GROUPS 1. DEFINE AND EXPLAIN THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE FOLLOWING. Interest group - An organization that is in some way to influence government actions and policy. Lobbyist - Professional who is hired by an interest group, or any of us who take the time to try to influence government. Phone calls, e- mail, and try to influence government and their actions. Ralph Nader through Sierra clubs Look em up in the book. One sentence answers. Ralph Nader - Consumer advocates - works for better consumer protection. –Ex: seat belts, air Bags, better labeling on products. Common Caus e - National citizens lobby with 250,000 members received major credit for passage of the election reforms laws of the 1970's. – a public interest group- works for more open, honest, accountable government. NOW National Organization of Women - Founded in 1966 and places more emphasis on issues pertaining specifically to the status of women. Has 260,000 members and tries to improve employment opportunities for women and has campaigned for the equal rights amendment. They defend the rights of lesbians and they oppose all forms of sexual discrimination. They have pledged to take action to bring women into full participation in the mainstream of American society now. Assuming all the privileges and responsibilities in fully equal partnership with men. Chamber of commerce - Represent the business community. Concerned with attracting tourists and consumers. New business. League of Women's Voters - Public Interest group who represent us for more honest government. Open meeting acts. Each election they publish a voters guide. Their main concern is educating voters so we can vote more intelligently & informed. ACLU - American Civil Liberties Union - Fight for the constitutional rights of any group who is denied their constitutional rights. –often represent unpopular groups (Ex: KKK, Nazis, Communists, Gays, etc.) Right to Life - Abortion - Ending legalized abortion. Leading ProLife organization. AARP - American Association of Retired People. Concerned the rights of Senior Citizens. Fighting age discrimination. Powerful Group because they vote in high percentages. AMA - American Medical Association - Concerned with government cuts into their profits. 297,000 members represent physicians and are highly active and have spent millions of dollars opposing national health insurance and other medical legislation. healthcare 27 AFL-CIO - American Federation of Labor Congress of Industrial organizations. Founded in 1881 by Samuel Gompers a London born cigar maker. The federation fought for bread and butter improvements like the eight hour work day, higher pay, fringe befits and restrictions on child labor. Began as a large group of smaller organized skilled trades. NRA - National Rifle Association - concerned with antigun control laws. –opposes gun control -protects 2nd Amendment right to bear arms. NOW - National Organization of Women - Leading Feminist group fighting sexual discrimination & for women’s rights. –supports equal rights amendment.. Sierra Club - Oldest environmentalist group around, Lobby for clean air and water and better funding for our national parks. Better funding for disposal of toxic waste and protection of endangered species, LULAC - The oldest Hispanic civil rights organization fighting to end race discrimination. NAACP - The oldest black civil rights organization fighting to end discrimination. 2. DISCUSS THE SEVEN TACTICS USED BY INTEREST GROUPS TO INFLUENCE THE GOVERNMENT. Techniques to influence government 1. Electioneering (O) most effective and expensive method. (usually first chosen method) ♦ Definition: (O) trying to get candidates sympathetic to your cause elected to office. 1st method chosen because if you are successful and get sympathetic candidates elected, you don’t have to work as hard to convince government to do what you want done. Best way to do this is: 1. Through campaign contributions. ♦ At the federal level, the most an individual can contribute to a campaign à $1,000 ♦ If you are a political action committee your limit is $5,000 in any one candidate in any one election. ♦ Each labor union or interest group is limited to one PAC each. 2. Endorsement Stand behind and give a stamp of approval to certain candidates. Sway Voters for the cause you stand for. –can gain candidates many votes they otherwise might not receive. 3. Volunteers Provide volunteer worker. 4. People who answer telephones, fill envelopes, and hang posters. Vast majority of campaign workers is volunteers. 2. Lobbying ♦ Definition: Face to face contact or verbal or written persuasion. ♦ Most effective Lobbyists are former members of government, but are also very expensive. Posses a wealth of connections, expertise, and technical know how. ♦ E- mail, Letters, Faxes, Phone calls, and Personal appearances. ♦ Providing Research and information. To bring about change by proving your cause with facts provided by personal or personally funded research. Statistics, facts, and research. ♦ Wining and Dining: 90% of budget spent on it because of effectiveness. – luncheons, breakfasts, dinne rs, receptions. 28 ♦ Providing free gifts. ♦ List of favorite women of government officials. Escorts. ♦ Letter writing campaign. –only type of Apr. campaign that DOES NOT require much money. healthcare 3. Persuasion-public opinion ♦ Media campaign- Expensive. – TV, radio, newspaper & magazine ads ♦ Billboards, films, speakers ♦ Write letters to the Editor – only type of Apr. campaign that DOES NOT require much money. 4. Influence appointment of sympathetic government officials ♦ Requires connections for personal visits to get your call through or to get your letter read.— ♦ Try to influence President, governor, city mayor or city manager to appoint the “right” people. 5. Litigation Using court system and filing a lawsuit. ♦ Must have a legal issue. Ex’s: ♦ Gun control ♦ Abortion ♦ Immigration ♦ Discrimination- civil rights ♦ 1st Amendments issues – speech, press, religion, assembly Advantage : Less expensive Advantage : Most objective & non-proportional branch of government is the judicial branch. Disadvantage : Time consuming- courts are slow – months or years before a final decision is reached. 6. Direct action Peaceful protest ♦ Civil Disobedience ♦ Picketing, marches, demonstrations, sit- ins ♦ Boycotts – economic pressure Advantage : Cheap & inexpensive, free media publicity Disadvantage : If violence results then your group takes the blame for the action even if it did not initiate it. ♦ Public views this tactic as used by troublemakers, radicals, “and un-American groups” – it can cause a backlash against your groups & hurt your cause. ♦ Martin Luther King (civil rights) & Anti- war movement used this tactic successfully – media publicity created a lot of public sympathy. 7. Illegalities ♦ Bribery ♦ Blackmail ♦ Extortion ♦ arson ♦ terrorism ♦ violence ♦ murder ♦ assault 29 ♦ Used by Radical groups, or Frustrated groups who were committed to democracy and peaceful change and feel that AS A LAST RESORT it is necessary to engage in criminal activity. Ex: Boston Tea Party. ♦ If caught personal cost is tremendous also only turns public opinion against you. Ultimate risk is death. ♦ Generally used as a technique of LAST RESORT healthcare --Business and Trade Lobbyists are them most successful and powerful. 80% of all registered lobbyists are representing business and industry. – They have more money and connections than all other groups. 3. EXPLAIN HOW ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS MAKE INTEREST GROUPS MORE POWERFUL IN TEXAS. 1. Diversity of State Economic Environment – the more diverse a state economy, the less powerful interest groups are – check and balance, in Texas: oil & gas dominates –this helps oil & gas lobbyist. 2. Resources Available To the Legislature - 3 S's ♦ Salary - pay - Lower the better more effected by bribery or influence. ♦ Session - length - Shorter the better. No time for research. ♦ Staff - Small poorly paid staff better - Less professional and influenced by lobbyists. ♦ Texas: raw salary -- $7,200/yr.; short session – 140 days every 2 years; small inadequate staff. –all 3 make Texas legislators more dependent on lobbyists. 3. Resources Available to the governor ♦ Weak or Strong Governor - Easier to lobby a weak figurehead –ranks 48th , 49th , or 50th –this helps interest groups ♦ Texas: very weak governor 4. Level of political Participation ♦ Voter turnout - Lower the turnout allows interest groups to more easily influence election results because their members are the ones voting. ♦ Texas – very low turnout – bottom 10 of 50 states – this helps interest groups. 5. Level of political party competition ♦ One party or 2 party state – Interest groups have more influence in a one party than a two party state because in a two party state interest groups must lobby both parties. – in a one party state they lobby & contribute money to just the dominant party. ♦ Texas – a one party Democratic state until 1980s. – this helped lobbyists 6. Legal framework (Constitution and Laws) Length ♦ Longer the better because it puts more restrictions on the government and interest groups. ♦ Texas- has a long, detailed, restrictive state constitution this helps interest groups 7. institutional framework (Bureaucratic Structure) ♦ strong executive - Governor has strength and a rigid chain of command – can appoint and remove all department heads – (his cabinet) ♦ Weak executive - Weak Governor, department heads are elected thus not loyal to the governor. ♦ Weak ones are more manipulative and some committees are more isolated and easily influenced. ♦ Texas – has a weak executive structure – this helps interest groups to more easily influence the bureaucracy. healthcare 30 4. COMPARE THE PROVISIONS OF THE 1995 FEDERAL LOBBY LAW WITH THE TEXAS LOBBY CONTROL LAW. a. The Old Federal Lobby Regulation Law (1946) had 3 loopholes: 1. Only paid lobbyists had to register 2. Only lobbyists whose pay was primarily for lobbying had to register – (lawyers and p. r. people who lobby can argue that their pay is primarily for “other non- lobbying services they provide – legal work p.r. work, etc.) 3. Only lobbyists who lobbied the courts in the executive branch didn’t have to register. b. New 1995 Federal Lobby Regulation Law(January) 1. Broadens, definition of a lobbyist: a lobbyist is defined as anyone who spends at least 20 percent of his or her time lobbying members of congress, their staffs, or executive branch officials. The registration requirement applies to organizations that spend more than $20,000 in one year or to individuals who are paid more than $5,000 annually for their work. c. Texas Lobby Control Law 1. Lobbyists must now report how much they are paid & specific issues, & bill numbers they are working to influence & a list of government contacted. d. House and Senate Rules: 1. Ban or limit most gifts to members of congress. - House – ban all gifts - Senate – gifts limited to $50 in value or no more than $100 from a single source in a year. 2. Bans all expense – paid trips, golf outings, etc., taking members to lunch, dinners. One advantage of interest groups Disadvantages of interest groups 1. Oversight Function (Term 1R) Keeping tabs on government. Other terms: 1. PACs Organizations that collect campaign contributions & give them to candidates sympathetic to their cause, a maximum of $5000 to any one candidate per election. 2. 1st Amendment – Protects interest groups – freedom of speech, press, assembly, and right to “petition government of a redress of grievances” – the right to lobby or communicate with government to influence government policies. healthcare 31 UNIT 6 – POLITICAL PARTIES PART A – U.S. 1. DEFINE A POLITICAL PARTY & ITS BASIC FUNCTION: Political Parties - are organizations who run candidates for office? They want to run government from within. Interest groups try to influence it from the outside. –by lobbying, electioneering etc. 2. COMPARE THE CURRENT DEMOCRATIC AND REPUBLICAN Hamilton PARTIES ON THE FOLLOWING ASPECTS: a. b. c. d. e. Ideology Issues Group support Images Geographical areas REPUBLICANS DEMOCRATS MAJOR ISSUES: MAJOR ISSUES: 1. Controlling inflation 1. Reducing unemployment 2. Reducing the role of government. 3. Strong Military Defense 4. Reducing Crime- Conservative strategy- use penalties & death penalty 5. Abortion- Pro Life 2. Protecting Free speech 3. Equality for blacks and other minorities 4. Equality for women Republican Supporters The more educated Higher income White collar and professional Conservatives Males Older voters Anglos Protestants Geographical Areas: Rural areas and small cities, and suburbs Mountain, Sunbelt, Midwest and plains states Democratic Supporter Grade school graduate – less educated Lower income Blue Collar Workers & Union Members Liberals Females Younger voters Blacks and other minorities Jewish and Catholics Geographical Areas: Urban and inner city voters East and West coast Northeast and south (South is gradually becoming less Democratic and more 2-party or slightly Republican) 5. Abortion – pro choice healthcare 32 Images (the Democratic Party Perspective): Republicans :(negative images) Democratic:(positive images) 1. dominated by big business 1. For the little man & common people 2. dominated by wealthy 2. Party of minorities, equality for all 3. economic conservative anti worker 3. Progressive party 4. Conservative- tied to status quo – afraid to 4. Party of the poor and under privileged change 5. party of the Depression 5. Party of social programs 6. insensitive to the poor 7. Radical Right, ultra – conservative Party Images (The Republican Party Perspective) Republicans : (positive images) Democrats: (negative images) 1. Free enterprise 1. dominated by labor unions 2. Individualism 2. dominated by minorities 3. Laissez faire – less government 3. radical liberal big spenders party 4. Middle of the road – moderate 4. party that promises anything to win 5. Fiscal restraint – lower taxes & spending 5. Party of war 6. Strong defense, peace 6. Ultra liberal, leftist party 7 Family values 3. DISCUSS THE ROLE AND TYPES OF THIRD PARTIES IN THE U.S. AND WHY THEY HAVE FAILED TO ATTRACT MUCH SUPPORT. A. History 1. U.S. the exception – most other democracies are multi-party (3 or more major parties) rather than two- party systems like the U.S. 2. First third parties in U.S. in 1830’s. 3. Only one third party has become a major party – Republicans in 1856 – they replaced the Whigs as the opposition to the Democrats. B. Types of Third Parties 1. Single Issue Third Party: Formed around one major issue that two major parties have ignored. If it attracts enough votes, one of two major parties steals the issue. 2. Economic Protest Third Parties: Examples: Greenbacks, Populist, Labor Reform, Union Labor. Formed by groups who feel ignored or written off by two major parties. Often feel they’ve been left out of economic prosperity and government. 2. Secessionist Third Parties: Examples: Bull Moose Progressive (T. Roosevelt 1912), 1924 LaFollette Progressive States Rights (Dixiecrats) of 1948, Henry Wallace Progressives of 1948, American Independent Party (George Wallace) of 1968. Formed by political leaders deserting one of the two major parties Republicans becoming too conservative and business dominated in 1912. G Wallace felt Democrats becoming too liberal and big government in 1968. Once these political leaders have made their point (and hurt their party) they later rejoin it, after next election. healthcare 33 3. Ideological Third Parties: Examples: Socialists, Socialist Worker’s, Communist, Libertarian. Strongly committed to a philosophy and refuse to compromise to attract more voters and support- would rather lose and be right than compromise. Usually are viewed as more radical by the American public – they demand some drastic changes in American society and government. They are unusual for third parties in that they last for many years 50-75 years longer. 4. Summary ♦ Usually appeal to a narrow or few groups or sectors. ♦ Usually short lived—last less than 10 years. ♦ Most have been regional – string in one area of the country ♦ Have done very poor in elections, elected no presidents, some congressmen, more successful at state level and especially state level. Why they have done poorly: ♦ American political culture “two party mentality”—2 parties best. ♦ Too narrow a focus and appeal to win a majority—too few issues ♦ Lack of money. ♦ Lack of Media Coverage ♦ If they become popular because of 1 or 2 issues, these issues are stolen by major party ♦ Americans feel they waste their vote if they vote for third parties. ♦ Rules of the game and elections- difficult to get on ballot, Electoral College ♦ Their radical image Contributions and Benefits 1. Publicized ignored issues: women’s vote, monopoly regulations, social programs 2. Represented ignored groups; farmers, blue collar workers, Mexican Americans (RUP). 3. Keep two major parties on their toes 4. Act as a safety valve-reduce likelihood of violence- given dissidents a peaceful way to work within the system. Ideas adopted that began as third party issues Women’s votes; regulation of monopolies; progressive income tax; direct election of U.S. Senators; rights of unions to organize strikes; and safety and health regulations. healthcare 34 UNIT 6 - POLITICAL PARTIES IN TEXAS PART B 1. DESCRIBE THE TEXAS DEMOCRATIC PARTY, ITS LIBERAL & CONSERVATIVE WINGS, & ITS ROLE IN TEXAS POLITICS. Objective 1 - Texas is dominated by Contradictory Conservative Democrats as a result of Reconstruction.- Until the 1980s, the Texas Democratic Party was dominated by white Conserva tive (Who are now gradually moving to the Republican Party) Texas has been a strong 1-party Democratic State for most of its history –until the 1980s. Why: 1. Slavery 2. Civil War 3. Reconstruction abuses 2. DESCRIBE THE TEXAS REPUBLICAN PARTY, ITS ROLE IN TEXAS POLITICS, WHY IT DID SO & THE REASONS FOR POLITICAL REALIGNMENT IN TEXAS. WHY IS TEXAS NOT A 2 PARTY STATE. Objective 2 – 4 reasons Texas finally became a two party state. (since 1980s) 1. Democratic Party became too Liberal. – in 1960s & 1970s 2. Ronald Reagan a conservative Republican, was elected to two consecutive terms in the 80’s his personal popularity rubbed off on the Republican Party in the South & boosted the Republican image in Texas. 3. Yankees moving to Texas. – many were Republicans 4. Fading impact of slavery and reconstruction upon our psyche – irrelevant to voting today. Objective 3 – Explain the 5 of the low level party competition in Texas: (Applied to Texas until 1980s) 1. Decrease voting turnout because of discouraging losses and surety of Democratic win. 2. Less voter interest and involvement, and brings about apathy. 3. Government Responsiveness declines – they don’t have to worry about losing their jobs. – The Democrats took our votes for granted. ♦ Corruption Increases – can’t vote out corruption if the same people win. ♦ Increase interest group strength because they only have to lobby & contribute money to one Party. The Democrats. healthcare 35